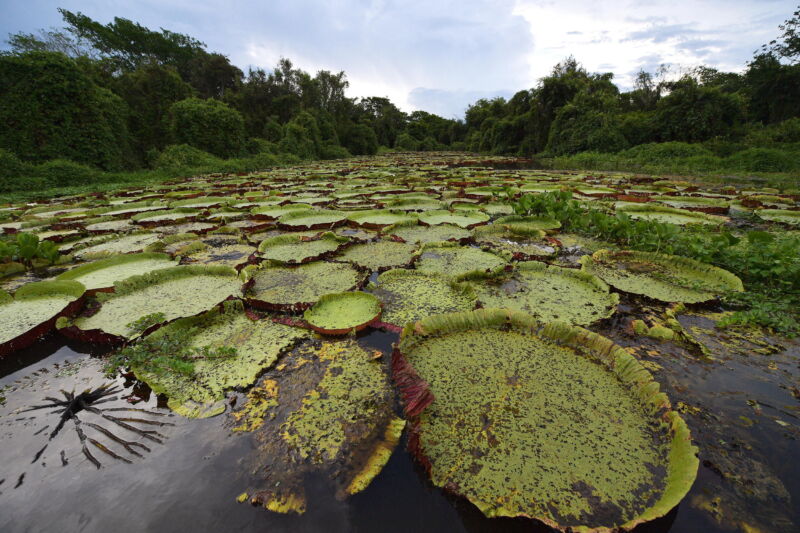
Magnify / A view of the Pantanal wetlands in Brazil. New analysis presentations a big chew of worldwide methane emissions are from rotting plants in tropical wetlands.Carl de Souza/AFP by means of Getty Pictures
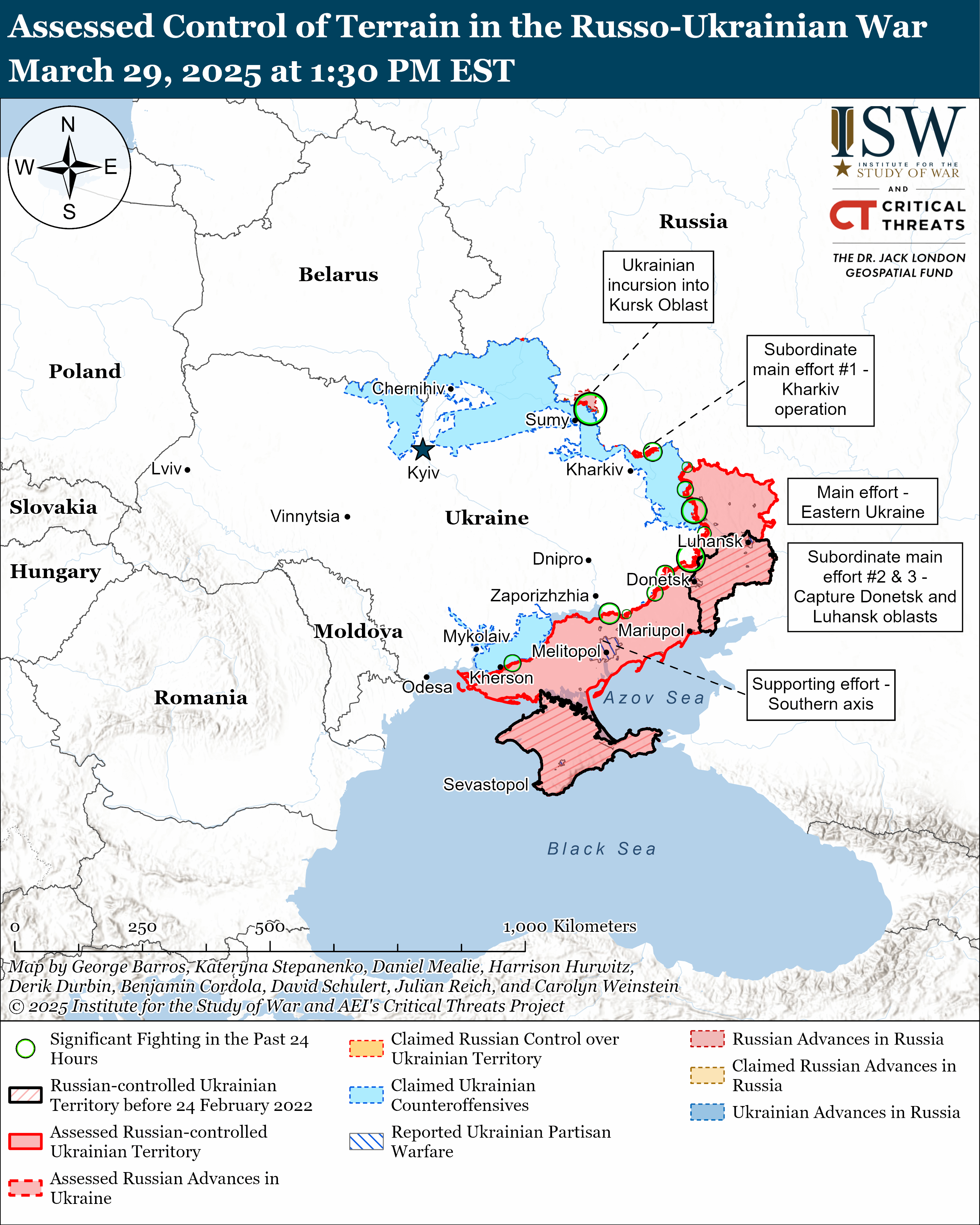
A 2021 pledge by means of greater than 100 countries to chop methane emissions from anthropogenic assets 30 % by means of 2030 may now not gradual international warming up to projected, as new analysis presentations that feedbacks within the weather device are boosting methane emissions from herbal assets, particularly tropical wetlands.
A brand new bother spot is within the Arctic, the place scientists just lately discovered swiftly massive methane emissions in iciness. And globally, the rise in water vapor brought about by means of international warming is slowing the velocity at which methane breaks down within the environment. If the ones feedbacks accentuate, scientists mentioned, it will outpace efforts to chop methane from fossil gasoline and different human assets.
Methane traps about 80 instances extra warmth than carbon dioxide over a 20-year length, and scientists estimate it’s liable for 20 to 30 % of weather warming because the get started of the economic age, when atmospheric methane was once at a focus of about 0.7 portions in step with million. It has zig-zagged upward since then, spiking with the primary fossil fuel increase within the Eighties, then leveling off relatively prior to an enormous surge began within the early 2000s. The quantity of methane within the environment reached about 1.9 ppm in 2023, just about 3 times the pre-industrial stage.
About 60 % of methane emissions are from fossil gasoline use, farming, landfills, and waste, with the remainder coming from rotting plants in wetlands within the tropics and Northern Hemisphere. In a paper printed July 30 in Frontiers in Science, a world crew of researchers wrote that “speedy discounts in methane emissions this decade are crucial to slowing warming within the close to long term… and maintaining low-warming carbon budgets inside of succeed in.”
The scientists discovered that the abrupt surge in methane emissions within the early 2000s is most certainly due basically to the reaction of wetlands to warming, with further contributions coming from fossil gasoline use, “implying that anthropogenic emissions will have to lower greater than anticipated to succeed in a given warming function.”
Expanding rainfall, a well-documented have an effect on of worldwide warming, is making wetlands higher and wetter, and a hotter international fosters extra plant enlargement, because of this extra decomposing subject matter that emits methane.
The rise of methane from herbal assets must spur much more efforts to chop emissions anyplace conceivable, together with from fossil gasoline use and agriculture, mentioned lead creator Drew Shindell, an Earth scientist with Duke College’s Nicholas College of the Setting.
Fresh measurements by means of a specifically provided jet display that methane emissions from oil and fuel operations in america are greater than 4 instances upper than EPA estimates and 8 instances more than fossil business goals. Addressing methane emissions from anthropogenic assets is a a very powerful a part of the weather motion equation, Shindell mentioned, together with the ones from agriculture.
“If we diminished the ones, we’d see a big lower in atmospheric concentrations,” he mentioned. “However reducing emissions from agriculture specifically is implausible within the close to time period, and even perhaps in the longer term.”
The find out about reaffirmed that speedy methane cuts are “crucial to slowing warming within the close to long term, restricting overshoot by means of the center of the century and maintaining low-warming carbon budgets inside of succeed in.” The researchers famous that the prices of lowering methane emissions are low in comparison to many different weather mitigations and that “legally binding rules and popular pricing are wanted” to inspire the deep cuts which might be wanted.
Learn about reveals new methane assets from dry permafrost
Scientists resolve the supply of methane by means of inspecting its carbon isotopes, and because 2007, the ones reviews display that the sign of methane constructed from organic assets “has been getting a lot more potent,” mentioned Euan Nisbet, an atmospheric scientist and methane professional on the College of Cambridge who was once now not concerned within the new paper.
“There are two explanations, either one of them most certainly proper,” he mentioned. “One is that there are much more cows puffing out. However the different one is that the herbal wetlands are turning on. That occurs within the tropics first, after which the permafrost melts in Canada, and all of sudden you get all kinds of methane coming off the Canadian swamps and the Siberian swamps as they rainy up.”
Even chilly, dry areas within the Arctic give a contribution to climate-warming methane air pollution greater than prior to now concept, consistent with a July 18 paper in Nature Communications that checked out dry permafrost spaces referred to as upland Yedoma Taliks discovered predominantly in northern Siberia, the place permafrost thaw most probably will accelerate methane manufacturing as microbes spoil down natural subject matter.