For astronomers, discovering a brand new black hollow orbiting an elderly purple dwarf celebrity is a thrilling to find in itself, but if that black hollow appears to be a “lacking hyperlink” stellar-mass black hollow, you’ll crank the thrill as much as 11! This is precisely what appears to be lurking in binary machine G3425, estimated to be round 5,800 light-years away.The visual part of G3425 is a purple large celebrity, the type of stellar frame you get when a celebrity exhausts its provide of hydrogen gas and will not behavior nuclear fusion in its core. This reasons its outer layers (the place fusion continues) to “puff out” to up to 100 instances the celebrity’s authentic width. Our personal celebrity, the solar, is recently in its heart age. Which means that in round 5 billion years, it’s going to input its purple large segment and swell as much as across the orbit of Mars, swallowing the internal planets, together with Earth. Even then, what the purple large solar nearly undoubtedly would possibly not have is a stellar-mass black hollow as a better half. The group’s analysis is revealed within the magazine Nature Astronomy. The purple dwarf on this machine has a mass of round 2.7 instances the mass of our solar, however what’s actually attention-grabbing to scientists is the mass of its compact darkish better half. This newfound black hollow was once weighed via a group led via Wang Track from the Nationwide Astronomical Observatories of the Chinese language Academy of Sciences (NAOC). Its mass is between 3.1 and four.4 instances that of the solar, almost certainly about 3.6 sun lots. “The black hollow falls throughout the well-known mass hole, making it some of the lightest black holes found out thus far,” Track informed Area.com. “This discovery no longer best confirms the lifestyles of mass-gap black holes but in addition displays that binaries containing low-mass black holes can continue to exist a supernova explosion.”Track and co-workers detected this stellar-mass black hollow in knowledge amassed via the Massive Sky Space Multi-Object Fiber Spectroscopic Telescope (LAMOST) and from the Gaia area telescope, which exactly measures the positions of billions of stars within the Milky Manner and past. This mixture of knowledge and strategies allowed the researchers to look at the black hollow’s gravitational “tug” on its better half purple dwarf celebrity, forcing it to show itself.Signal as much as the publication for the most recent updates on rocket launches, skywatching occasions and extra!Comparable: Scientists waited ages to discover a ‘lacking hyperlink’ black hollow — then stumbled upon 2Mystery of the lacking massesBlack holes have only a few defining traits, a incontrovertible fact that physicist John Wheeler as soon as described via pronouncing, “Black holes don’t have any hair.” Along with electrical price and angular momentum, some of the traits black holes do have that permits astronomers to set them aside is their mass.The kings of mass are the supermassive black holes that lurk on the hearts of maximum, if no longer all, huge galaxies, and feature lots thousands and thousands to billions of instances that of the solar. Extra diminutive are elusive intermediate-mass black holes, that have lots between 100 and 100,000 sun lots. Either one of all these black holes are too huge to shape when a celebrity runs out of gas for nuclear fusion and after repeated collapses and growth episodes, leading to a whole cave in beneath its personal gravity. Thus, they develop via greedily feasting on subject round them or via merging with different black holes over and over.The smallest astrophysical black holes that we all know of include so-called stellar mass black holes, which we discover with lots as much as 100 instances that of the solar. Those black holes are simply the proper measurement to be born when a celebrity no less than 8 instances as huge because the solar can not fuse heavier and heavier components, and thus cannot generate the power to fight towards the inward push of its personal gravity. An indication appearing the 3 forms of astrophysical black holes, staring from probably the most huge at the left to the least huge at the proper (Symbol credit score: Robert Lea (created with Canva))During the last 60 years or so, astronomers have discovered dozens of stellar-mass black holes that are compatible inside of a distribution of five to twenty-five sun lots. Thus far, so excellent, however there’s a drawback.Theories of black hollow start recommend that once a celebrity has misplaced the vast majority of its mass by way of an amazing supernova explosion that indicators gravity’s victory, the ones stars that cling on to simply 3 times the mass of the solar will have to nonetheless be capable of shape a stellar-mass black hollow. So, with that mentioned, the query turns into: the place are all of the 3 to five sun mass black holes?
An indication appearing the 3 forms of astrophysical black holes, staring from probably the most huge at the left to the least huge at the proper (Symbol credit score: Robert Lea (created with Canva))During the last 60 years or so, astronomers have discovered dozens of stellar-mass black holes that are compatible inside of a distribution of five to twenty-five sun lots. Thus far, so excellent, however there’s a drawback.Theories of black hollow start recommend that once a celebrity has misplaced the vast majority of its mass by way of an amazing supernova explosion that indicators gravity’s victory, the ones stars that cling on to simply 3 times the mass of the solar will have to nonetheless be capable of shape a stellar-mass black hollow. So, with that mentioned, the query turns into: the place are all of the 3 to five sun mass black holes?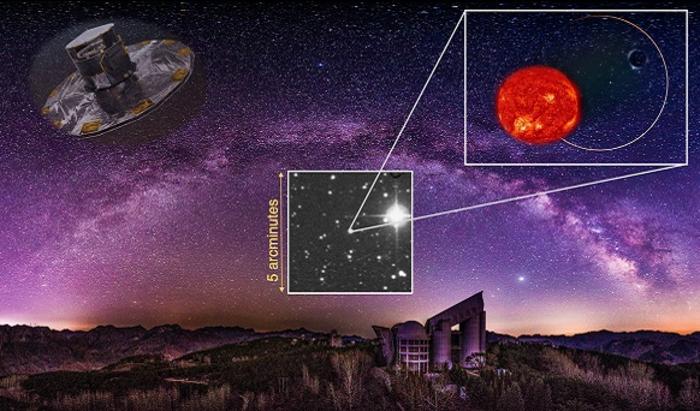 An indication of the G3425 with a purple dwarf celebrity and a black hollow. (Symbol credit score: Wang Track)One risk is that there’s some mechanism that comes into play all over a supernova that forestalls black holes with 3 to five sun lots from forming. On the other hand, lower-mass black holes is also much more likely to get disrupted via “kicks” dropped at them all over a supernova explosion and, due to this fact, much less prone to linger in a binary with a visual better half that makes them more uncomplicated to identify.This arises from the truth that all black holes, regardless of the mass, are bounded via a light-trapping floor referred to as an match horizon that makes them successfully invisible. Black holes in a binary, like the only in G3425, may also be inferred via the impact they’ve on their visual better half. Thus, an unaccompanied “supernova-kicked” black hollow would possibly not be visual via those results as a result of they’ve no better half to have an effect on.If that’s the case, how did this black hollow organize to continue to exist that mechanism and/or withstand the kick that are supposed to have despatched it spiraling clear of its better half?Every other puzzle surrounds the program. G3425 is a large binary with an orbital length of roughly 880 Earth days. The orbit has 0 “eccentricity,” because of this that this can be a near-perfect circle. The group cannot recently provide an explanation for this via same old binary evolutionary processes. “Probably the most unexpected factor is the huge round orbit of the binary,” Track mentioned. “The formation of this sort of binary, particularly involving a low-mass black hollow, gifts an important problem to present theories of binary evolution and supernova explosion.”The formation of this purple dwarf/black hollow binary with a shockingly huge round orbit would possibly problem present binary evolution and supernova explosion theories, but it surely has delivered a couple of positives.Those findings end up that quiet and invisible items in binaries may also be detected by way of the impact they’ve on their partners and that uncovering lurking low-mass black holes can ship insights into the evolution of binary methods.
An indication of the G3425 with a purple dwarf celebrity and a black hollow. (Symbol credit score: Wang Track)One risk is that there’s some mechanism that comes into play all over a supernova that forestalls black holes with 3 to five sun lots from forming. On the other hand, lower-mass black holes is also much more likely to get disrupted via “kicks” dropped at them all over a supernova explosion and, due to this fact, much less prone to linger in a binary with a visual better half that makes them more uncomplicated to identify.This arises from the truth that all black holes, regardless of the mass, are bounded via a light-trapping floor referred to as an match horizon that makes them successfully invisible. Black holes in a binary, like the only in G3425, may also be inferred via the impact they’ve on their visual better half. Thus, an unaccompanied “supernova-kicked” black hollow would possibly not be visual via those results as a result of they’ve no better half to have an effect on.If that’s the case, how did this black hollow organize to continue to exist that mechanism and/or withstand the kick that are supposed to have despatched it spiraling clear of its better half?Every other puzzle surrounds the program. G3425 is a large binary with an orbital length of roughly 880 Earth days. The orbit has 0 “eccentricity,” because of this that this can be a near-perfect circle. The group cannot recently provide an explanation for this via same old binary evolutionary processes. “Probably the most unexpected factor is the huge round orbit of the binary,” Track mentioned. “The formation of this sort of binary, particularly involving a low-mass black hollow, gifts an important problem to present theories of binary evolution and supernova explosion.”The formation of this purple dwarf/black hollow binary with a shockingly huge round orbit would possibly problem present binary evolution and supernova explosion theories, but it surely has delivered a couple of positives.Those findings end up that quiet and invisible items in binaries may also be detected by way of the impact they’ve on their partners and that uncovering lurking low-mass black holes can ship insights into the evolution of binary methods.
‘Lacking hyperlink’ black hollow lurks in bizarre binary machine with purple large celebrity