A gentle lack of mind tissue is a herbal a part of growing older, however probably the most longest-running mind scan research has now published some folks’s neural connections become worse quicker than others after they hit heart age.
In line with a decades-long trial that started in 1995, those that display upper losses in white subject – the tissue that comprises nerve fibers – have an 86 p.c higher chance of growing gentle cognitive impairment (MCI).
In comparison to the ones and not using a metabolic illness, the ones with kind 2 diabetes misplaced considerably extra white subject through the years, and this workforce in the long run confronted a 41 p.c upper chance of growing MCI.
What is extra, folks with biomarkers of dementia of their cerebrospinal fluid (CFS) had a just about 50 p.c upper chance of cognitive impairment.
If a person had each diabetes and biomarkers of amyloid plaques (which might be related to Alzheimer’s illness), that chance jumps to 55 p.c.
Earlier research have additionally proven that vital losses in white subject are tied to circumstances of dementia, and that metabolic issues can raise an individual’s chance of cognitive decline.
However that is the primary learn about to turn a synergistic dating between diabetes and amyloid plaques in relation to their affect on white subject.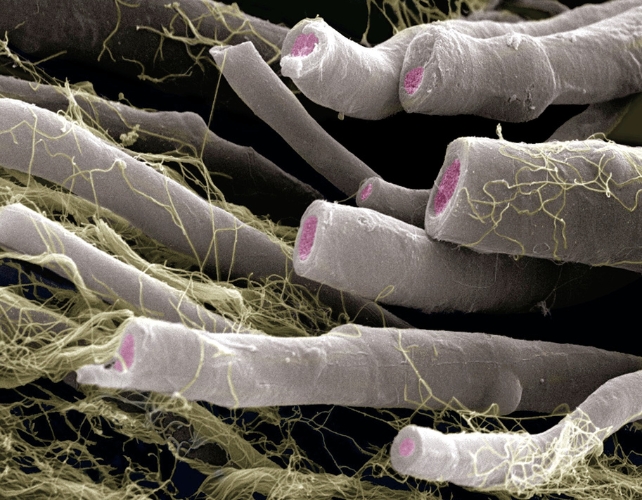 Coloured scanning electron micrograph of myelinated nerve fibers (axons). Axons are the principle part of white subject within the mind. (Science Picture Library/Canva)”Those findings spotlight that white subject quantity adjustments are carefully related to cognitive serve as in growing older, suggesting that white subject degeneration would possibly play a an important position in cognitive decline,” write the authors of the learn about, led via neuroscientists at Johns Hopkins College in the USA.
Coloured scanning electron micrograph of myelinated nerve fibers (axons). Axons are the principle part of white subject within the mind. (Science Picture Library/Canva)”Those findings spotlight that white subject quantity adjustments are carefully related to cognitive serve as in growing older, suggesting that white subject degeneration would possibly play a an important position in cognitive decline,” write the authors of the learn about, led via neuroscientists at Johns Hopkins College in the USA.
“As insulin resistance performs a vital position within the formation of amyloid plaques, diabetes would possibly advertise Alzheimer’s illness pathology, leading to an previous development from standard cognition to MCI.”
The long-term learn about used to be performed amongst a gaggle of 185 individuals, who had been most commonly well-educated and White, with a circle of relatives historical past of dementia.
It isn’t transparent how properly the findings will translate to extra various populations, however maximum long-term MRI research so far had been restricted to lower than a decade, and plenty of most effective take two time issues into consideration.
This latest learn about is impressively lengthy, albeit small, monitoring the mind styles and sizes of individuals at more than one issues of their lives.
For as much as 27 years, scientists ceaselessly scanned the brains of individuals, who began the trial with unimpaired cognition between the ages of 20 and 76.
On the finish of the trial, 60 individuals had stepped forward to gentle cognitive impairment (MCI), and eight of the ones individuals went directly to broaden dementia.
Every individual had their mind scanned about 5 instances, and in accordance with the ones photographs, it kind of feels that it is standard as you age to progressively lose cortical grey subject, which comprises neuron our bodies, in addition to white subject, which conducts messages between neurons.
What’s odd, on the other hand, is a extra speedy deterioration in white subject, beginning in heart age. Individuals who skilled the best declines in white subject volumes, yr to yr, had been a ways much more likely to broaden signs of MCI.
Whilst most effective 8 individuals had a prognosis of kind 2 diabetes, the authors say their effects recommend “that controlling diabetes would possibly lend a hand scale back the chance of Alzheimer’s dementia later in existence as a modifiable chance issue.”
Fresh analysis, for example, has proven that some medicine that deal with kind 2 diabetes are connected to a 35 p.c decrease chance of dementia in sufferers.
Doctor-scientist Shohei Fujita, who used to be now not concerned within the learn about, reviewed the findings in an invited statement for JAMA’s Neurology.
Fujita applauds the “prolonged time period” of the trial, and he hopes the findings “permit researchers and clinicians to broaden centered interventions for the ones maximum vulnerable to innovative mind adjustments.”
Significantly, 63 p.c of the cohort had been girls, and Fujita issues out that “gender and race also are an important variables that should be thought to be” in long run longitudinal analysis.
In spite of everything, cognitive decline and dementia don’t affect everybody in the similar method. The way in which each and every particular person mind shrinks with age is sure to be extremely variable.The learn about used to be revealed in JAMA Community.
Kind 2 Diabetes Connected to Speeded up Mind Shrinkage, Find out about Finds












