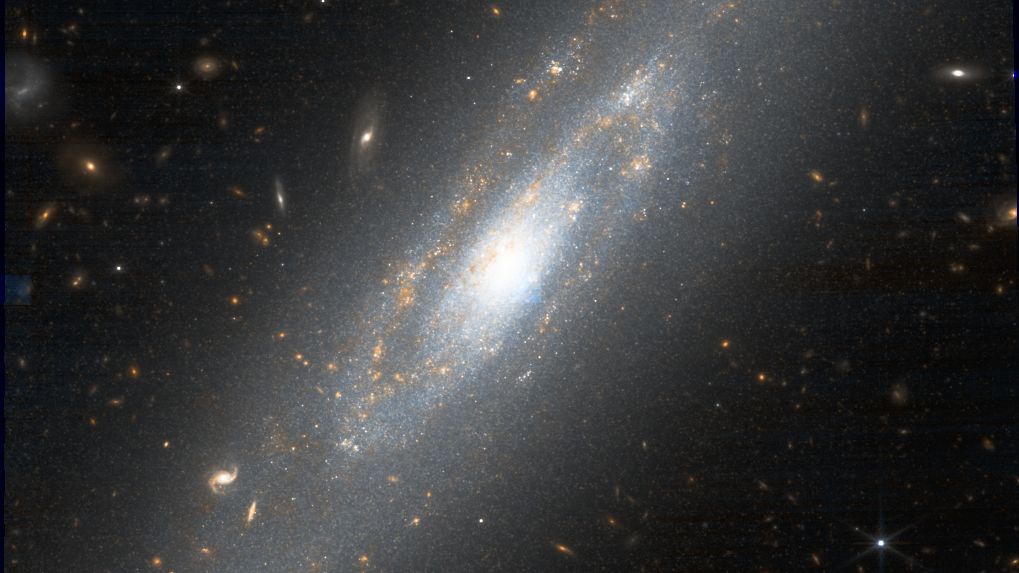
It could seem that James Webb House Telescope observations of 10 within sight galaxies suggests the Hubble stress — which is a puzzling discrepancy in measurements in regards to the price of the growth of the universe — will not be actual finally.The James Webb House Telescope’s observations put the typical price of the Hubble consistent (H0), key in figuring out the speed at which the universe is increasing, at 69.96 kilometers in step with 2nd in step with megaparsec. That is certainly in line with predictions stemming from the usual style of cosmology, which must sound like an finish to the problem — however the findings additionally spotlight a important war of words.In 2013, the Ecu House Company’s Planck challenge measured the Hubble consistent to be 67.4 kilometers in step with 2nd in step with megaparsecs. In different phrases, because of this each and every megaparsec (one million parsecs, or 3.26 million light-years) is increasing via 67.4 kilometers (41.9 miles) each and every 2nd. The Planck science staff was once ready to infer this price of the Hubble consistent via measuring the basic homes of the universe captured within the mild of the cosmic microwave background (CMB) after which making use of our usual style of cosmology to expect the growth price. Assuming the usual style is right kind, this system must be correct to inside of 1%.Moreover, measurements via a staff led via Adam Riess of Johns Hopkins College, who’ve been the usage of the Hubble House Telescope to measure cosmic enlargement the usage of sort Ia supernovas, which might be the explosions of white dwarf stars, beg to range. Kind Ia supernovas have a standardizable most brightness, which means astronomers can measure how a long way away they will have to be in keeping with how brilliant they seem. This distance is then in comparison to their redshift, since the sooner the universe is increasing, the higher an object’s redshift. That manner places H0 at 73.2 kilometers in step with 2nd in step with megaparsec, implying that the universe is increasing sooner than the usual style predicts. It is this war of words that scientists describe because the Hubble stress.Comparable: James Webb House Telescope complicates increasing universe paradox via checking Hubble’s workAnd now, the brand new paintings led via Wendy Freedman of the College of Chicago raises some tough questions. Freedman’s staff, operating on a mission known as the Chicago–Carnegie–Hubble Program (CCHP), used the JWST to measure the space to 10 reasonably within sight galaxies that experience all been noticed to have had a kind Ia supernova prevalence. The gap measurements had been then cross-checked via 3 impartial method.Breaking house information, the most recent updates on rocket launches, skywatching occasions and extra!The primary of those 3 impartial strategies is referred to as the “tip of the pink massive department,” which describes the utmost brightness that advanced sun-like stars known as pink giants can achieve. The second one manner comes to one thing known as the J-region asymptotic massive department, which refers to a taste of pink massive stars which can be wealthy in carbon and that experience equivalent intrinsic infrared brightnesses. The 3rd cross-check was once finished with Cepheid variable stars, that have a duration–luminosity relation first came upon via Henrietta Swan Leavitt in 1908, which connects the duration of pulsation with most luminosity. In different phrases, just by measuring how lengthy a celebrity takes to pulse, we will calculate what its most brightness must be and examine that to how brilliant apparently within the night time sky to infer how a long way away it will have to be.The CCHP staff measured H0 as 69.85 km/s/Mpc the usage of the top of the pink massive department, they usually measured 67.96 km/s/Mpc the usage of the carbon stars. Up to now, so excellent — the related error bars surround the Planck size of H0, hanging them in excellent settlement with the usual style.The Cepheid variables, although, weren’t taking part in ball. From them, the CCHP staff arrived at a price of 72.04 km/s/Mpc, which isn’t in settlement with the opposite measurements. Taken in combination, the 4 strategies give a reasonable price of 69.96 km/s/Mpc.”In accordance with those new JWST information and the usage of 3 impartial strategies, we don’t to find robust proof for a Hubble stress,” stated Freedman in a observation. “On the contrary, it looks as if our usual cosmological style for explaining the evolution of the universe is keeping up.”But, the Cepheid variable measurements do appear to proceed to supply stress. Cepheids shape the ground rung of the cosmic distance ladder, with sort Ia supernovas as the following rung up as a result of they are able to be noticed out to bigger distance than Cepheids. Within the paintings via Riess’ workforce — Supernova H0 for the Equation of State, or SH0ES for brief — Cepheids are the most important for calibrating the kind Ia supernova measurements. Alternatively, Freedman has prior to now expressed considerations a few doable downside known as “crowding.” Even though the Hubble House Telescope has sufficiently robust solution to spot Cepheid variable stars in different galaxies, it’s conceivable that low-mass stars very just about a Cepheid can also be unresolved and finally end up blurring in with the sunshine from the Cepheid, thus affecting clinical effects.Previous this yr, Riess led a staff that used the JWST to double-check Hubble’s observations of Cepheids and got here to the belief that crowding was once now not a subject matter. Alternatively, of their analysis paper, Freedman and fellow researchers indicate that the 2 strategies least suffering from crowding — the top of the pink massive department and the carbon stars — give values in line with the usual style.Whilst consideration will now center of attention on measurements of galactic distances the usage of Cepheid variables, extra measurements with the JWST of galaxies with sort Ia supernovae can be valuable for confirming the consequences from those 10 galaxies. Alternatively, sort Ia supernovas in galaxies that still have resolvable Cepheids, pink giants and carbon stars are reasonably uncommon, which means it’s going to take a while to get a big sufficient pattern.The consequences from the CCHP staff led via Freedman are these days to be had as a pre-print, and feature been submitted for peer assessment at The Astrophysical Magazine.
James Webb House Telescope provides to the complicated drama of Hubble stress