The James Webb Area Telescope has given us a view of the earliest moments of galaxy formation within the Universe.Additionally it is printed a couple of surprises. Such a is the semblance of small, extremely redshifted gadgets nicknamed “little pink dots (LRDs).”
We are not totally certain what they’re, however a brand new learn about issues to a solution.
Probably the most issues we do find out about those gadgets is that their spectra are extremely broadened via motional Doppler. This means that the fuel emitting gentle is spinning across the central area at an incredible velocity, orbiting at greater than 1,000 kilometers consistent with 2d.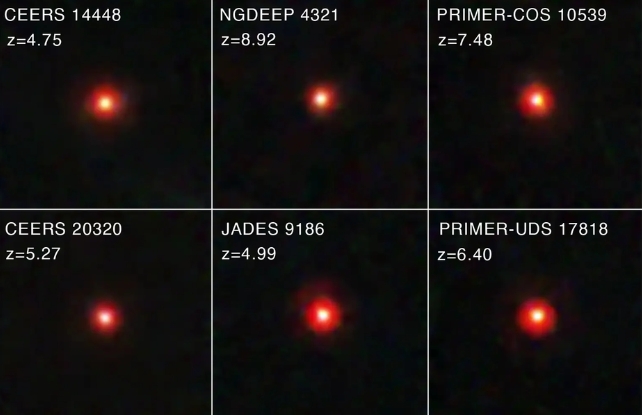 Photographs of little pink dots observed in different deep-sky surveys of JWST. (NASA/ESA/CSA/STScI/Dale Kocevski (Colby School))This means the fabric is orbiting a supermassive black hollow, which powers lively galactic nuclei (AGN). The issue with the AGN type for the little pink dots is that their depth within the infrared spectrum is flat. Additionally they emit little or no within the X-ray and radio levels, which is ordinary for AGNs.
Photographs of little pink dots observed in different deep-sky surveys of JWST. (NASA/ESA/CSA/STScI/Dale Kocevski (Colby School))This means the fabric is orbiting a supermassive black hollow, which powers lively galactic nuclei (AGN). The issue with the AGN type for the little pink dots is that their depth within the infrared spectrum is flat. Additionally they emit little or no within the X-ray and radio levels, which is ordinary for AGNs.
To discover this thriller additional, this new paintings appears to be like at 12 LRDs for which JWST has collected high-resolution spectra. The group then when put next the information to fashions of supermassive black holes.
The fashions assumed a hastily spinning accretion disk surrounding the black hollow embedded inside a tender galactic cloud. First of all, they discovered that the encircling cloud would want to be extremely ionized. With a dense layer of loose electrons surrounding the galaxy, a lot of the X-rays and radio gentle can be absorbed.
In fact, if the shroud is dense sufficient to dam X-rays and radio, the black hollow would want to be producing power at an incredible charge to make the LRDs vivid within the pink and infrared.
In response to observations, the black holes must accrete mass at on the subject of the Eddington Prohibit, which is the utmost charge for subject accretion. Past that charge, the depth of sunshine produced is so sturdy that it could push subject away quicker than gravity may just pull it in combination.
All of this paints an image that LRDs are very younger supermassive black holes which are briefly rising to adulthood. That is supported via estimates of the mass of those black holes on this newest learn about, which places them at round 10,000 to one million sun plenty, which is way smaller than conventional supermassive black holes.
This type would additionally lend a hand to provide an explanation for why we do not see nearer LRDs at decrease redshifts. Their accumulation of subject on the Eddington restrict approach they’d briefly transparent the ionized cloud surrounding them.
As this cloud clears, LRDs would begin to resemble the standard lively galactic nuclei we see all through the cosmos.
Reference: V. Rusakov, et al., JWST’s little pink dots: an rising inhabitants of younger, low-mass AGN cocooned in dense ionized fuel, arXiv preprint arXiv:2503.16595 (2025)This text was once at first printed via Universe Nowadays. Learn the unique article.
‘Little Crimson Dots’ in Early Universe May Be Black Holes Working at Most