Abstract: Scientists have advanced magnetic nanodiscs that allow centered mind stimulation with out invasive implants or genetic changes. The tiny discs, activated via an exterior magnetic box, ship electric pulses to neurons, appearing attainable in treating neurological stipulations.Preliminary exams in mice demonstrated that those nanodiscs successfully stimulate mind areas related to praise and motor keep watch over, with fewer international frame responses in comparison to conventional implants. The learn about marks a step towards new, much less invasive remedies for mind problems.Long run enhancements purpose to make stronger the discs’ electrical impulse output for even larger efficacy. With additional analysis, those nanodiscs may just change into treasured equipment in neurological analysis and remedy.Key Details:Nanodiscs ship electric stimulation when activated via an exterior magnet.Checking out in mice confirmed efficient stimulation of mind spaces associated with praise and motor purposes.Long run analysis will focal point on amplifying the nanodiscs’ electrical output for scientific use.Supply: MITNovel magnetic nanodiscs may provide a far much less invasive manner of stimulating portions of the mind, paving the way in which for stimulation remedies with out implants or genetic amendment, MIT researchers document.The scientists envision that the tiny discs, which might be about 250 nanometers throughout (about 1/500 the width of a human hair), can be injected at once into the specified location within the mind. From there, they might be activated at any time just by making use of a magnetic box out of doors the frame. 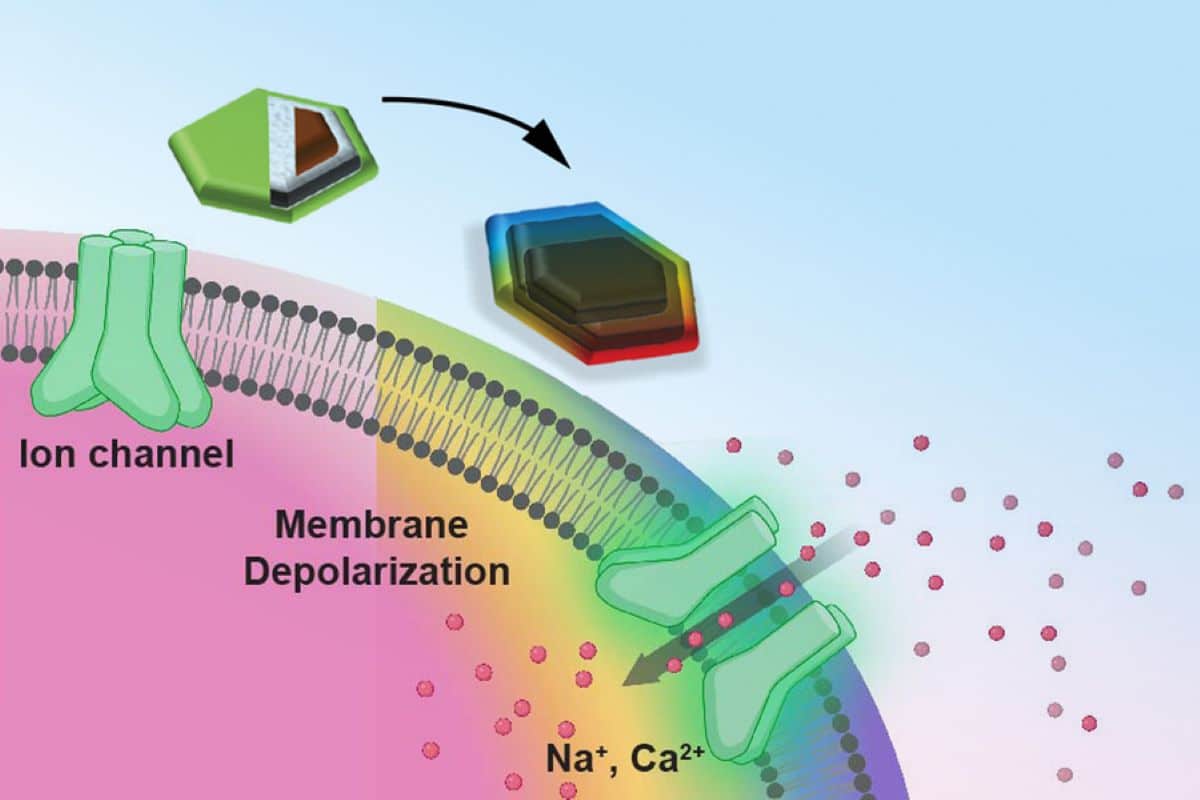 The magnetic core of the nanodisc is magnetostrictive, this means that it adjustments form when magnetized. The rainbow nanodisc at the proper is converting form, bearing in mind the purple mind neuron to be stimulated. Credit score: The researchers.The brand new debris may just temporarily to find packages in biomedical analysis, and ultimately, after enough trying out, may well be implemented to scientific makes use of.The advance of those nanoparticles is described within the magazine Nature Nanotechnology, in a paper via Polina Anikeeva, a professor in MIT’s departments of Fabrics Science and Engineering and Mind and Cognitive Sciences, graduate scholar Ye Ji Kim, and 17 others at MIT and in Germany.Deep mind stimulation (DBS) is a not unusual scientific process that makes use of electrodes implanted within the goal mind areas to regard signs of neurological and psychiatric stipulations equivalent to Parkinson’s illness and obsessive-compulsive dysfunction.In spite of its efficacy, the surgical issue and scientific headaches related to DBS restrict the selection of instances the place such an invasive process is warranted. The brand new nanodiscs may provide a a lot more benign manner of accomplishing the similar effects.During the last decade different implant-free strategies of manufacturing mind stimulation had been advanced. Then again, those approaches have been incessantly restricted via their spatial answer or skill to focus on deep areas.For the previous decade, Anikeeva’s Bioelectronics crew in addition to others within the box used magnetic nanomaterials to transduce faraway magnetic indicators into mind stimulation. Then again, those magnetic strategies depended on genetic changes and will’t be utilized in people.Since all nerve cells are delicate to electric indicators, Kim, a graduate scholar in Anikeeva’s crew, hypothesized {that a} magnetoelectric nanomaterial that may successfully convert magnetization into electric attainable may just be offering a trail towards faraway magnetic mind stimulation. Making a nanoscale magnetoelectric subject matter was once, then again, an impressive problem.Kim synthesized novel magnetoelectric nanodiscs and collaborated with Noah Kent, a postdoc in Anikeeva’s lab with a background in physics who’s a 2d writer of the learn about, to know the houses of those debris.The construction of the brand new nanodiscs is composed of a two-layer magnetic core and a piezoelectric shell. The magnetic core is magnetostrictive, this means that it adjustments form when magnetized.This deformation then induces pressure within the piezoelectric shell which produces a various electric polarization. During the aggregate of the 2 results, those composite debris can ship electric pulses to neurons when uncovered to magnetic fields.One key to the discs’ effectiveness is their disc form. Earlier makes an attempt to make use of magnetic nanoparticles had used round debris, however the magnetoelectric impact was once very susceptible, says Kim. This anisotropy complements magnetostriction via over a 1000-fold, provides Kent.The group first added their nanodiscs to cultured neurons, which allowed then to turn on those cells on call for with brief pulses of magnetic box. This stimulation didn’t require any genetic amendment.They then injected small droplets of magnetoelectric nanodiscs resolution into particular areas of the brains of mice. Then, merely turning on a reasonably susceptible electromagnet close by caused the debris to unencumber a tiny jolt of electrical energy in that mind area.The stimulation might be switched off and on remotely via the switching of the electromagnet. {That electrical} stimulation “had an affect on neuron job and on habits,” Kim says.The group discovered that the magnetoelectric nanodiscs may just stimulate a deep mind area, the ventral tegmental space, this is related to emotions of praise.The group additionally stimulated any other mind space, the subthalamic nucleus, related to motor keep watch over.“That is the area the place electrodes generally get implanted to control Parkinson’s illness,” Kim explains.The researchers have been in a position to effectively reveal the modulation of motor keep watch over in the course of the debris. Particularly, via injecting nanodiscs handiest in a single hemisphere, the researchers may just induce rotations in wholesome mice via making use of magnetic box.The nanodiscs may just cause the neuronal job related with standard implanted electrodes handing over delicate electric stimulation. The authors completed subsecond temporal precision for neural stimulation with their means but seen considerably lowered international frame responses as in comparison to the electrodes, doubtlessly bearing in mind even more secure deep mind stimulation.The multilayered chemical composition and bodily form and dimension of the brand new multilayered nanodiscs is what made exact stimulation conceivable.Whilst the researchers effectively higher the magnetostrictive impact, the second one a part of the method, changing the magnetic impact into {an electrical} output, nonetheless wishes extra paintings, Anikeeva says.Whilst the magnetic reaction was once one thousand occasions larger, the conversion to an electrical impulse was once handiest 4 occasions more than with standard round debris.“This large enhancement of one thousand occasions didn’t utterly translate into the magnetoelectric enhancement,” says Kim.“That’s the place a large number of the longer term paintings shall be targeted, on ensuring that the thousand occasions amplification in magnetostriction will also be transformed into one thousand occasions amplification within the magnetoelectric coupling.”What the group discovered, when it comes to the way in which the debris’ shapes impacts their magnetostriction, was once reasonably surprising. “It’s roughly a brand new factor that simply seemed once we attempted to determine why those debris labored so effectively,” says Kent.Anikeeva provides: “Sure, it’s a record-breaking particle, however it’s no longer as record-breaking because it might be.” That continues to be a subject matter for additional paintings, however the group has concepts about how you can make additional growth.Whilst those nanodiscs may just in theory already be implemented to elementary analysis the usage of animal fashions, to translate them to scientific use in people will require a number of extra steps, together with large-scale protection research, “which is one thing educational researchers aren’t essentially maximum well-positioned to do,” Anikeeva says.“After we to find that those debris are in point of fact helpful in a specific scientific context, then we consider that there shall be a pathway for them to go through extra rigorous broad animal protection research.”The group integrated researchers affiliated with MIT’s departments of Fabrics Science and Engineering, Electric Engineering and Pc Science, Chemistry, and Mind and Cognitive Sciences; the Analysis Laboratory of Electronics; the McGovern Institute for Mind Analysis; and the Koch Institute for Integrative Most cancers Analysis; and from the Friedrich-Alexander College of Erlangen, Germany.Investment: The paintings was once supported, partially, via the Nationwide Institutes of Well being, the Nationwide Middle for Complementary and Integrative Well being, the Nationwide Institute for Neurological Issues and Stroke, the McGovern Institute for Mind Analysis, and the Ok. Lisa Yang and Hock E. Tan Middle for Molecular Therapeutics in Neuroscience.About this neurotech analysis newsAuthor: David L. Chandler
The magnetic core of the nanodisc is magnetostrictive, this means that it adjustments form when magnetized. The rainbow nanodisc at the proper is converting form, bearing in mind the purple mind neuron to be stimulated. Credit score: The researchers.The brand new debris may just temporarily to find packages in biomedical analysis, and ultimately, after enough trying out, may well be implemented to scientific makes use of.The advance of those nanoparticles is described within the magazine Nature Nanotechnology, in a paper via Polina Anikeeva, a professor in MIT’s departments of Fabrics Science and Engineering and Mind and Cognitive Sciences, graduate scholar Ye Ji Kim, and 17 others at MIT and in Germany.Deep mind stimulation (DBS) is a not unusual scientific process that makes use of electrodes implanted within the goal mind areas to regard signs of neurological and psychiatric stipulations equivalent to Parkinson’s illness and obsessive-compulsive dysfunction.In spite of its efficacy, the surgical issue and scientific headaches related to DBS restrict the selection of instances the place such an invasive process is warranted. The brand new nanodiscs may provide a a lot more benign manner of accomplishing the similar effects.During the last decade different implant-free strategies of manufacturing mind stimulation had been advanced. Then again, those approaches have been incessantly restricted via their spatial answer or skill to focus on deep areas.For the previous decade, Anikeeva’s Bioelectronics crew in addition to others within the box used magnetic nanomaterials to transduce faraway magnetic indicators into mind stimulation. Then again, those magnetic strategies depended on genetic changes and will’t be utilized in people.Since all nerve cells are delicate to electric indicators, Kim, a graduate scholar in Anikeeva’s crew, hypothesized {that a} magnetoelectric nanomaterial that may successfully convert magnetization into electric attainable may just be offering a trail towards faraway magnetic mind stimulation. Making a nanoscale magnetoelectric subject matter was once, then again, an impressive problem.Kim synthesized novel magnetoelectric nanodiscs and collaborated with Noah Kent, a postdoc in Anikeeva’s lab with a background in physics who’s a 2d writer of the learn about, to know the houses of those debris.The construction of the brand new nanodiscs is composed of a two-layer magnetic core and a piezoelectric shell. The magnetic core is magnetostrictive, this means that it adjustments form when magnetized.This deformation then induces pressure within the piezoelectric shell which produces a various electric polarization. During the aggregate of the 2 results, those composite debris can ship electric pulses to neurons when uncovered to magnetic fields.One key to the discs’ effectiveness is their disc form. Earlier makes an attempt to make use of magnetic nanoparticles had used round debris, however the magnetoelectric impact was once very susceptible, says Kim. This anisotropy complements magnetostriction via over a 1000-fold, provides Kent.The group first added their nanodiscs to cultured neurons, which allowed then to turn on those cells on call for with brief pulses of magnetic box. This stimulation didn’t require any genetic amendment.They then injected small droplets of magnetoelectric nanodiscs resolution into particular areas of the brains of mice. Then, merely turning on a reasonably susceptible electromagnet close by caused the debris to unencumber a tiny jolt of electrical energy in that mind area.The stimulation might be switched off and on remotely via the switching of the electromagnet. {That electrical} stimulation “had an affect on neuron job and on habits,” Kim says.The group discovered that the magnetoelectric nanodiscs may just stimulate a deep mind area, the ventral tegmental space, this is related to emotions of praise.The group additionally stimulated any other mind space, the subthalamic nucleus, related to motor keep watch over.“That is the area the place electrodes generally get implanted to control Parkinson’s illness,” Kim explains.The researchers have been in a position to effectively reveal the modulation of motor keep watch over in the course of the debris. Particularly, via injecting nanodiscs handiest in a single hemisphere, the researchers may just induce rotations in wholesome mice via making use of magnetic box.The nanodiscs may just cause the neuronal job related with standard implanted electrodes handing over delicate electric stimulation. The authors completed subsecond temporal precision for neural stimulation with their means but seen considerably lowered international frame responses as in comparison to the electrodes, doubtlessly bearing in mind even more secure deep mind stimulation.The multilayered chemical composition and bodily form and dimension of the brand new multilayered nanodiscs is what made exact stimulation conceivable.Whilst the researchers effectively higher the magnetostrictive impact, the second one a part of the method, changing the magnetic impact into {an electrical} output, nonetheless wishes extra paintings, Anikeeva says.Whilst the magnetic reaction was once one thousand occasions larger, the conversion to an electrical impulse was once handiest 4 occasions more than with standard round debris.“This large enhancement of one thousand occasions didn’t utterly translate into the magnetoelectric enhancement,” says Kim.“That’s the place a large number of the longer term paintings shall be targeted, on ensuring that the thousand occasions amplification in magnetostriction will also be transformed into one thousand occasions amplification within the magnetoelectric coupling.”What the group discovered, when it comes to the way in which the debris’ shapes impacts their magnetostriction, was once reasonably surprising. “It’s roughly a brand new factor that simply seemed once we attempted to determine why those debris labored so effectively,” says Kent.Anikeeva provides: “Sure, it’s a record-breaking particle, however it’s no longer as record-breaking because it might be.” That continues to be a subject matter for additional paintings, however the group has concepts about how you can make additional growth.Whilst those nanodiscs may just in theory already be implemented to elementary analysis the usage of animal fashions, to translate them to scientific use in people will require a number of extra steps, together with large-scale protection research, “which is one thing educational researchers aren’t essentially maximum well-positioned to do,” Anikeeva says.“After we to find that those debris are in point of fact helpful in a specific scientific context, then we consider that there shall be a pathway for them to go through extra rigorous broad animal protection research.”The group integrated researchers affiliated with MIT’s departments of Fabrics Science and Engineering, Electric Engineering and Pc Science, Chemistry, and Mind and Cognitive Sciences; the Analysis Laboratory of Electronics; the McGovern Institute for Mind Analysis; and the Koch Institute for Integrative Most cancers Analysis; and from the Friedrich-Alexander College of Erlangen, Germany.Investment: The paintings was once supported, partially, via the Nationwide Institutes of Well being, the Nationwide Middle for Complementary and Integrative Well being, the Nationwide Institute for Neurological Issues and Stroke, the McGovern Institute for Mind Analysis, and the Ok. Lisa Yang and Hock E. Tan Middle for Molecular Therapeutics in Neuroscience.About this neurotech analysis newsAuthor: David L. Chandler
Supply: MIT
Touch: David L. Chandler – MIT
Symbol: The picture is credited to Neuroscience NewsOriginal Analysis: Open get right of entry to.
“Magnetoelectric nanodiscs allow wi-fi transgene-free neuromodulation” via Polina Anikeeva et al. Nature NanotechnologyAbstractMagnetoelectric nanodiscs allow wi-fi transgene-free neuromodulationDeep mind stimulation with implanted electrodes has reworked neuroscience research and remedy of neurological and psychiatric stipulations. Finding much less invasive possible choices to deep mind stimulation may just extend its scientific and analysis packages. Nanomaterial-mediated transduction of magnetic fields into electrical potentials has been explored as a way for faraway neuromodulation.Right here we synthesize magnetoelectric nanodiscs (MENDs) with a core–double-shell Fe3O4–CoFe2O4–BaTiO3 structure (250 nm diameter and 50 nm thickness) with environment friendly magnetoelectric coupling.We discover powerful responses to magnetic box stimulation in neurons adorned with MENDs at a density of one µg mm−2 regardless of individual-particle potentials underneath the neuronal excitation threshold. We advise a type for repetitive subthreshold depolarization that, mixed with cable idea, helps our observations in vitro and informs magnetoelectric stimulation in vivo.Injected into the ventral tegmental space or the subthalamic nucleus of genetically intact mice at concentrations of one mg ml−1, MENDs allow faraway keep watch over of praise or motor behaviours, respectively.Those findings set the degree for mechanistic optimization of magnetoelectric neuromodulation against packages in neuroscience analysis.
Magnetic Nanodiscs Be offering Implant-Loose Mind Stimulation – Neuroscience Information