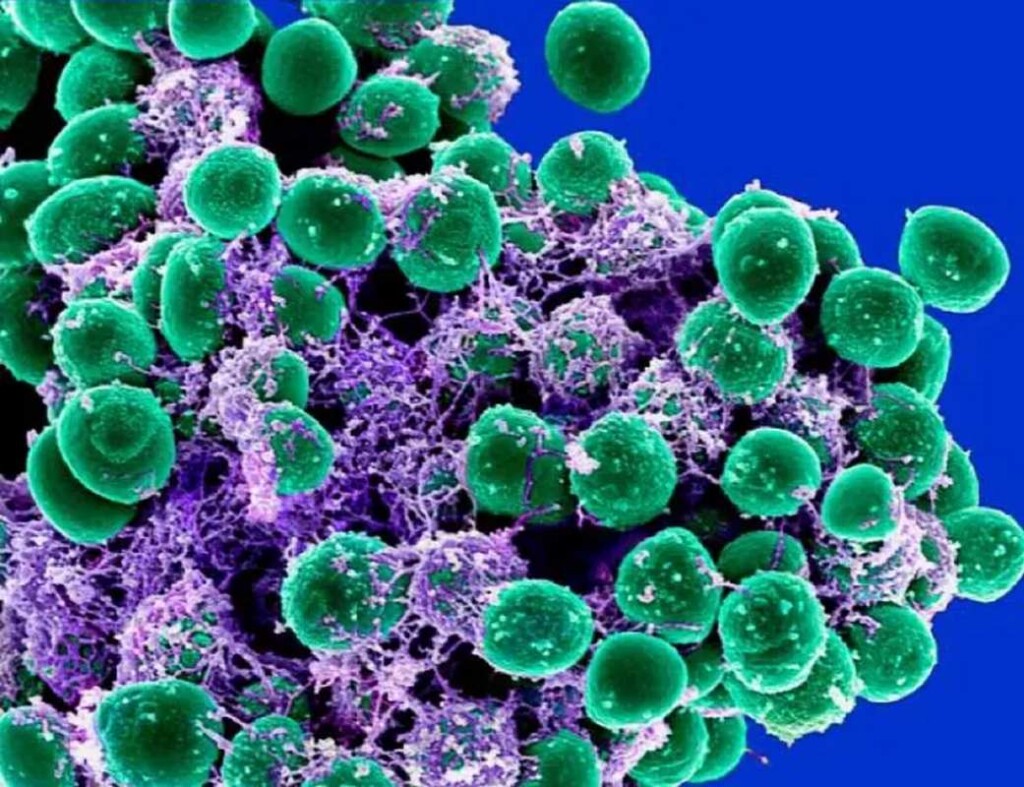
What came about? Any other day, every other battery discovery. Researchers have unveiled a promising lithium manganese oxide battery era that hits 820 watt-hours in line with kilogram of power with out electric breakdown, making standard lithium batteries part as thick. The lithium-ion batteries that energy our telephones, laptops, and electrical vehicles steadily use nickel and cobalt of their cathodes, which may make them dear and not more environmentally pleasant because of the intensive mining they require. On the other hand, this new discovery has changed that treasured steel with manganese. In keeping with a find out about printed in ACS Central Science this week, nanostructured lithium manganese oxide cathodes can reach very good power potency of as much as 820 Wh/Kg. That is aggressive with these days’s prime quality nickel cathodes (round 750 Wh/kg), and higher than different less expensive lithium choices at 500 Wh/kg. Top power density is just one a part of the disturbance. Those manganese cathodes additionally function speedy charging functions, which may be very helpful for EVs the place you do not need to be plugged right into a charging station for hours. On most sensible of that, in contrast to different manganese batteries, they do not appear to be afflicted by electric injury. Electric decay is a phenomenon through which electric power decreases over the years, lowering potency and electric reaction. It is not uncommon in manganese merchandise.

As for the way the researchers solved the issue, it comes right down to tracking the crystal construction and segment transitions in lithium manganese oxide on the nanoscale. By means of synthesizing the nanostructured shape and the monoclinic layer ruled, they have been in a position to stabilize the fabric in essentially the most optimum order. The nanoscale monoclinic crystal construction is the important thing that unlocks the real doable of manganese as a battery electrode. It permits for a segment shift that forestalls the cathode from increase in an overly low state. The one problem is that manganese is extremely soluble and will dissolve over the years within the battery. Tackling the issue stays a problem, however researchers have discovered it may be mitigated through the usage of extremely concentrated electrolytes and lithium phosphate coatings.
Leap forward 820 Wh/kg battery ditches nickel and cobalt for manganese




/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25782341/google_willow_chip.png)