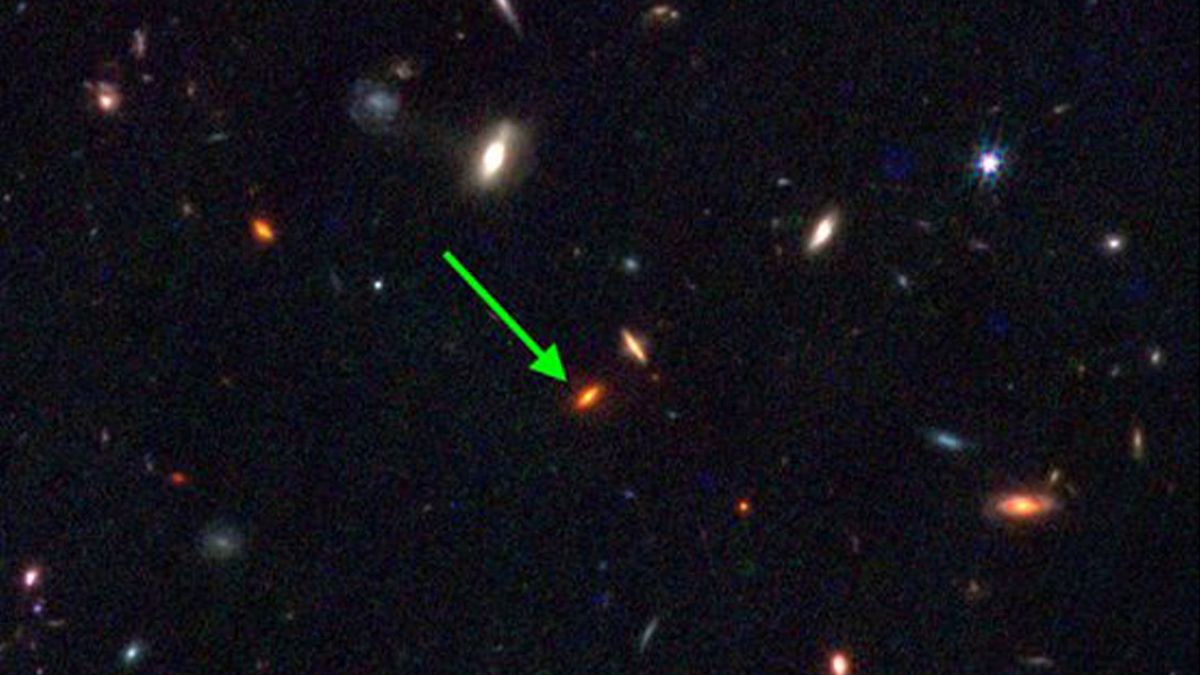
The James Webb Area Telescope (JWST) has discovered a galaxy within the early universe that is so large, it mustn’t exist, posing a “vital problem” to the usual style of cosmology, in line with the learn about authors.The galaxy, referred to as ZF-UDS-7329, comprises extra stars than the Milky Method, in spite of having shaped most effective 800 million years into the universe’s 13.8 billion-year lifestyles span. This implies they had been by hook or by crook born with out darkish topic seeding their formation, opposite to what the usual style of galaxy formation suggests.How this can have took place is unclear, however similar to earlier JWST discoveries of alternative inexplicably large galaxies within the early universe, it threatens to upend our figuring out of the way the primary topic within the universe shaped. The researchers revealed their findings Feb. 14 within the magazine Nature.Comparable: After 2 years in area, the James Webb telescope has damaged cosmology. Can or not it’s fastened?”Having those extraordinarily large galaxies so early within the universe is posing vital demanding situations to our usual style of cosmology,” learn about co-author Claudia Lagos, an affiliate professor of astronomy on the World Centre for Radio Astronomy Analysis, stated in a remark. It is because large darkish topic buildings, which might be regarded as important parts for containing early galaxies in combination, didn’t but have time to shape this early within the universe, Lagos added.Mild travels at a set velocity throughout the vacuum of area, so the deeper we glance into the universe, the extra far off mild we intercept and the additional again in time we see. That is what enabled the researchers to make use of JWST to identify ZF-UDS-7329 more or less 11.5 billion years up to now.By way of learning the spectra of sunshine coming from the celebrities of this extraordinarily far-off galaxy, the researchers discovered that the celebrities had been born 1.5 billion years previous to that commentary, or more or less 13 billion years in the past.Astronomers are not sure when the first actual globules of stars started to clump into the galaxies we see as of late, however cosmologists up to now estimated that the method started slowly throughout the first few hundred million years after the Giant Bang.Present theories recommend that halos of darkish topic (a mysterious and invisible substance believed to make up 25% of the current universe) blended with fuel to shape the primary seedlings of galaxies. After 1 billion to two billion years of the universe’s lifestyles, the early protogalaxies then reached youth, forming into dwarf galaxies that started devouring one every other to develop into ones like our personal.However the brand new discovery has confounded this view: Now not most effective has the galaxy crystallized with out sufficient darkish topic having constructed as much as seed it, however now not lengthy after a unexpected burst of celebrity formation, the galaxy impulsively turned into quiescent — that means its celebrity formation ceased.”This pushes the bounds of our present figuring out of the way galaxies shape and evolve,” learn about co-author Themiya Nanayakkara, an astronomer on the Swinburne College of Generation in Australia, stated within the remark. “The important thing query now’s how they shape so speedy very early within the universe, and what mysterious mechanisms result in preventing them forming stars impulsively when the remainder of the universe is doing so.”The researchers’ subsequent steps shall be to seek for extra galaxies like this. In the event that they to find any, it might significantly contradict prior concepts of the way galaxies shaped, they stated.