Abstract: Sound stimulation can manipulate mind waves all the way through REM sleep, a degree an important for reminiscence and cognition. The usage of complex era, researchers had been ready to extend the frequency of mind oscillations that decelerate in dementia sufferers, doubtlessly making improvements to reminiscence purposes.The non-invasive method may just pave the best way for cutting edge therapies for dementia by means of concentrated on mind job all the way through sleep. This manner provides hope for boosting reminiscence and cognition with minimum disruption to sufferers’ lives.Key Details:Sound stimulation will increase mind wave frequency all the way through REM sleep.REM sleep is connected to reminiscence and cognitive purposes, which gradual in dementia.This non-invasive method may just result in new dementia therapies.Supply: College of SurreyBrain waves may also be manipulated while in fast eye motion (REM) sleep, a snooze degree related to reminiscence and cognition, a brand new learn about from the College of Surrey unearths. Novel era, the use of sound stimulation, permits scientists to hurry up mind job which turns into slower in sufferers with dementia all the way through this sleep degree. All through this distinctive learn about, Surrey scientists in collaboration with the United Kingdom Dementia Analysis Institute Centre for Care Analysis and Era at Imperial Faculty London, used a just lately evolved era, closed-loop auditory stimulation, which goals mind oscillations all the way through sleep in an actual approach.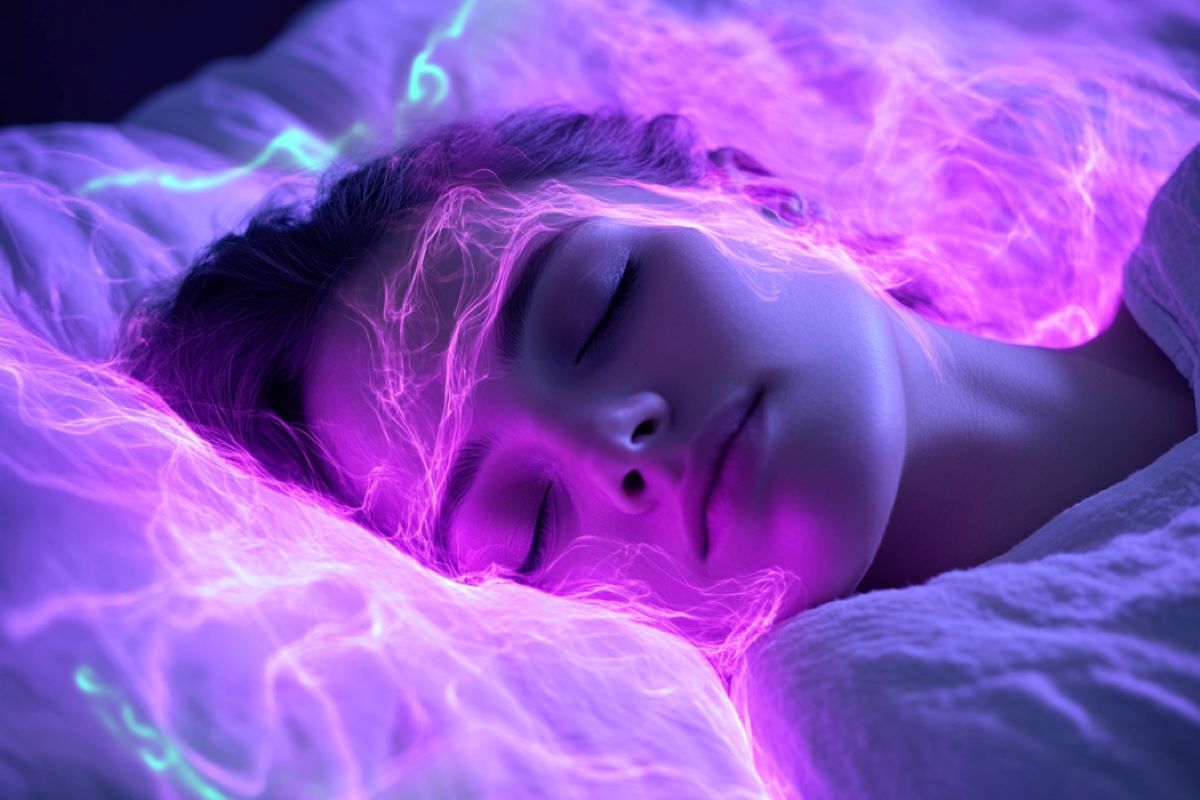  Relying on which a part of the cycle used to be focused by means of the auditory stimuli, oscillations changed into both sooner or slower demonstrating that mind waves may also be manipulated. Credit score: Neuroscience NewsWith this era, sounds are timed to hit mind waves at specific portions (e.g. waxing and waning part) of the oscillation. Sounds had been administered correctly with a pace of six (concentrated on theta waves) or ten (concentrated on alpha waves) instances in keeping with 2nd. For the primary time, this used to be executed all the way through the REM duration of sleep when mind job is very similar to wakefulness, however motion is inhibited. Dr Valeria Jaramillo, Swiss Nationwide Science Basis postdoctoral fellow on the Surrey Sleep Analysis Centre and College of Psychology each on the College of Surrey, Rising Chief at the United Kingdom Dementia Analysis Institute and primary writer of the e-newsletter mentioned:“Mind oscillations help within the running of the mind and the way it learns and keeps data. Mind oscillations all the way through REM sleep were implicated in reminiscence purposes – on the other hand, their actual position stays in large part unclear.In dementia, mind job all the way through REM sleep turns into slower, which is related to a discount within the talent to keep in mind positive lifestyles occasions and retain data.“Stimulating mind waves with sound can building up their frequency and this will assist to raised know how mind oscillations in REM sleep advertise cognition and the way REM sleep may also be progressed in the ones with dementia.”To analyze the impact of stimulation,18 contributors had been recruited and had been monitored in a single day on the Surrey Sleep Analysis Centre. Their sleep used to be incessantly monitored by way of electrodes put on their scalp, and the mind oscillations had been analysed in real-time in order that auditory stimuli may well be administered at actual portions of the oscillations with out waking contributors.Relying on which a part of the cycle used to be focused by means of the auditory stimuli, oscillations changed into both sooner or slower demonstrating that mind waves may also be manipulated.Professor Derk-Jan Dijk, Director of the Surrey Sleep Analysis Centre on the College of Surrey, UK Dementia Analysis Institute Crew Chief and senior writer of the e-newsletter, mentioned: “This may pave the best way for a brand new manner on learn how to deal with sufferers with dementia, because the method is non-invasive and undertaken while they’re asleep, lessening the disruption to their lives and enabling us to be extra focused in our manner.”Dr Ines Violante, Senior Lecturer in Mental Neuroscience on the College of Surrey and senior writer of the e-newsletter, mentioned:“The usage of sound stimulation to switch mind oscillations while an individual sleeps displays healing promise. There may be lately no remedy for dementia, simplest drugs that may decelerate illness development or quickly assist an individual with their signs, so it is necessary that we expect innovatively to expand new remedy choices.“Sound stimulation, which is a non-invasive affordable method, has the possible to do exactly this.”About this sleep and neuroscience analysis newsAuthor: Natasha Meredith
Relying on which a part of the cycle used to be focused by means of the auditory stimuli, oscillations changed into both sooner or slower demonstrating that mind waves may also be manipulated. Credit score: Neuroscience NewsWith this era, sounds are timed to hit mind waves at specific portions (e.g. waxing and waning part) of the oscillation. Sounds had been administered correctly with a pace of six (concentrated on theta waves) or ten (concentrated on alpha waves) instances in keeping with 2nd. For the primary time, this used to be executed all the way through the REM duration of sleep when mind job is very similar to wakefulness, however motion is inhibited. Dr Valeria Jaramillo, Swiss Nationwide Science Basis postdoctoral fellow on the Surrey Sleep Analysis Centre and College of Psychology each on the College of Surrey, Rising Chief at the United Kingdom Dementia Analysis Institute and primary writer of the e-newsletter mentioned:“Mind oscillations help within the running of the mind and the way it learns and keeps data. Mind oscillations all the way through REM sleep were implicated in reminiscence purposes – on the other hand, their actual position stays in large part unclear.In dementia, mind job all the way through REM sleep turns into slower, which is related to a discount within the talent to keep in mind positive lifestyles occasions and retain data.“Stimulating mind waves with sound can building up their frequency and this will assist to raised know how mind oscillations in REM sleep advertise cognition and the way REM sleep may also be progressed in the ones with dementia.”To analyze the impact of stimulation,18 contributors had been recruited and had been monitored in a single day on the Surrey Sleep Analysis Centre. Their sleep used to be incessantly monitored by way of electrodes put on their scalp, and the mind oscillations had been analysed in real-time in order that auditory stimuli may well be administered at actual portions of the oscillations with out waking contributors.Relying on which a part of the cycle used to be focused by means of the auditory stimuli, oscillations changed into both sooner or slower demonstrating that mind waves may also be manipulated.Professor Derk-Jan Dijk, Director of the Surrey Sleep Analysis Centre on the College of Surrey, UK Dementia Analysis Institute Crew Chief and senior writer of the e-newsletter, mentioned: “This may pave the best way for a brand new manner on learn how to deal with sufferers with dementia, because the method is non-invasive and undertaken while they’re asleep, lessening the disruption to their lives and enabling us to be extra focused in our manner.”Dr Ines Violante, Senior Lecturer in Mental Neuroscience on the College of Surrey and senior writer of the e-newsletter, mentioned:“The usage of sound stimulation to switch mind oscillations while an individual sleeps displays healing promise. There may be lately no remedy for dementia, simplest drugs that may decelerate illness development or quickly assist an individual with their signs, so it is necessary that we expect innovatively to expand new remedy choices.“Sound stimulation, which is a non-invasive affordable method, has the possible to do exactly this.”About this sleep and neuroscience analysis newsAuthor: Natasha Meredith
Supply: College of Surrey
Touch: Natasha Meredith – College of Surrey
Symbol: The picture is credited to Neuroscience NewsOriginal Analysis: Open get entry to.
“Closed-loop auditory stimulation concentrated on alpha and theta oscillations all the way through REM sleep induces phase-dependent energy and frequency adjustments” by means of Ines Violante et al. SleepAbstractClosed-loop auditory stimulation concentrated on alpha and theta oscillations all the way through REM sleep induces phase-dependent energy and frequency changesStudy objectivesAlpha and theta oscillations represent the waking human electroencephalogram (EEG) and may also be modulated by means of closed-loop auditory stimulation (CLAS). Those oscillations additionally happen all the way through fast eye motion (REM) sleep, however their serve as right here stays elusive. CLAS represents a promising software to pinpoint how those mind oscillations give a contribution to mind serve as in people. Right here we examine whether or not CLAS can modulate alpha and theta oscillations all the way through REM sleep in a phase-dependent approach.MethodsWe recorded high-density EEG all the way through a longer in a single day sleep duration in 18 wholesome younger adults. Auditory stimulation used to be delivered all the way through each phasic and tonic REM sleep in alternating 6 s ON and six s OFF home windows. All through the ON home windows, stimuli had been phase-locked to 4 orthogonal stages of ongoing alpha or theta oscillations detected in a frontal electrode.ResultsThe stages of ongoing alpha and theta oscillations had been focused with excessive accuracy all the way through REM sleep. Alpha and theta CLAS caused phase-dependent adjustments in energy and frequency on the goal location. Frequency-specific results had been seen for alpha trough (rushing up) and emerging (slowing down) and theta trough (rushing up) stipulations. CLAS-induced phase-dependent adjustments had been seen all the way through each REM sleep substages, despite the fact that auditory evoked potentials had been very a lot decreased in phasic in comparison to tonic REM sleep.ConclusionsThis learn about supplies proof that sooner REM sleep rhythms may also be modulated by means of CLAS in a phase-dependent approach. This gives a brand new technique to examine how modulation of REM sleep oscillations impacts the contribution of this vigilance state to mind serve as.
Manipulating Mind Waves All through Sleep With Sound – Neuroscience Information