Referred to as circulation formations, those channels may well be etched on our bodies that would appear inhospitable to liquid as a result of they’re uncovered to the extraordinary vacuum stipulations of house.
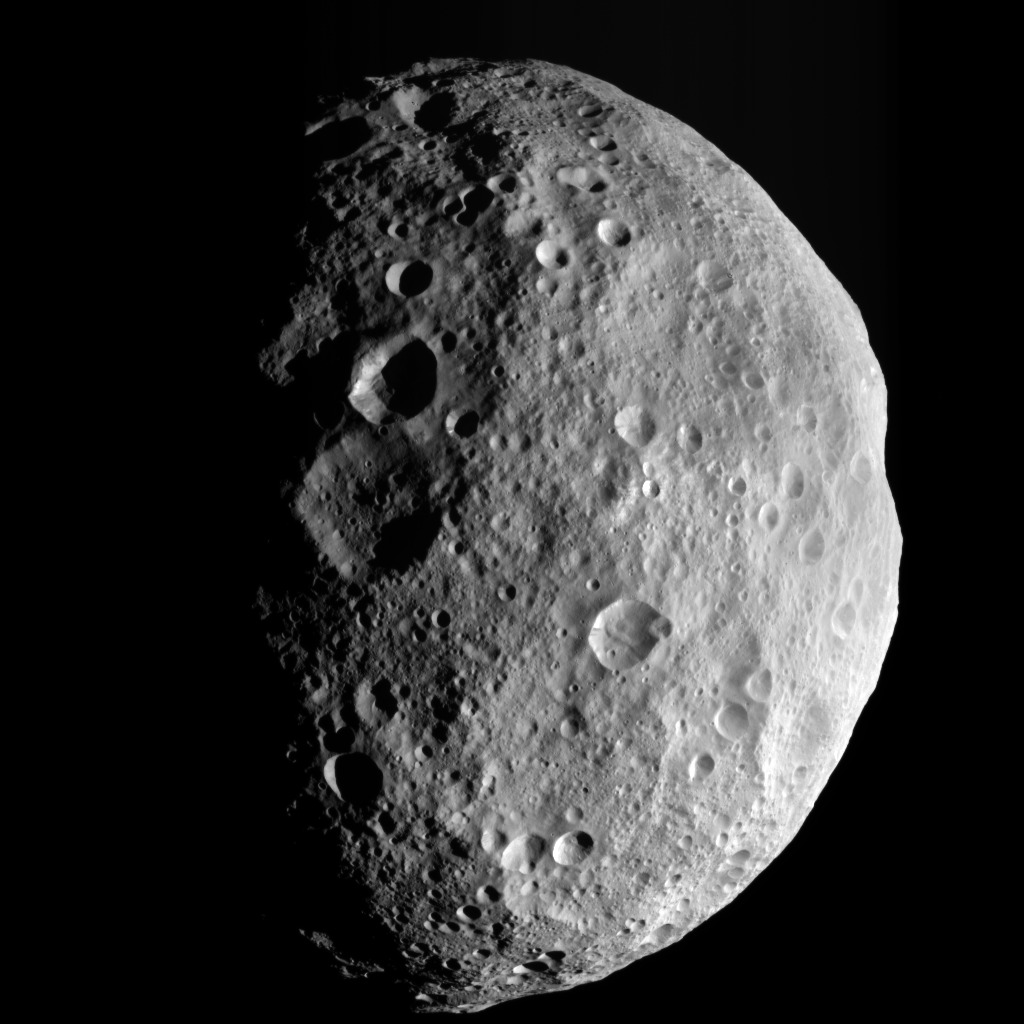
Pocked with craters, the surfaces of many celestial our bodies in our sun machine supply transparent proof of a 4.6-billion-year battering by means of meteoroids and different house particles. However on some worlds, together with the enormous asteroid Vesta that NASA’s First light challenge explored, the surfaces additionally comprise deep channels, or gullies, whose origins aren’t totally understood.
A chief speculation holds that they shaped from dry particles flows pushed by means of geophysical processes, comparable to meteoroid affects, and adjustments in temperature because of Solar publicity. A up to date NASA-funded learn about, alternatively, supplies some proof that affects on Vesta will have caused a less-obvious geologic procedure: surprising and transient flows of water that carved gullies and deposited enthusiasts of sediment. By way of the usage of lab apparatus to imitate stipulations on Vesta, the learn about, which seemed in Planetary Science Magazine, detailed for the primary time what the liquid may well be made from and the way lengthy it will circulation earlier than freezing.
Even supposing the life of frozen brine deposits on Vesta is unconfirmed, scientists have prior to now hypothesized that meteoroid affects can have uncovered and melted ice that lay below the outside of worlds like Vesta. In that state of affairs, flows attributable to this procedure can have etched gullies and different floor options that resemble the ones on Earth.
However how may airless worlds — celestial our bodies with out atmospheres and uncovered to the serious vacuum of house — host liquids at the floor lengthy sufficient for them to circulation? The sort of procedure would run opposite to the working out that liquids temporarily destabilize in a vacuum, converting to a fuel when the force drops.
“Now not most effective do affects cause a circulation of liquid at the floor, the liquids are lively lengthy sufficient to create particular floor options,” mentioned mission chief and planetary scientist Jennifer Scully of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California, the place the experiments have been performed. “However for a way lengthy? Maximum liquids transform volatile temporarily on those airless our bodies, the place the vacuum of house is unyielding.”
The vital part seems to be sodium chloride — desk salt. The experiments discovered that during stipulations like the ones on Vesta, natural water iced up nearly immediately, whilst briny liquids stayed fluid for no less than an hour. “That’s lengthy sufficient to shape the flow-associated options recognized on Vesta, that have been estimated to require as much as a 30 minutes,” mentioned lead creator Michael J. Poston of the Southwest Analysis Institute in San Antonio.
Introduced in 2007, the First light spacecraft traveled to the primary asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter to orbit Vesta for 14 months and Ceres for nearly 4 years. Sooner than finishing in 2018, the challenge exposed proof that Ceres have been house to a subsurface reservoir of brine and would possibly nonetheless be shifting brines from its internal to the outside. The hot analysis provides insights into processes on Ceres however makes a speciality of Vesta, the place ice and salts would possibly produce briny liquid when heated by means of an affect, scientists mentioned.
To re-create Vesta-like stipulations that may happen after a meteoroid affect, the scientists trusted a take a look at chamber at JPL known as the Grimy Underneath-vacuum Simulation Testbed for Icy Environments, or DUSTIE. By way of impulsively decreasing the air force surrounding samples of liquid, they mimicked the surroundings round fluid that involves the outside. Uncovered to hoover stipulations, natural water iced up immediately. However salty fluids hung round longer, proceeding to circulation earlier than freezing.
The brines they experimented with have been somewhat over an inch (a couple of centimeters) deep; scientists concluded the flows on Vesta which are yards to tens of yards deep would take even longer to refreeze.
The researchers have been additionally in a position to re-create the “lids” of frozen subject material idea to shape on brines. Necessarily a frozen most sensible layer, the lids stabilize the liquid underneath them, protective it from being uncovered to the vacuum of house — or, on this case the vacuum of the DUSTIE chamber — and serving to the liquid circulation longer earlier than freezing once more.
This phenomenon is very similar to how on Earth lava flows farther in lava tubes than when uncovered to chill floor temperatures. It additionally fits up with modeling analysis performed round doable dust volcanoes on Mars and volcanoes that can have spewed icy subject material from volcanoes on Jupiter’s moon Europa.
“Our effects give a contribution to a rising frame of labor that makes use of lab experiments to know the way lengthy liquids final on quite a few worlds,” Scully mentioned.
To find extra details about NASA’s First light challenge right here:
Gretchen McCartney
Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif.
818-287-4115
gretchen.p.mccartney@jpl.nasa.gov
Karen Fox / Molly Wasser
NASA Headquarters, Washington
202-358-1600
karen.c.fox@nasa.gov / molly.l.wasser@nasa.gov
2024-178












:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-2188460679-4f112c9e9def4df98120dc4919bbd105.jpg)
