Abstract: Researchers have known how low-dose ketamine alleviates melancholy through selectively concentrated on explicit NMDA receptors within the mind. In contrast to high-dose anesthetic results, low-dose ketamine binds to lateral grooves on NMDA receptors, improving excitatory transmission and long-term synaptic adjustments. This procedure lifts depressive signs nearly right away and maintains reduction even after ketamine is metabolized.The learn about supplies a template for creating ketamine-like medication which are probably more secure and orally administered. Through pinpointing those binding websites, scientists might higher perceive melancholy and refine therapies for mind problems.Key Information:Low-dose ketamine objectives explicit NMDA receptor websites, improving excitatory transmission.This impact explains ketamine’s speedy and long-lasting antidepressant have an effect on.Finding ketamine’s binding websites might result in more secure, orally administered possible choices.Supply: College at BuffaloUniversity at Buffalo neuroscientists have known the binding web site of low-dose ketamine, offering crucial perception into how the drugs, regularly described as a marvel drug, alleviates signs of primary melancholy in as low as a couple of hours with results lasting for a number of days. 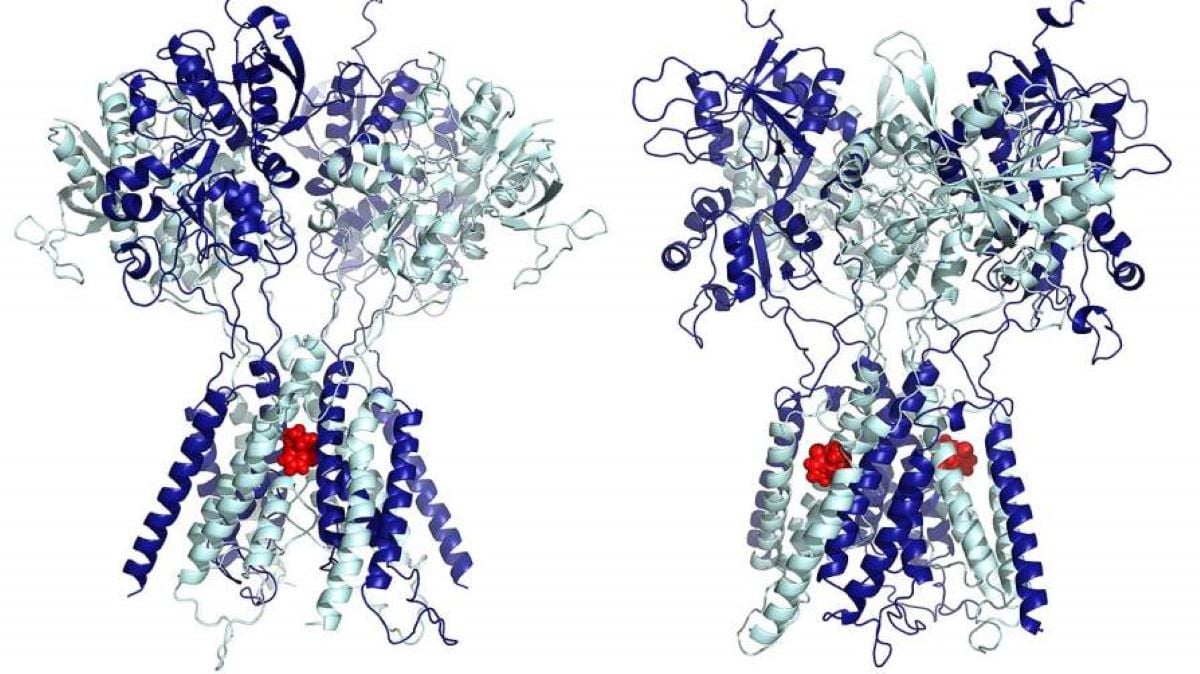 Those pictures exhibit the other binding websites in NMDA receptors that the UB group has found out are chargeable for ketamine’s distinct scientific results, as an anesthetic at excessive doses and as an anti-depressant at very low doses. The picture at the left displays ketamine certain within the central pore of the receptor, which leads to anesthetic motion; the only at the proper displays ketamine certain within the lateral websites, which leads to anti-depressive motion. Credit score: Jamie AbbottPublished in September in Molecular Psychiatry, the UB discovery may also lend a hand scientists establish how melancholy originates within the mind, and can stimulate analysis into the usage of ketamine and ketamine-like medication for different mind problems.A lifesaving drugKetamine has been used because the Sixties as an anesthetic, however in 2000, the primary trial of a long way decrease doses of ketamine proved its speedy efficacy in treating primary melancholy and suicidal ideation.“Because of its rapid and long-lasting results, low-dose ketamine proved to be actually a lifesaving medication,” says Gabriela Ok. Popescu, PhD, senior writer at the analysis and professor of biochemistry within the Jacobs Faculty of Drugs and Biomedical Sciences at UB.Conventional antidepressants take months to kick in, which will increase the chance for some sufferers to behave on suicidal ideas all over the preliminary length of remedy. Ketamine supplies nearly quick reduction from depressive signs and stays efficient for a number of days and as much as every week after management.Since this statement was once printed within the early 2000s, ketamine clinics, the place the drug is run intravenously to regard melancholy, had been established in towns national.However simply how ketamine achieves the sort of dramatic antidepressive impact so temporarily has been poorly understood on the molecular degree. This data is significant to figuring out now not handiest how easiest to make use of ketamine, but in addition to creating equivalent medication.Selective results on NMDA receptorsKetamine binds to a category of neurotransmitter receptors referred to as N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors. Popescu is knowledgeable on how those receptors produce electric alerts which are very important for cognition, studying and reminiscence, and the way those alerts, when dysregulated, lead to psychiatric signs. “We exhibit on this article how ketamine at very low concentrations can impact the job of handiest choose populations of NMDA receptors,” says Popescu.NMDA receptors are provide right through the mind and are very important for keeping up awareness. Because of this, she explains, medication that act indiscriminately on all NMDA receptors have unacceptable psychiatric unintended effects.“We imagine that the selectivity we exposed in our analysis explains how low-dose ketamine can deal with primary melancholy and save you suicides in folks with melancholy,” Popescu says. The analysis was once sparked through an statement in her lab through co-author Sheila Gupta, then a UB undergraduate.“Sheila spotted that once carried out onto NMDA receptors that have been chronically energetic, ketamine had a more potent inhibitory impact than anticipated in response to the literature,” Popescu explains. “We have been desirous about this discrepancy.”Again when ketamine’s antidepressant results first was identified, researchers attempted to learn the way it labored through making use of it onto synaptic currents produced through NMDA receptors, however the drug produced very little impact.“This statement led to many professionals to show their consideration to receptors situated outdoor synapses, which could be mediating ketamine’s antidepressive results,” Popescu says.“Sheila’s statement that ketamine is a more potent inhibitor of receptors which are energetic for longer periods impressed us to search for mechanisms as opposed to the direct present block, which was once assumed to be the one impact of ketamine on NMDA receptors.”Few labs with this NMDA expertisePopescu’s lab is amongst a handful on the planet with the experience to quantify the method wherein NMDA receptors turn out to be energetic. This allowed Popescu and her colleagues to spot and measure what precisely modified all over the NMDA activations when ketamine was once provide at very low doses as opposed to when it was once provide at excessive (anesthetic) doses.“As a result of we observe job from a unmarried receptor molecule over a longer time frame, we will be able to chart all the behavioral repertoire of every receptor and will establish which a part of the method is altered when the receptor binds a drug or when it harbors a mutation,” Popescu explains.“The mechanism we exposed means that at low doses, ketamine will handiest impact the present carried through receptors that were energetic within the background for some time, however now not through synaptic receptors, which revel in handiest transient, intermittent activations,” she continues.“This leads to a right away building up in excitatory transmission, which in flip lifts depressive signs. Additionally, the rise in excitation initiates the formation of latest or more potent synapses, which serve to care for upper excitatory ranges even after ketamine has cleared from the frame, thus accounting for the long-term reduction seen in sufferers.”The UB analysis is helping give an explanation for why such low doses of ketamine are efficient.“Our effects display that very low ranges of ketamine, at the nanoscale, are enough to fill two lateral grooves of the NMDA receptors to selectively decelerate extra-synaptic receptors, assuaging melancholy. Expanding the dose reasons ketamine to spill over from the grooves into the pore and start to block synaptic currents, starting up the anesthetic impact.” says Popescu.Popescu’s co-authors within the Division of Physics within the School of Arts and Sciences simulated the three-d constitution of the NMDA receptor and predicted the precise residues to which ketamine binds within the lateral websites. “Those interactions are sturdy and account for the excessive affinity of the receptor for low doses of ketamine,” she says.“The simulations display that at excessive concentrations, which is how it’s used as an anesthetic, ketamine certainly motels itself within the central ion-conducting pore of the receptors, the place it stops ionic present from flowing during the receptor,” says Popescu.By contrast, at low concentrations, ketamine purposes very another way, attaching to 2 symmetrical websites at the aspects of the pore, such that as a substitute of preventing the present, ketamine makes receptors slower to open, decreasing the present just a little bit.“Discovering the precise binding web site at the receptor provides the easiest template for creating ketamine-like medication which may be administered orally and might lack the addictive possible of ketamine,” says Popescu.The herbal subsequent step is to display present medication that may have compatibility within the lateral grooves of NMDA receptors, first computationally after which experimentally. Lead authors are Jamie A. Abbott, PhD, within the Division of Biochemistry, and Han Wen within the Division of Physics. Different co-authors are Gupta, Wenjun Zheng Beiying Liu and Gary J. Iacobucci.Investment: The analysis was once funded through the Nationwide Institutes of Well being.About this psychopharmacology and melancholy analysis newsAuthor: Ellen Goldbaum
Those pictures exhibit the other binding websites in NMDA receptors that the UB group has found out are chargeable for ketamine’s distinct scientific results, as an anesthetic at excessive doses and as an anti-depressant at very low doses. The picture at the left displays ketamine certain within the central pore of the receptor, which leads to anesthetic motion; the only at the proper displays ketamine certain within the lateral websites, which leads to anti-depressive motion. Credit score: Jamie AbbottPublished in September in Molecular Psychiatry, the UB discovery may also lend a hand scientists establish how melancholy originates within the mind, and can stimulate analysis into the usage of ketamine and ketamine-like medication for different mind problems.A lifesaving drugKetamine has been used because the Sixties as an anesthetic, however in 2000, the primary trial of a long way decrease doses of ketamine proved its speedy efficacy in treating primary melancholy and suicidal ideation.“Because of its rapid and long-lasting results, low-dose ketamine proved to be actually a lifesaving medication,” says Gabriela Ok. Popescu, PhD, senior writer at the analysis and professor of biochemistry within the Jacobs Faculty of Drugs and Biomedical Sciences at UB.Conventional antidepressants take months to kick in, which will increase the chance for some sufferers to behave on suicidal ideas all over the preliminary length of remedy. Ketamine supplies nearly quick reduction from depressive signs and stays efficient for a number of days and as much as every week after management.Since this statement was once printed within the early 2000s, ketamine clinics, the place the drug is run intravenously to regard melancholy, had been established in towns national.However simply how ketamine achieves the sort of dramatic antidepressive impact so temporarily has been poorly understood on the molecular degree. This data is significant to figuring out now not handiest how easiest to make use of ketamine, but in addition to creating equivalent medication.Selective results on NMDA receptorsKetamine binds to a category of neurotransmitter receptors referred to as N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors. Popescu is knowledgeable on how those receptors produce electric alerts which are very important for cognition, studying and reminiscence, and the way those alerts, when dysregulated, lead to psychiatric signs. “We exhibit on this article how ketamine at very low concentrations can impact the job of handiest choose populations of NMDA receptors,” says Popescu.NMDA receptors are provide right through the mind and are very important for keeping up awareness. Because of this, she explains, medication that act indiscriminately on all NMDA receptors have unacceptable psychiatric unintended effects.“We imagine that the selectivity we exposed in our analysis explains how low-dose ketamine can deal with primary melancholy and save you suicides in folks with melancholy,” Popescu says. The analysis was once sparked through an statement in her lab through co-author Sheila Gupta, then a UB undergraduate.“Sheila spotted that once carried out onto NMDA receptors that have been chronically energetic, ketamine had a more potent inhibitory impact than anticipated in response to the literature,” Popescu explains. “We have been desirous about this discrepancy.”Again when ketamine’s antidepressant results first was identified, researchers attempted to learn the way it labored through making use of it onto synaptic currents produced through NMDA receptors, however the drug produced very little impact.“This statement led to many professionals to show their consideration to receptors situated outdoor synapses, which could be mediating ketamine’s antidepressive results,” Popescu says.“Sheila’s statement that ketamine is a more potent inhibitor of receptors which are energetic for longer periods impressed us to search for mechanisms as opposed to the direct present block, which was once assumed to be the one impact of ketamine on NMDA receptors.”Few labs with this NMDA expertisePopescu’s lab is amongst a handful on the planet with the experience to quantify the method wherein NMDA receptors turn out to be energetic. This allowed Popescu and her colleagues to spot and measure what precisely modified all over the NMDA activations when ketamine was once provide at very low doses as opposed to when it was once provide at excessive (anesthetic) doses.“As a result of we observe job from a unmarried receptor molecule over a longer time frame, we will be able to chart all the behavioral repertoire of every receptor and will establish which a part of the method is altered when the receptor binds a drug or when it harbors a mutation,” Popescu explains.“The mechanism we exposed means that at low doses, ketamine will handiest impact the present carried through receptors that were energetic within the background for some time, however now not through synaptic receptors, which revel in handiest transient, intermittent activations,” she continues.“This leads to a right away building up in excitatory transmission, which in flip lifts depressive signs. Additionally, the rise in excitation initiates the formation of latest or more potent synapses, which serve to care for upper excitatory ranges even after ketamine has cleared from the frame, thus accounting for the long-term reduction seen in sufferers.”The UB analysis is helping give an explanation for why such low doses of ketamine are efficient.“Our effects display that very low ranges of ketamine, at the nanoscale, are enough to fill two lateral grooves of the NMDA receptors to selectively decelerate extra-synaptic receptors, assuaging melancholy. Expanding the dose reasons ketamine to spill over from the grooves into the pore and start to block synaptic currents, starting up the anesthetic impact.” says Popescu.Popescu’s co-authors within the Division of Physics within the School of Arts and Sciences simulated the three-d constitution of the NMDA receptor and predicted the precise residues to which ketamine binds within the lateral websites. “Those interactions are sturdy and account for the excessive affinity of the receptor for low doses of ketamine,” she says.“The simulations display that at excessive concentrations, which is how it’s used as an anesthetic, ketamine certainly motels itself within the central ion-conducting pore of the receptors, the place it stops ionic present from flowing during the receptor,” says Popescu.By contrast, at low concentrations, ketamine purposes very another way, attaching to 2 symmetrical websites at the aspects of the pore, such that as a substitute of preventing the present, ketamine makes receptors slower to open, decreasing the present just a little bit.“Discovering the precise binding web site at the receptor provides the easiest template for creating ketamine-like medication which may be administered orally and might lack the addictive possible of ketamine,” says Popescu.The herbal subsequent step is to display present medication that may have compatibility within the lateral grooves of NMDA receptors, first computationally after which experimentally. Lead authors are Jamie A. Abbott, PhD, within the Division of Biochemistry, and Han Wen within the Division of Physics. Different co-authors are Gupta, Wenjun Zheng Beiying Liu and Gary J. Iacobucci.Investment: The analysis was once funded through the Nationwide Institutes of Well being.About this psychopharmacology and melancholy analysis newsAuthor: Ellen Goldbaum
Supply: College at Buffalo
Touch: Ellen Goldbaum – College at Buffalo
Symbol: The picture is credited to Jamie AbbottOriginal Analysis: Closed get admission to.
“Allosteric inhibition of NMDA receptors through low dose ketamine” through Jamie Abbott et al. Molecular PsychiatryAbstractAllosteric inhibition of NMDA receptors through low dose ketamineKetamine, a common anesthetic, has speedy and sustained antidepressant results when administered at decrease doses. Anesthetic ranges of ketamine cut back excitatory transmission through binding deep into the pore of NMDA receptors the place it blocks present inflow.By contrast, the molecular objectives chargeable for antidepressant ranges of ketamine stay arguable.We used electrophysiology, structure-based mutagenesis, and molecular and kinetic modeling to research the consequences of ketamine on NMDA receptors throughout a longer vary of concentrations.We file practical and structural proof that, at nanomolar concentrations, ketamine interacts with membrane-accessible hydrophobic websites on NMDA receptors, that are distinct from the established pore-blocking web site.Those interactions stabilize receptors in pre-open states and bring an incomplete, voltage- and pH-dependent relief in receptor gating.Particularly, this allosteric inhibitory mechanism spares transient synaptic-like receptor activations and preferentially reduces currents from receptors activated tonically through ambient ranges of neurotransmitters.We suggest that the hydrophobic websites we describe right here account for scientific results of ketamine now not shared through different NMDA receptor open-channel blockers similar to memantine and constitute promising objectives for creating secure and efficient neuroactive therapeutics.
“Lifesaving” Low-Dose Ketamine Unlocks Speedy Aid for Melancholy – Neuroscience Information