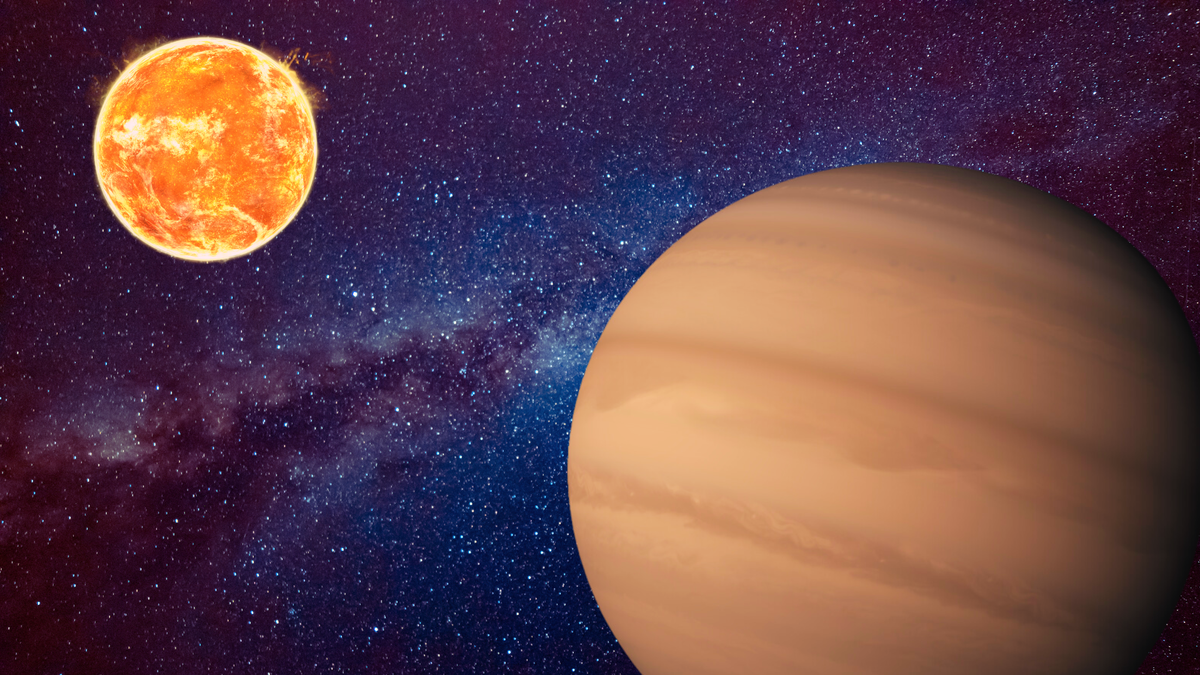
Jupiter-like planets is also a commonplace prevalence within the interplanetary area close to our sun machine, particularly round stars very similar to our solar, a brand new learn about suggests.If long term observations ascertain this speculation, it could imply the structure of our sun machine isn’t as unusual as it’s conventionally regarded as to be.The surroundings wherein our sun machine shaped remains to be an open query, however earlier analysis has get a hold of two main theories. One concept posits the machine was once birthed in a metal-rich surroundings, because of a close-by big name that went supernova. In keeping with the idea, the big name would have returned heavy metals, constituted of lighter components combining throughout eons, to our younger sun machine. An opposing concept suggests our solar shaped from a molecular cloud of fuel and mud in a low-density surroundings as a substitute.Similar: Friendless ‘scorching Jupiter’ exoplanets might not be so lonely after allWith the newest discovering that Jupiter-like fuel giants are commonplace amongst different sun-like stars within the within sight cosmos, the brand new learn about “is bringing new effects supporting the view that the sun machine shaped in a quiet, low density surroundings,” Raffaele Gratton, a researcher on the Padua Astronomical Observatory in Italy and the lead creator of the brand new learn about, instructed Area.com. “Extra in depth research someday might assist explain this factor.”To reach at their conclusions, Gratton and his colleagues analyzed knowledge of a close-by shifting staff of stars referred to as the β Percent Transferring Crew (BPMG). This staff, which is living more or less 130 light-years from Earth, is composed of 146 stars assumed to had been born from the similar molecular cloud on the identical time, this means that they are anticipated to have a identical chemical make-up. Round stars on this staff, earlier analysis has already noticed 4 Jupiter-like planets — however the brand new learn about all for 30 stars that have been about 0.8 instances extra huge than the solar. 20 of those stars are more likely to host Jupiter-like planets in solid orbits, consistent with the brand new learn about.The potential of fuel giants present round those stars is slightly sudden, as all 30 stars studied within the new analysis are simply 20 million years previous — method more youthful than the 100 million-year-old solar round which our personal Jupiter is believed to have taken form.Even if the BPMG staff of stars is the nearest such cluster to Earth, and fashions have steered Jupiter-like planets might shape simply round stars on this class, finding out the ones planets is difficult. Very similar to how fuel giants orbit some distance clear of our solar, Jupiter-like planets in different sun methods most probably circle their stars at slightly massive distances too — such a lot in order that they are able to take tens of years to finish just one orbit, stated Gratton. So, telescopes gazing such methods will have to acquire knowledge throughout a number of many years to be able to hit upon a planet crossing in entrance of its big name, an tournament referred to as a transit. From our perspective, transits are detected when the big name’s brightness dips in brief because the planet crosses the big name from one edge to the opposite. That is recently essentially the most typical option to hit upon exoplanets.The decades-long orbits of Jupiter-like planets imply present knowledge about transits is insufficient, as we want no less than 3 transits for detecting a planet, stated Gratton.”Best thirty years in the past, we didn’t know of any planet out of doors the sun machine, so it will have to now not be sudden that we nonetheless have difficulties in finding some elegance of planets,” he added. At this time, “we’re best ready to hit upon essentially the most huge a few of the Jupiter-like planets.”For example, previous this yr, researchers were given a peek into a shocking, still-forming planetary machine 5,000 light-years clear of Earth whose dusty clumps may just sooner or later manifest into fuel giants like Jupiter.The brand new analysis is described in a paper printed Tuesday (Oct. 16) within the magazine Nature Communications.
Jupiter-like exoplanets expose our sun machine might not be so distinctive in any case








:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():focal(746x727:748x729)/Pregnant-California-Teacher-Dies-Hiking-Trip-Greece-010425-01-536f5e95c7244fb6b5d26a10fa4dac38.jpg)




