Scientists have discovered that surprisingly large black holes appear to be absent from the diffuse outer halo of the Milky Approach. The invention may just spell dangerous information for theories that recommend the universe’s maximum mysterious type of “stuff,” darkish topic, consists of primordial black holes that shaped within the first moments after the Giant Bang.Darkish topic is puzzling as a result of, regardless of being successfully invisible as it does now not have interaction with gentle, this substance makes up round 86% of the topic within the identified universe. That implies, for each and every 1 gram of “on a regular basis topic” that composes stars, planets, moons and people, there are over 6 grams of darkish topic. Scientists can infer the presence of darkish topic through its interactions with gravity and the affect it has on on a regular basis topic and lightweight. But, regardless of this and the ubiquity of darkish topic, scientists do not know what it may well be composed of.Comparable: If the Giant Bang created miniature black holes, the place are they?The brand new darkish topic effects come from a glance again via two decades of observations performed through a crew of scientists from the Optical Gravitational Lensing Experiment (OGLE) survey on the Astronomical Observatory of the College of Warsaw.”The character of darkish topic stays a thriller. Maximum scientists assume it’s composed of unknown basic debris,” crew chief Przemek Mróz, from the College of Warsaw’s Astronomical Observatory, mentioned in a observation. “Sadly, regardless of many years of efforts, no experiment, together with experiments performed with the Huge Hadron Collider, has discovered new debris that may be accountable for darkish topic.”The brand new findings do not simply forged doubt on black holes as an cause of darkish topic; additionally they deepen the thriller of why stellar-mass black holes detected past the Milky Approach appear to be extra large than the ones inside of our galaxies’ limits.Breaking area information, the most recent updates on rocket launches, skywatching occasions and extra!Our primordial black holes are lacking!The crew’s hunt for black holes within the Milky Approach’s halo owes its origins to the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) and its sister gravitational wave detector, Virgo, which appear to have exposed a inhabitants of surprisingly massive stellar-mass black holes.Till the primary detection of gravitational waves, which used to be produced through LIGO and Virgo in 2015, scientists have been discovering that our galaxy’s inhabitants of stellar-mass black holes, born from the gravitational cave in of big stars, tended to have lots between 5 and 20 instances that of the solar.Gravitational wave observations of mergers between stellar-mass black holes point out a extra far-off inhabitants of black holes with a lot more mass, an identical to between 20 and 100 suns. “Explaining why those two populations of black holes are so other is likely one of the greatest mysteries of recent astronomy,” Mróz identified. A diagram appearing the huge distinction in scale between supermassive black holes and hypothetical primordial black holes. (Symbol credit score: Robert Lea (created with Canva))One imaginable cause of this better inhabitants of black holes is that they’re leftovers from a length simply after the Giant Bang that shaped now not from the cave in of big stars however from overly dense patches of primordial gasoline and mud.”We all know that the early universe used to be now not preferably homogeneous — small density fluctuations gave upward thrust to present galaxies and galaxy clusters,” Mróz mentioned. “An identical density fluctuations, in the event that they exceed a essential density distinction, would possibly cave in and shape black holes.”Those “primordial black holes” have been first postulated through Stephen Hawking over 50 years in the past however have remained frustratingly elusive. Which may be as a result of smaller examples would hastily “leak” a type of thermal power referred to as Hawking radiation and in the end evaporating, which means they wouldn’t exist within the present epoch of the 13.8 billion-year-old cosmos. But, this hindrance hasn’t stopped some physicists from positing primordial black holes as a imaginable cause of darkish topic.Darkish topic is estimated to contain 90% to 95% of the Milky Approach’s mass. That implies, if darkish topic is product of primordial black holes, our galaxy must comprise many of those historical our bodies. Black holes do not emit gentle as a result of they’re sure through a light-trapping floor referred to as an “match horizon.” That implies we will be able to’t “see” black holes until they feed on topic round them and forged their shadow on it. However, identical to darkish topic, black holes do have interaction with gravity.Mróz and co-workers have been thus ready to show to Albert Einstein’s 1915 concept of gravity, common relativity, and a idea it presented to seek for primordial black holes within the Milky Approach.Einstein lends a handEinstein’s concept of common relativity says gadgets of mass warp the very cloth of area and time, united as a unmarried entity referred to as “spacetime.” Gravity is a results of that curvature, and the extra large an object is, the extra excessive the warping of spacetime it reasons and, thus, the higher the “gravity” it generates.No longer most effective does this curvature inform planets how one can orbit round stars, and inform stars how one can race across the facilities in their house galaxies, however it additionally bends the trail of sunshine coming from background stars and galaxies. The nearer to the thing of mass that gentle travels, the extra its trail is “bent.”Other paths of sunshine from a unmarried background object can thus be bent, transferring the plain location of the background object. Every so often, the impact may also motive the background object to look in more than one puts in the similar symbol of the sky. Different instances, gentle from the background object is amplified, and that object is magnified. This phenomenon is referred to as “gravitational lensing,” and the intervening frame is named a gravitational lens. Vulnerable examples of this impact are referred to as “microlensing.”
A diagram appearing the huge distinction in scale between supermassive black holes and hypothetical primordial black holes. (Symbol credit score: Robert Lea (created with Canva))One imaginable cause of this better inhabitants of black holes is that they’re leftovers from a length simply after the Giant Bang that shaped now not from the cave in of big stars however from overly dense patches of primordial gasoline and mud.”We all know that the early universe used to be now not preferably homogeneous — small density fluctuations gave upward thrust to present galaxies and galaxy clusters,” Mróz mentioned. “An identical density fluctuations, in the event that they exceed a essential density distinction, would possibly cave in and shape black holes.”Those “primordial black holes” have been first postulated through Stephen Hawking over 50 years in the past however have remained frustratingly elusive. Which may be as a result of smaller examples would hastily “leak” a type of thermal power referred to as Hawking radiation and in the end evaporating, which means they wouldn’t exist within the present epoch of the 13.8 billion-year-old cosmos. But, this hindrance hasn’t stopped some physicists from positing primordial black holes as a imaginable cause of darkish topic.Darkish topic is estimated to contain 90% to 95% of the Milky Approach’s mass. That implies, if darkish topic is product of primordial black holes, our galaxy must comprise many of those historical our bodies. Black holes do not emit gentle as a result of they’re sure through a light-trapping floor referred to as an “match horizon.” That implies we will be able to’t “see” black holes until they feed on topic round them and forged their shadow on it. However, identical to darkish topic, black holes do have interaction with gravity.Mróz and co-workers have been thus ready to show to Albert Einstein’s 1915 concept of gravity, common relativity, and a idea it presented to seek for primordial black holes within the Milky Approach.Einstein lends a handEinstein’s concept of common relativity says gadgets of mass warp the very cloth of area and time, united as a unmarried entity referred to as “spacetime.” Gravity is a results of that curvature, and the extra large an object is, the extra excessive the warping of spacetime it reasons and, thus, the higher the “gravity” it generates.No longer most effective does this curvature inform planets how one can orbit round stars, and inform stars how one can race across the facilities in their house galaxies, however it additionally bends the trail of sunshine coming from background stars and galaxies. The nearer to the thing of mass that gentle travels, the extra its trail is “bent.”Other paths of sunshine from a unmarried background object can thus be bent, transferring the plain location of the background object. Every so often, the impact may also motive the background object to look in more than one puts in the similar symbol of the sky. Different instances, gentle from the background object is amplified, and that object is magnified. This phenomenon is referred to as “gravitational lensing,” and the intervening frame is named a gravitational lens. Vulnerable examples of this impact are referred to as “microlensing.”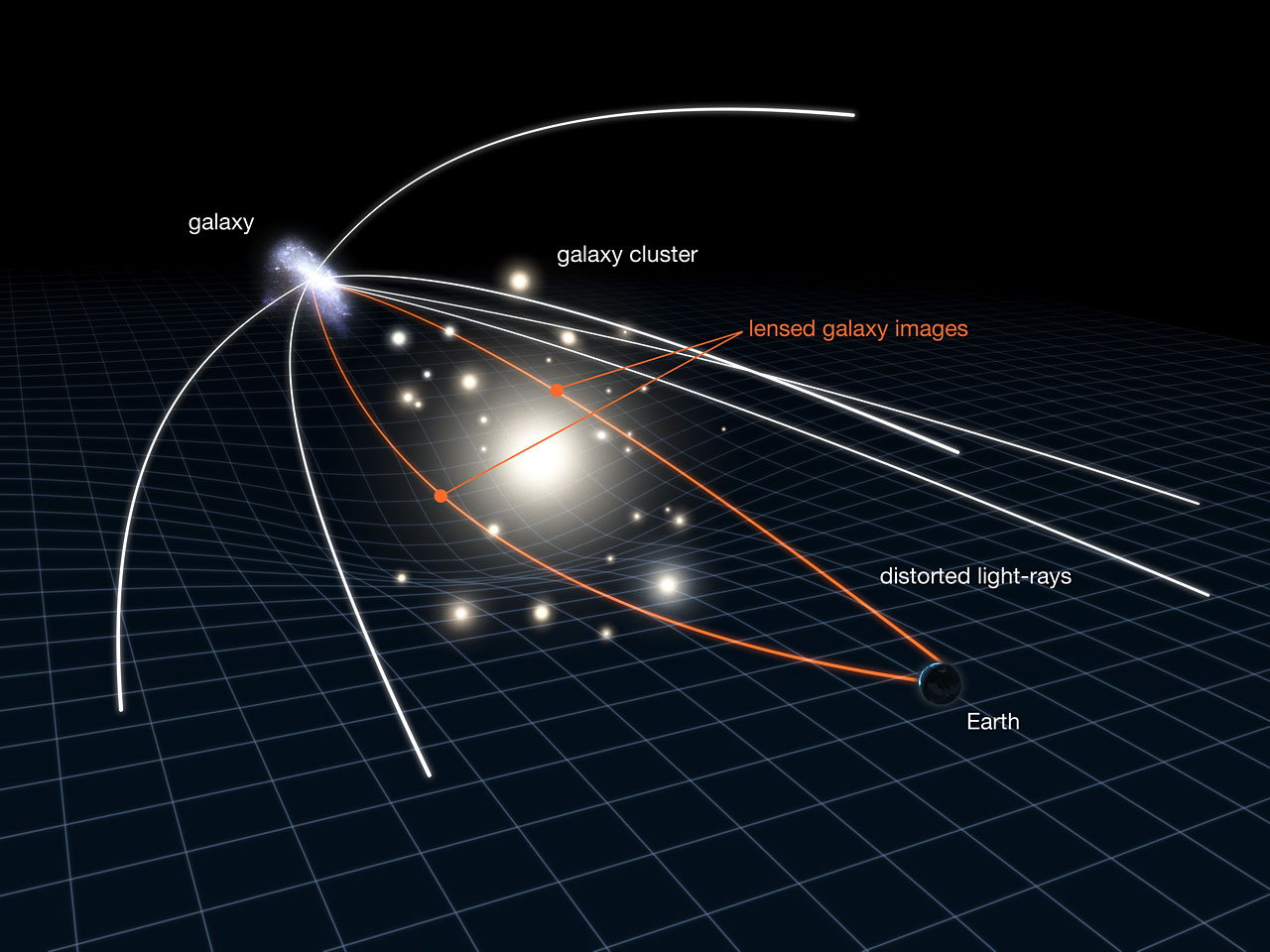 A diagram presentations how gentle from a background object is curved through a foreground frame. (Symbol credit score: NASA, ESA & L. Calçada)If a primordial black hollow within the Milky Approach passes between Earth and a background celebrity, then we must see microlensing results on that celebrity for a temporary time period.”Microlensing happens when 3 gadgets — an observer on Earth, a supply of sunshine, and a lens — nearly preferably align in area,” OGLE survey Idea Investigator Andrzej Udalski, mentioned within the observation. “All through a microlensing match, the supply’s gentle is also deflected and magnified, and we practice a short lived brightening of the supply’s gentle.”How lengthy gentle from the background supply is brightened will depend on the mass of the lensing frame that passes between it and Earth, with gadgets of higher mass inducing longer microlensing occasions. An object across the mass of the solar must motive a brightening for round every week; for lensing our bodies with lots 100 instances that of the solar, alternatively, the brightening must final so long as a number of years. Earlier makes an attempt had been made to make use of microlensing to stumble on primordial black holes and learn about darkish topic. Prior experiments appeared to display that black holes much less large than the solar and may just contain underneath 10% of darkish topic. The problem with those experiments, alternatively, used to be they weren’t delicate to extraordinarily long-timescale microlensing occasions. Thus, as a result of extra large black holes (very similar to the ones just lately detected with gravitational-wave detectors) would motive longer occasions, those experiments were not delicate to that inhabitants of black holes both.
A diagram presentations how gentle from a background object is curved through a foreground frame. (Symbol credit score: NASA, ESA & L. Calçada)If a primordial black hollow within the Milky Approach passes between Earth and a background celebrity, then we must see microlensing results on that celebrity for a temporary time period.”Microlensing happens when 3 gadgets — an observer on Earth, a supply of sunshine, and a lens — nearly preferably align in area,” OGLE survey Idea Investigator Andrzej Udalski, mentioned within the observation. “All through a microlensing match, the supply’s gentle is also deflected and magnified, and we practice a short lived brightening of the supply’s gentle.”How lengthy gentle from the background supply is brightened will depend on the mass of the lensing frame that passes between it and Earth, with gadgets of higher mass inducing longer microlensing occasions. An object across the mass of the solar must motive a brightening for round every week; for lensing our bodies with lots 100 instances that of the solar, alternatively, the brightening must final so long as a number of years. Earlier makes an attempt had been made to make use of microlensing to stumble on primordial black holes and learn about darkish topic. Prior experiments appeared to display that black holes much less large than the solar and may just contain underneath 10% of darkish topic. The problem with those experiments, alternatively, used to be they weren’t delicate to extraordinarily long-timescale microlensing occasions. Thus, as a result of extra large black holes (very similar to the ones just lately detected with gravitational-wave detectors) would motive longer occasions, those experiments were not delicate to that inhabitants of black holes both. 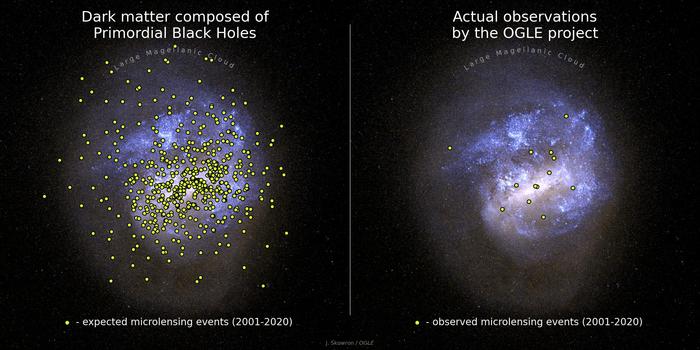 At the left the predicted gravitational lensing occasions if primordial black holes account for darkish topic. At the proper, the true lensing occasions noticed through OGLE between 2001 and 2020 (Symbol credit score: J. Skowron / OGLE. Background symbol of the Huge Magellanic Cloud: generated with bsrender written through Kevin Loch, the use of the ESA/Gaia database)This crew advanced sensitivity to long-lasting microlensing occasions through turning to 20-year-long tracking of virtually 80 million stars positioned in a satellite tv for pc galaxy or the Milky Approach referred to as the Huge Magellanic Cloud (LMC).The studied knowledge, described as “the longest, biggest, and maximum correct photometric observations of stars within the LMC within the historical past of recent astronomy” through Udalski, used to be accrued through the OGLE venture from 2001 to 2020 right through its 3rd and fourth working stages. The crew in comparison the microlensing occasions observed through OGLE to the theoretically predicted quantity of such occasions, assuming that the Milky Approach’s darkish topic is made up of primordial black holes.”If all of the darkish topic within the Milky Approach used to be composed of black holes of 10 sun lots, we must have detected 258 microlensing occasions,” Mróz mentioned. “For 100 sun mass black holes, we anticipated 99 microlensing occasions. For 1000 sun mass black holes — 27 microlensing occasions.”Against this to those estimated quantities of occasions, the crew most effective discovered 12 microlensing occasions within the OGLE knowledge. Additional research published all of those occasions may well be defined through the identified stars within the Milky Approach and within the LMC itself. After those calculations, the crew discovered black holes of 10 sun lots may just contain at maximum 1.2% of darkish topic, smaller 100 sun mass black holes may just account for not more than 3.0% of darkish topic and 1000 sun mass black holes may just most effective contain 11% of darkish topic.”That signifies that vast black holes can compose, at maximum, a couple of % of darkish topic,” Mróz defined.”Our observations point out that primordial black holes can not contain a vital fraction of the darkish topic and, concurrently, give an explanation for the noticed black hollow merger charges measured through LIGO and Virgo,” Udalski concluded. “Our effects will stay in astronomy textbooks for many years to return.”This leaves astronomers to go back to the drafting board to provide an explanation for the commentary of overly large stellar-mass black holes past the Milky Approach whilst physicists proceed to puzzle over the actual nature of darkish topic. The crew’s analysis is printed on June 24 the journals Nature and the Astrophysical Magazine Complement Collection.
At the left the predicted gravitational lensing occasions if primordial black holes account for darkish topic. At the proper, the true lensing occasions noticed through OGLE between 2001 and 2020 (Symbol credit score: J. Skowron / OGLE. Background symbol of the Huge Magellanic Cloud: generated with bsrender written through Kevin Loch, the use of the ESA/Gaia database)This crew advanced sensitivity to long-lasting microlensing occasions through turning to 20-year-long tracking of virtually 80 million stars positioned in a satellite tv for pc galaxy or the Milky Approach referred to as the Huge Magellanic Cloud (LMC).The studied knowledge, described as “the longest, biggest, and maximum correct photometric observations of stars within the LMC within the historical past of recent astronomy” through Udalski, used to be accrued through the OGLE venture from 2001 to 2020 right through its 3rd and fourth working stages. The crew in comparison the microlensing occasions observed through OGLE to the theoretically predicted quantity of such occasions, assuming that the Milky Approach’s darkish topic is made up of primordial black holes.”If all of the darkish topic within the Milky Approach used to be composed of black holes of 10 sun lots, we must have detected 258 microlensing occasions,” Mróz mentioned. “For 100 sun mass black holes, we anticipated 99 microlensing occasions. For 1000 sun mass black holes — 27 microlensing occasions.”Against this to those estimated quantities of occasions, the crew most effective discovered 12 microlensing occasions within the OGLE knowledge. Additional research published all of those occasions may well be defined through the identified stars within the Milky Approach and within the LMC itself. After those calculations, the crew discovered black holes of 10 sun lots may just contain at maximum 1.2% of darkish topic, smaller 100 sun mass black holes may just account for not more than 3.0% of darkish topic and 1000 sun mass black holes may just most effective contain 11% of darkish topic.”That signifies that vast black holes can compose, at maximum, a couple of % of darkish topic,” Mróz defined.”Our observations point out that primordial black holes can not contain a vital fraction of the darkish topic and, concurrently, give an explanation for the noticed black hollow merger charges measured through LIGO and Virgo,” Udalski concluded. “Our effects will stay in astronomy textbooks for many years to return.”This leaves astronomers to go back to the drafting board to provide an explanation for the commentary of overly large stellar-mass black holes past the Milky Approach whilst physicists proceed to puzzle over the actual nature of darkish topic. The crew’s analysis is printed on June 24 the journals Nature and the Astrophysical Magazine Complement Collection.
Lacking Milky Approach black holes are dangerous information for this darkish topic concept









/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25806329/Screenshot_2024_12_26_at_5.43.25_PM.jpeg)


