The James Webb House Telescope (JWST) has detected a considerable abundance of carbon-monoxide ice in a large cloud of molecular fuel, nicknamed “The Brick,” that sits close to the middle of our Milky Means galaxy.The Brick — which has a correct designation of G0.253+0.016 — is living in what astronomers discuss with because the Central Molecular Zone, an enormous agglomeration of nebulas totaling 60 million instances the mass of our solar.Many of those clouds are busy forming stars, however The Brick were given its title as a result of this is a darkish slab set towards the furnace of the Galactic Middle. Why The Brick has but to actually get started forming stars stays a thriller. One conceivable clarification is that this is a younger cloud that hasn’t had an opportunity to shape stars but; any other is that fuel inside The Brick is simply too turbulent, or is being propped up and due to this fact averted from collapsing through magnetic fields. It’s such gaseous cave in that generally ends up in superstar formation.Now, the JWST has deepened the thriller much more. The spaceborne observatory has found out a ton of carbon-monoxide ice in The Brick. Similar: Earth-like planets might shape even in harsh environments, James Webb House Telescope unearths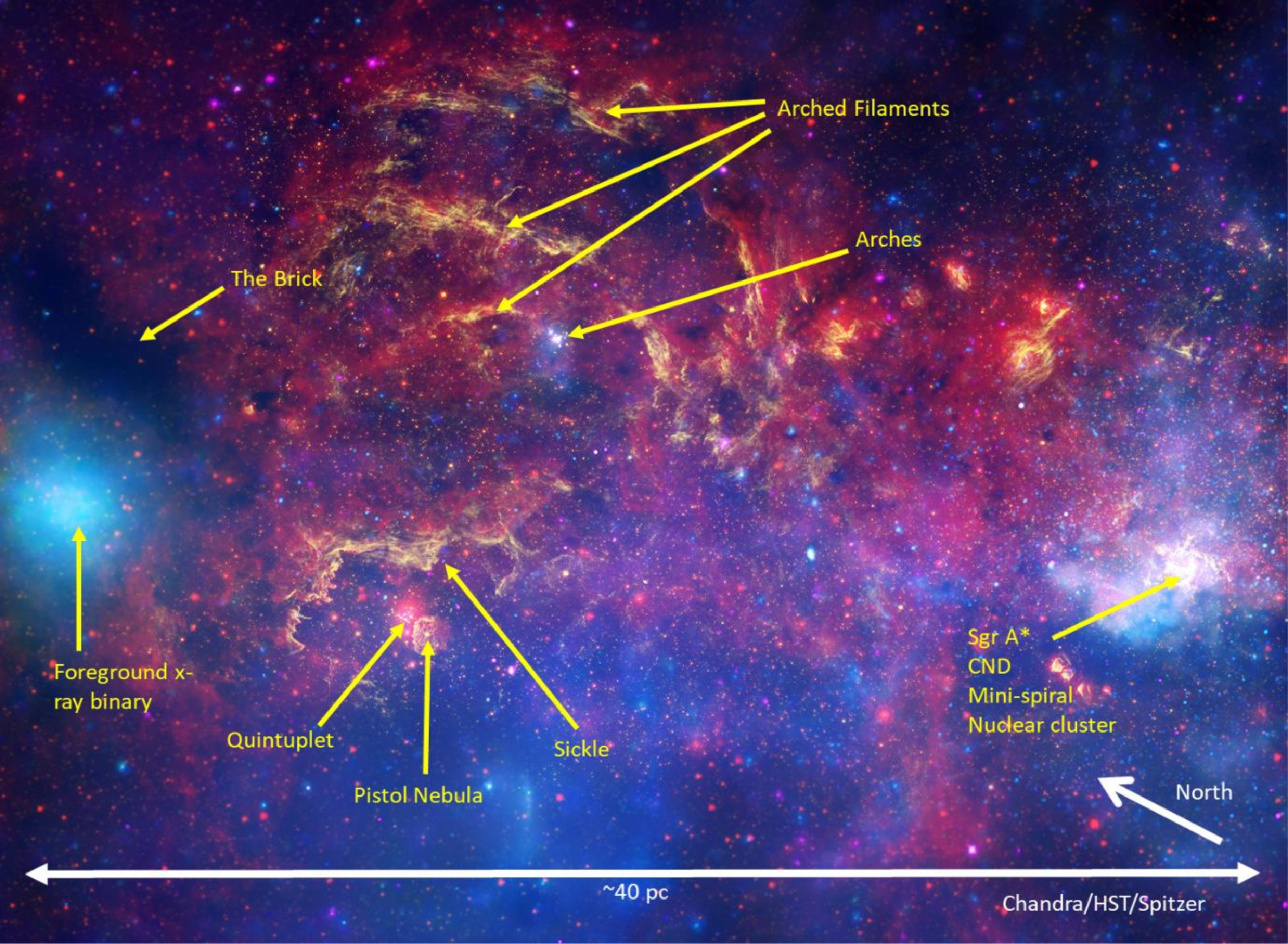 A picture of the Central Molecular Zone, with a number of options categorised, together with The Brick. (Symbol credit score: NASA/Chandra/HST/ESA/STScI/Q. D. Wang/Spitzer/Churchwell et al.)Carbon-monoxide ice has been detected within the Galactic Middle sooner than, condensing on debris of mud, however it’s normally tricky to come across within the interstellar medium. Subsequently, no person actually knew how a lot ice is within the nebulas on the heart of the galaxy. That is why astronomers led through Adam Ginsburg of the College of Florida had been shocked when the JWST’s Close to-Infrared Digicam (NIRCam) detected such a lot of the substance.”Our observations compellingly display that ice may be very prevalent there, to the purpose that each commentary someday should take it under consideration,” mentioned Ginsburg in a commentary.Big name formation calls for very chilly prerequisites to start out, with molecular fuel plunging to temperatures as little as ten levels above absolute 0. Absolute 0, for context, is the bottom conceivable temperature within the universe. Then again, in spite of the ice’s abundance, the JWST measured that fuel in The Brick is unusually heat in comparison to different molecular clouds.Your next step, the group says, is to make use of the JWST to find what different ices are to be present in The Brick and different close by nebulas within the Galactic Middle.”We do not know, for instance, the relative quantities of carbon monoxide, water and carbon dioxide, and sophisticated molecules,” mentioned Ginsburg. “With spectroscopy, we will be able to measure the ones and get some sense of ways chemistry progresses over the years in those clouds.”Finding out the middle of our galaxy will have cosmological repercussions. Big name-forming prerequisites on the whole within the Galactic Middle are regarded as our closest reflect of the star-forming prerequisites within the early universe. Some theories additionally counsel supermassive black holes had been born from the gravitational cave in of extraordinarily huge molecular clouds. Then again, one spanner within the works of this idea has at all times been the thriller of what averted the collapsing clouds from fragmenting and forming a number of stars quite than one black hollow. Clues to the solutions could be discovered within the opaque confines of nebulas like The Brick.The brand new findings had been printed at the Dec. 4 in The Astrophysical Magazine. A preprint is to be had right here.
A picture of the Central Molecular Zone, with a number of options categorised, together with The Brick. (Symbol credit score: NASA/Chandra/HST/ESA/STScI/Q. D. Wang/Spitzer/Churchwell et al.)Carbon-monoxide ice has been detected within the Galactic Middle sooner than, condensing on debris of mud, however it’s normally tricky to come across within the interstellar medium. Subsequently, no person actually knew how a lot ice is within the nebulas on the heart of the galaxy. That is why astronomers led through Adam Ginsburg of the College of Florida had been shocked when the JWST’s Close to-Infrared Digicam (NIRCam) detected such a lot of the substance.”Our observations compellingly display that ice may be very prevalent there, to the purpose that each commentary someday should take it under consideration,” mentioned Ginsburg in a commentary.Big name formation calls for very chilly prerequisites to start out, with molecular fuel plunging to temperatures as little as ten levels above absolute 0. Absolute 0, for context, is the bottom conceivable temperature within the universe. Then again, in spite of the ice’s abundance, the JWST measured that fuel in The Brick is unusually heat in comparison to different molecular clouds.Your next step, the group says, is to make use of the JWST to find what different ices are to be present in The Brick and different close by nebulas within the Galactic Middle.”We do not know, for instance, the relative quantities of carbon monoxide, water and carbon dioxide, and sophisticated molecules,” mentioned Ginsburg. “With spectroscopy, we will be able to measure the ones and get some sense of ways chemistry progresses over the years in those clouds.”Finding out the middle of our galaxy will have cosmological repercussions. Big name-forming prerequisites on the whole within the Galactic Middle are regarded as our closest reflect of the star-forming prerequisites within the early universe. Some theories additionally counsel supermassive black holes had been born from the gravitational cave in of extraordinarily huge molecular clouds. Then again, one spanner within the works of this idea has at all times been the thriller of what averted the collapsing clouds from fragmenting and forming a number of stars quite than one black hollow. Clues to the solutions could be discovered within the opaque confines of nebulas like The Brick.The brand new findings had been printed at the Dec. 4 in The Astrophysical Magazine. A preprint is to be had right here.
James Webb House Telescope gazes into ‘The Brick,’ a gloomy nebula close to the Milky Means’s middle