New analysis could have delivered unhealthy information for scientists who concept that they had came upon a “lacking hyperlink” black hollow in a dense Milky Method celebrity cluster.The brand new findings indicate that, fairly than a unprecedented intermediate-mass black hollow, there’s a cluster of stellar-mass black holes in Omega Centauri, believed to be the stays of an historical galaxy cannibalized through the Milky Method.”The quest for elusive intermediate-mass black holes continues,” mentioned learn about staff member Justin Learn, a scientist on the College of Surrey in England. “There may just nonetheless be one on the middle of Omega Centauri, however our paintings means that it will have to be lower than about 6,000 instances the mass of the solar and reside along a cluster of stellar mass black holes.”Astronomers had been first tipped off to the conceivable presence of a black hollow in Omega Centauri, which comprises an estimated 10 million stars, once they spotted that a few of the ones stars had been transferring quicker than anticipated.Comparable: Elusive medium-size black holes might shape in dense ‘birthing nests’Final yr, a staff of astronomers performed an investigation with the Hubble House Telescope and believed that they discovered an intermediate-mass black hollow with a mass identical to round 8,200 suns.A reanalysis of that celebrity cluster, alternatively, signifies that this won’t were the case finally.Breaking area information, the most recent updates on rocket launches, skywatching occasions and extra!Why do ‘lacking hyperlink’ black holes subject?As their identify suggests, intermediate-mass black holes occupy the area between stellar mass black holes (with 10 to one,000 sun lots) and supermassive black holes that take a seat on the center of galaxies, with lots equivalent to tens of millions and even billions of suns.The reputed discovery of an intermediate-mass black hollow so on the subject of Earth was once thrilling as a result of those black holes, regarded as a the most important hyperlink within the chain of mergers that is helping black holes succeed in supermassive standing, were notoriously elusive. That is even though scientists suppose they will have to be commonplace within the universe.This is as a result of, like every black holes, they’re bounded through a one-way light-trapping floor referred to as an tournament horizon. This implies black holes can most effective be noticed when surrounded through subject that they feed directly to develop, and which heats with tidal forces to generate shiny mild.Intermediate black holes are regarded as “stalled” or “frozen in time,” as a result of they lack fuel and mud round them to feed upon. This additionally manner they are successfully invisible, because the most effective technique to infer their presence is the impact their gravity has on stars round them. A demonstration appearing the 3 varieties of astrophysical black holes, staring from essentially the most large at the left to the least large at the proper (Symbol credit score: Robert Lea (created with Canva))Interactions with the gravity of an intermediate-mass black hollow on the center of Omega Centauri had been concept to have sped up stars within the middle of this dense cluster to excessive speeds.”We’ve lengthy identified about supermassive black holes at galaxy facilities and smaller stellar-mass black holes inside our personal galaxy,” staff member and Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias researcher Andrés Bañares Hernández mentioned in a remark.”Then again, the theory of intermediate-mass black holes, which might bridge the space between those extremes, stays unproven,” he added. “Via finding out Omega Centauri — a remnant of a dwarf galaxy — we’ve been in a position to refine our strategies and take a step ahead in working out whether or not such black holes exist and what position they could play within the evolution of celebrity clusters and galaxies.”This paintings is helping get to the bottom of a two-decade-long debate and opens new doorways for long term exploration.”
A demonstration appearing the 3 varieties of astrophysical black holes, staring from essentially the most large at the left to the least large at the proper (Symbol credit score: Robert Lea (created with Canva))Interactions with the gravity of an intermediate-mass black hollow on the center of Omega Centauri had been concept to have sped up stars within the middle of this dense cluster to excessive speeds.”We’ve lengthy identified about supermassive black holes at galaxy facilities and smaller stellar-mass black holes inside our personal galaxy,” staff member and Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias researcher Andrés Bañares Hernández mentioned in a remark.”Then again, the theory of intermediate-mass black holes, which might bridge the space between those extremes, stays unproven,” he added. “Via finding out Omega Centauri — a remnant of a dwarf galaxy — we’ve been in a position to refine our strategies and take a step ahead in working out whether or not such black holes exist and what position they could play within the evolution of celebrity clusters and galaxies.”This paintings is helping get to the bottom of a two-decade-long debate and opens new doorways for long term exploration.”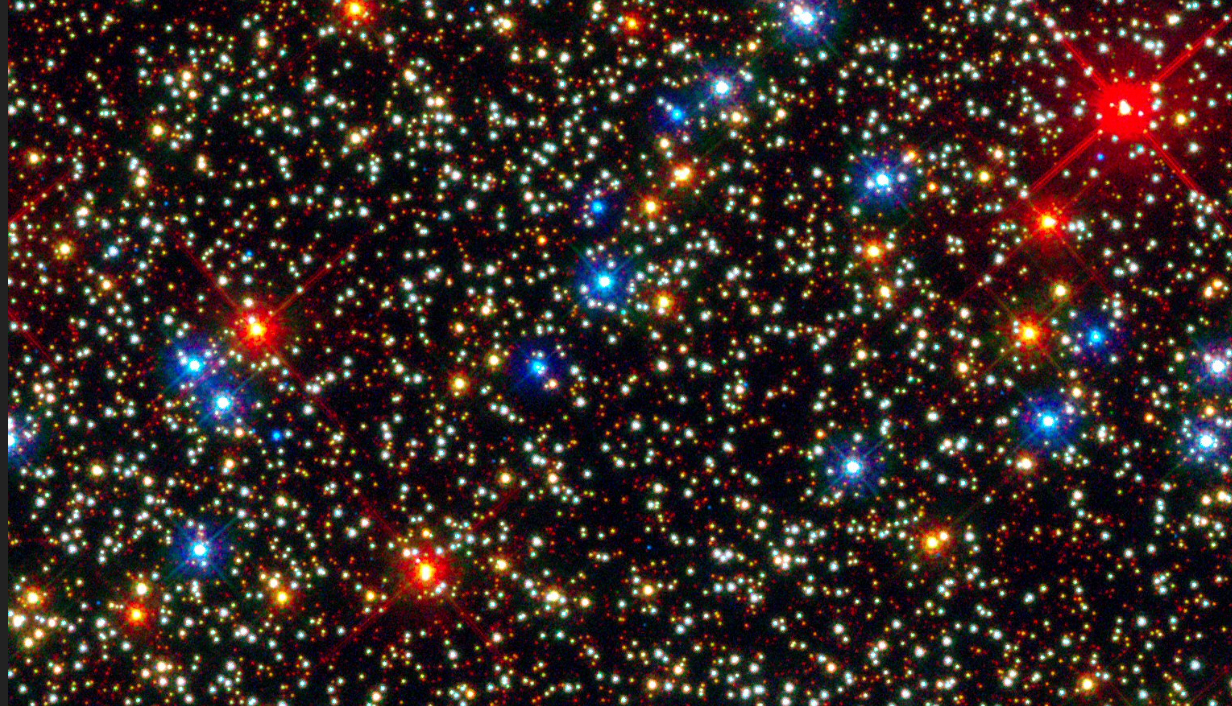 The dense celebrity cluster Omega Centauri. (Symbol credit score: NASA/ESA/Anderson/van der Marel)Some other conceivable reason behind the seen celebrity velocities is a cluster of stellar-mass black holes, that are predicted to develop in dense celebrity clusters like this one.Then again, astronomers imagine that interactions with different stars would most likely have “slingshotted” those extra diminutive black holes out of the program. That left an intermediate-mass black hollow because the perhaps reason behind the high-velocity stars on the center of Omega Centauri —till now.Within the new learn about, researchers factored in every other vital information supply when taking into consideration Omega Centauri, which considerably modified issues.Conserving time with cosmic lighthousesThe further information got here from “cosmic lighthouses” referred to as pulsars.Pulsars are hastily spinning cosmic remnants referred to as neutron stars that shape when large stars run out of gasoline and cave in beneath their very own gravity.As those lifeless stars spin as rapid as 700 instances in step with 2d, in addition they blast out beams of radiation from their poles. Those beams sweep around the universe like the sunshine from a cosmic lighthouse.Once they swivel to indicate at Earth, pulsars brighten, making them seem to pulse. As a result of this pseudo pulsing is extremely periodic when thought to be en masse in what scientists name a pulsar timing array, those cosmic lighthouses change into right into a extremely correct time-keeping device.
The dense celebrity cluster Omega Centauri. (Symbol credit score: NASA/ESA/Anderson/van der Marel)Some other conceivable reason behind the seen celebrity velocities is a cluster of stellar-mass black holes, that are predicted to develop in dense celebrity clusters like this one.Then again, astronomers imagine that interactions with different stars would most likely have “slingshotted” those extra diminutive black holes out of the program. That left an intermediate-mass black hollow because the perhaps reason behind the high-velocity stars on the center of Omega Centauri —till now.Within the new learn about, researchers factored in every other vital information supply when taking into consideration Omega Centauri, which considerably modified issues.Conserving time with cosmic lighthousesThe further information got here from “cosmic lighthouses” referred to as pulsars.Pulsars are hastily spinning cosmic remnants referred to as neutron stars that shape when large stars run out of gasoline and cave in beneath their very own gravity.As those lifeless stars spin as rapid as 700 instances in step with 2d, in addition they blast out beams of radiation from their poles. Those beams sweep around the universe like the sunshine from a cosmic lighthouse.Once they swivel to indicate at Earth, pulsars brighten, making them seem to pulse. As a result of this pseudo pulsing is extremely periodic when thought to be en masse in what scientists name a pulsar timing array, those cosmic lighthouses change into right into a extremely correct time-keeping device.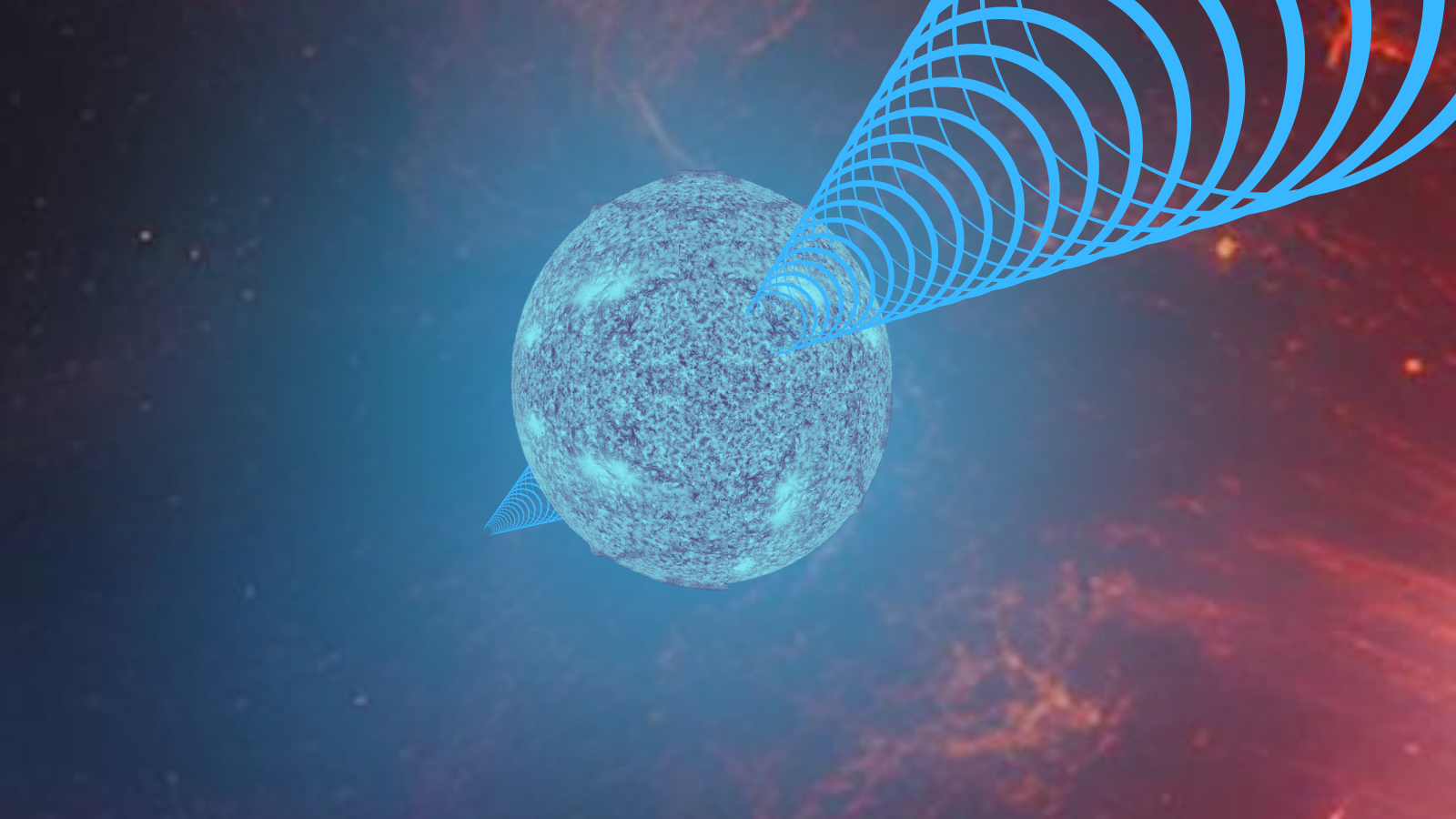 A demonstration of a pulsar, a hastily spinning neutron celebrity that sweeps beams of radiation via area like a cosmic lighthouse (Symbol credit score: Robert Lea (created with Canva))Adjustments within the timing of pulsars can point out the presence of intense gravitational fields accelerating those lifeless stars. The addition of pulsar information allowed the staff to probe the gravitational fields on the center of Omega Centauri in larger element.This allowed the staff to tell apart between the impact of an intermediate black hollow and a cluster of stellar-mass black holes. The staff decided that the latter was once the perhaps reason behind the speed of stars on the middle of Omega Centauri.The staff is not too disheartened through their findings. Learn, for one, thinks it is just a question of time prior to astronomers get started turning up intermediete-mass black holes.”There may be each and every likelihood people discovering one [an intermediate-mass black hole] quickly,” Learn mentioned. “Increasingly more pulsar accelerations are coming, permitting us to look into the facilities of dense celebrity clusters and hunt for black holes extra exactly than ever prior to.”Within the intervening time, the staff’s analysis may just assist astronomers higher perceive the mechanisms that start pulsars.”The formation of pulsars may be an lively box of analysis, as a result of numerous them have lately been detected,” Hernández concluded. “Omega Centauri is a perfect setting to check fashions in their formation, which we’ve been in a position to do for the primary time in our research.”The staff’s analysis has been authorised for newsletter within the magazine Astronomy & Astrophysics.
A demonstration of a pulsar, a hastily spinning neutron celebrity that sweeps beams of radiation via area like a cosmic lighthouse (Symbol credit score: Robert Lea (created with Canva))Adjustments within the timing of pulsars can point out the presence of intense gravitational fields accelerating those lifeless stars. The addition of pulsar information allowed the staff to probe the gravitational fields on the center of Omega Centauri in larger element.This allowed the staff to tell apart between the impact of an intermediate black hollow and a cluster of stellar-mass black holes. The staff decided that the latter was once the perhaps reason behind the speed of stars on the middle of Omega Centauri.The staff is not too disheartened through their findings. Learn, for one, thinks it is just a question of time prior to astronomers get started turning up intermediete-mass black holes.”There may be each and every likelihood people discovering one [an intermediate-mass black hole] quickly,” Learn mentioned. “Increasingly more pulsar accelerations are coming, permitting us to look into the facilities of dense celebrity clusters and hunt for black holes extra exactly than ever prior to.”Within the intervening time, the staff’s analysis may just assist astronomers higher perceive the mechanisms that start pulsars.”The formation of pulsars may be an lively box of analysis, as a result of numerous them have lately been detected,” Hernández concluded. “Omega Centauri is a perfect setting to check fashions in their formation, which we’ve been in a position to do for the primary time in our research.”The staff’s analysis has been authorised for newsletter within the magazine Astronomy & Astrophysics.
‘Lacking hyperlink’ black hollow discovered? No longer so rapid, new learn about says













