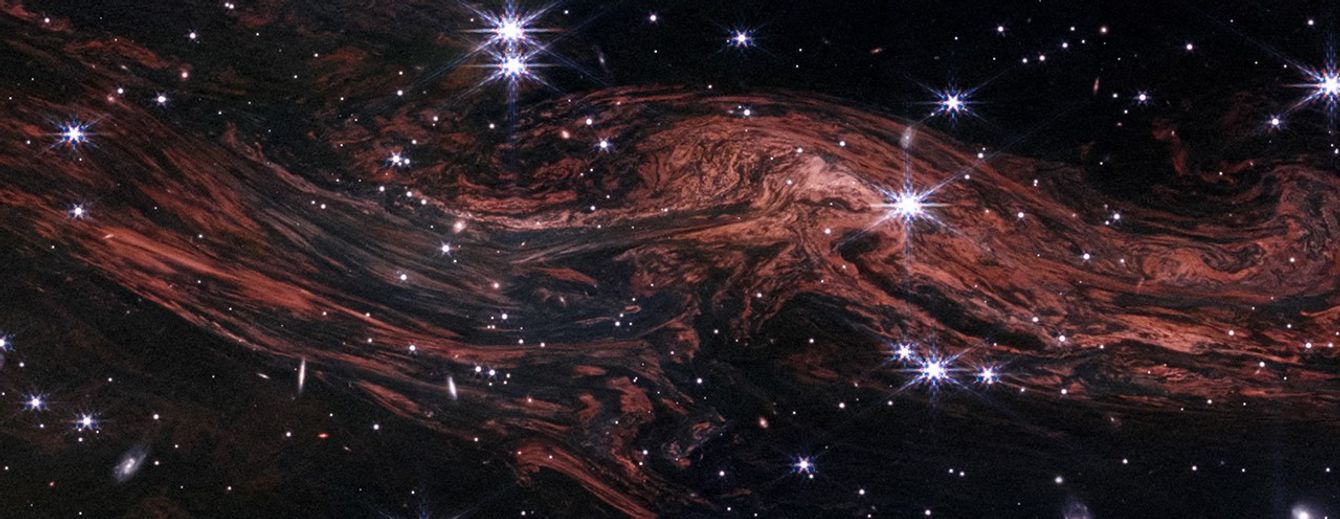
Supernovas within the early universe simply hit other. Particularly when the celebrities that exploded used to be a stellar monster 20 instances the mass of the solar.The use of the James Webb House Telescope (JWST), astronomers have came upon one of the crucial far-off and, thus, earliest star-killing supernovas ever noticed. This blast, which rocked the cosmos round 2 billion years after the Large Bang, marked the demise of simply this type of monster celebrity.This supernova, detected as a part of the JWST Complex Deep Extragalactic Survey (JADES) program, may lend a hand scientists upload extra element to the cosmic image of stellar lifestyles and demise they’re recently development.The supernova, designated AT 2023adsv, erupted round 11.4 billion years in the past in an enormous early galaxy. Excitingly, this stellar explosion is also moderately other from the supernovas that experience took place extra just lately within the native universe. Specifically, the high-energy blast turns out to had been excessively violent.”The primary stars had been significantly other than the celebrities nowadays. They had been large, they had been scorching, and so they had in point of fact gargantuan explosions,” JADES crew member and House Telescope Science Institute (STScI) researcher David Coulter stated on the 245th assembly of the American Astronomical Society (AAS) in Nationwide Harbor, Maryland, on Monday (Jan. 13). “We do not know the way many [supernovas] the JWST will to find however we will begin to push to the start of those first stars and hope to peer their explosions.”A tale of stellar lifestyles, demise, and rebirthThe early universe used to be moderately dull in comparison to the fashionable cosmos, particularly when taking into account its chemical contents. That is as it used to be in large part hydrogen, the lightest and most simple part, with some helium, the second one lightest part. There existed within the toddler universe only a smattering of heavier parts, which astronomers moderately confusingly discuss with as “metals.”The primary technology of stars, referred to as Inhabitants III stars (no longer Inhabitants I stars as you would be expecting, possibly), used to be born from overdense patches on this ingredient-light cosmic soup. Those stars started to fuse hydrogen and helium into heavier parts.When probably the most large stars (with lots in way over 8 instances that of the solar) reached the top in their provides of gas for nuclear fusion, their cores collapsed, growing black holes or neutron stars, whilst their metal-rich outer layers had been blasted away in supernova explosions.This procedure seeded clouds of hydrogen and helium within the first galaxies with heavy parts. This intended that after overdense patches in those enriched clouds collapsed to create new stars, this 2nd technology of stars (Inhabitants II) used to be extra metal-rich than the primary.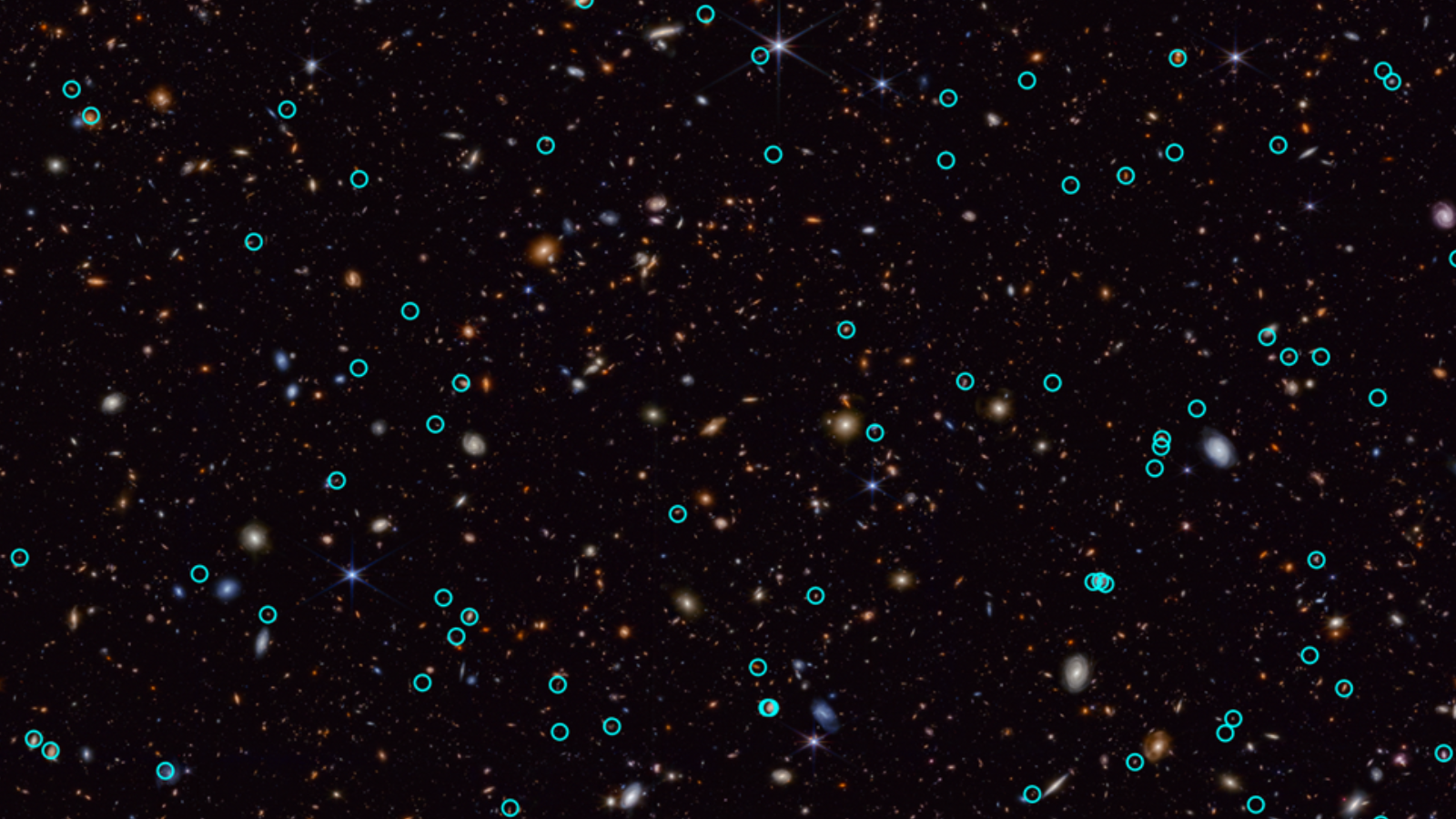 JADES Deep Box makes use of observations taken through NASA’s James Webb House Telescope (JWST) appearing the positioning of newly came upon supernova explosions (Symbol credit score: NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, JADES Collaboration)This repeated to start a 3rd technology of much more metal-abundant stars. That is the 3rd technology of stellar our bodies, Inhabitants I stars (once more, no longer Pop III stars as you would be expecting ), to which our celebrity, the solar, belongs.On the other hand, whilst this may increasingly look like a case of cosmic historical past repeating, there used to be one thing other concerning the first spherical of supernovas.Scientists assume that the metal-poor nature of those stars would have brought about them to are living shorter lives. It might have additionally made the supernova explosions that mark the top of those lives extra violent than the deaths of later descendant stars.Breaking area information, the most recent updates on rocket launches, skywatching occasions and extra!Those early supernovas must be extremely shiny and thus visual to the JWST. Certainly, the JADES collaboration, which research the start and evolution of the earliest galaxies, has so far noticed over 80 historical supernovas.”Learning far-off supernova explosions is the one method to discover the person stars that populate those early galaxies,” crew member and College of Arizona in Tucson researcher Christa DeCoursey stated in a commentary. “The sheer selection of detections plus the nice distances to those supernovas are the 2 most enjoyable results from our survey.”
JADES Deep Box makes use of observations taken through NASA’s James Webb House Telescope (JWST) appearing the positioning of newly came upon supernova explosions (Symbol credit score: NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, JADES Collaboration)This repeated to start a 3rd technology of much more metal-abundant stars. That is the 3rd technology of stellar our bodies, Inhabitants I stars (once more, no longer Pop III stars as you would be expecting ), to which our celebrity, the solar, belongs.On the other hand, whilst this may increasingly look like a case of cosmic historical past repeating, there used to be one thing other concerning the first spherical of supernovas.Scientists assume that the metal-poor nature of those stars would have brought about them to are living shorter lives. It might have additionally made the supernova explosions that mark the top of those lives extra violent than the deaths of later descendant stars.Breaking area information, the most recent updates on rocket launches, skywatching occasions and extra!Those early supernovas must be extremely shiny and thus visual to the JWST. Certainly, the JADES collaboration, which research the start and evolution of the earliest galaxies, has so far noticed over 80 historical supernovas.”Learning far-off supernova explosions is the one method to discover the person stars that populate those early galaxies,” crew member and College of Arizona in Tucson researcher Christa DeCoursey stated in a commentary. “The sheer selection of detections plus the nice distances to those supernovas are the 2 most enjoyable results from our survey.”
An early supernova with a twistThe chemical composition of AT 2023adsv way it stands proud as some of the earliest of those supernovas.”This supernova is to this point away and due to this fact to this point again in time that after the sunshine used to be first coming to us the universe used to be lower than 2 billion years previous,” Coulter persevered. “That signifies that this mild were touring 6 billion years sooner than the solar ever shaped.”So this Supernova additionally came about in an atmosphere that turns out significantly other than the surroundings that our house celebrity lives in nowadays.” AT 2023adsv, a supernova came upon in a galaxy at a redshift of three.6. Its progenitor starexploded when the universe used to be most effective 2 billion years previous. (Symbol credit score: NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, JADES Collaboration)Whilst AT 2023adsv does resemble the metal-poor setting of the early universe through which the celebrity that exploded to release it used to be born, there’s a twist or two.”Apparently to be an in depth cousin to native supernovas seen in in a similar fashion pristine environments,” Coulter stated within the commentary. “On the other hand, the resemblance stops there — 2023adsv seems to had been as soon as a specifically large celebrity, possibly as much as 20 instances the mass of our solar.” Stars of such monstrous sizes are scarce within the native and recent universe. 2023adsv additionally exploded with round two times the calories of the typical supernova induced through close by large stars.”The excessive explosion calories of 2023adsv may point out that the homes of supernova explosions may had been other within the early universe, however we want extra observations to substantiate this concept,” crew member and Nationwide Astronomical Observatory of Japan theorist Takashi Moriya stated.The JWST gets a hand in looking for the earliest and maximum far-off cosmic explosion in 2026 when NASA is ready to release its subsequent main area telescope, the Nancy Grace Roman House Telescope.Present estimates counsel Roman’s large box of view will find hundreds of early supernovas for the delicate infrared eye of the JWST to hone in on and examine.The crew’s analysis used to be introduced on the 245th assembly of the AAS on Monday, and a preprint paper is to be had at the repository web page arXiv.
AT 2023adsv, a supernova came upon in a galaxy at a redshift of three.6. Its progenitor starexploded when the universe used to be most effective 2 billion years previous. (Symbol credit score: NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, JADES Collaboration)Whilst AT 2023adsv does resemble the metal-poor setting of the early universe through which the celebrity that exploded to release it used to be born, there’s a twist or two.”Apparently to be an in depth cousin to native supernovas seen in in a similar fashion pristine environments,” Coulter stated within the commentary. “On the other hand, the resemblance stops there — 2023adsv seems to had been as soon as a specifically large celebrity, possibly as much as 20 instances the mass of our solar.” Stars of such monstrous sizes are scarce within the native and recent universe. 2023adsv additionally exploded with round two times the calories of the typical supernova induced through close by large stars.”The excessive explosion calories of 2023adsv may point out that the homes of supernova explosions may had been other within the early universe, however we want extra observations to substantiate this concept,” crew member and Nationwide Astronomical Observatory of Japan theorist Takashi Moriya stated.The JWST gets a hand in looking for the earliest and maximum far-off cosmic explosion in 2026 when NASA is ready to release its subsequent main area telescope, the Nancy Grace Roman House Telescope.Present estimates counsel Roman’s large box of view will find hundreds of early supernovas for the delicate infrared eye of the JWST to hone in on and examine.The crew’s analysis used to be introduced on the 245th assembly of the AAS on Monday, and a preprint paper is to be had at the repository web page arXiv.
James Webb House Telescope discovers some of the earliest ‘in point of fact gargantuan’ supernovas ever noticed