The Eu House Company (ESA) has narrowed down proposals for a long run medium-sized (M-class) undertaking. On Wednesday (Nov. 8), the overall 3 proposals had been published to be M-Matisse, Plasma Observatory and Theseus, that have various targets starting from learning the consequences of the sun winds on each Earth and Mars to analyzing high-energy blasts of radiation from a ways past the sun gadget. The ESA referred to as for those M-class proposals in 2021, and the release of the profitable undertaking is about provisionally for halfway throughout the 2030s. A complete of 27 proposals had been submitted, which each ESA scientists and outdoor mavens assessed. The missions had been narrowed down to 5 proposals in Nov. 2022. The ones then went thru “Segment 0” research between Jan. and Sept. 2023, all through which era initial undertaking designs had been drawn up and anticipated science returns had been assessed.Comparable: Mars orbiter spies a tiny Earth and moon from the Crimson Planet (footage) Meet the M-class finalists!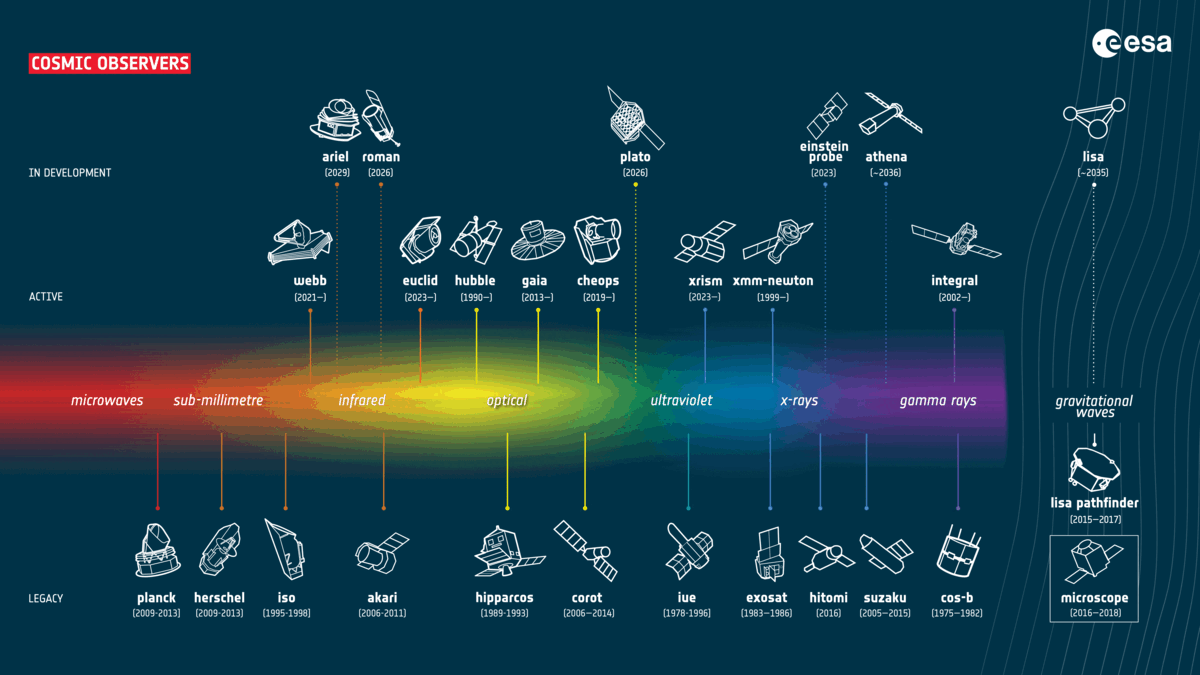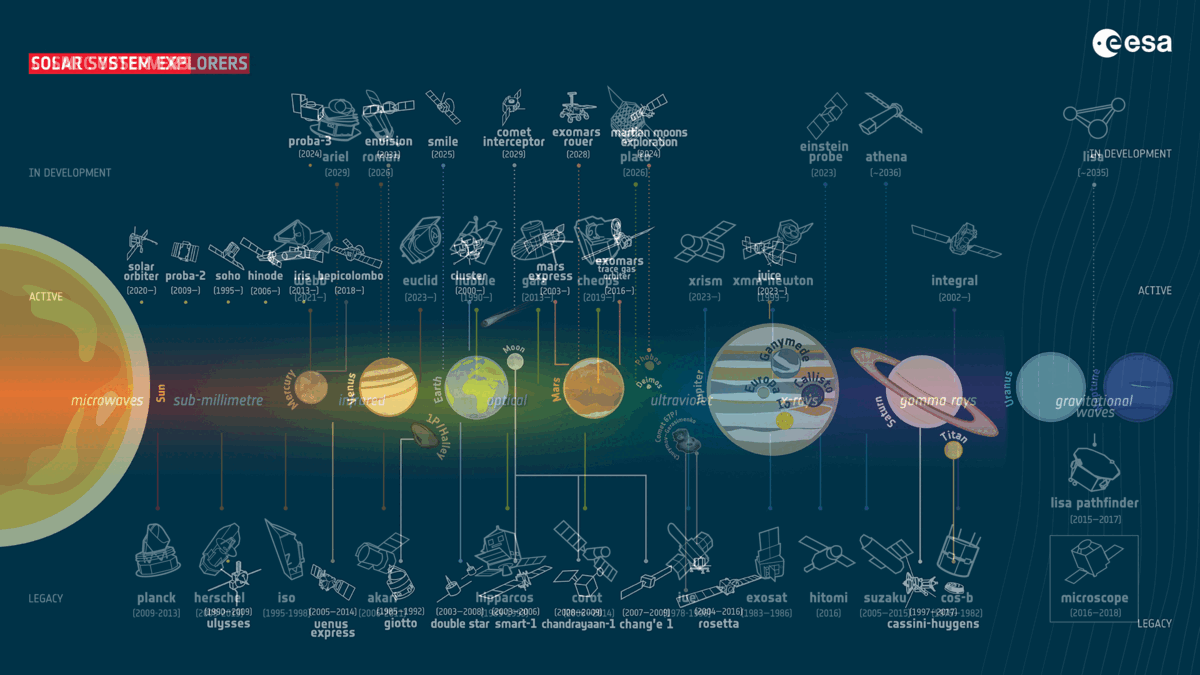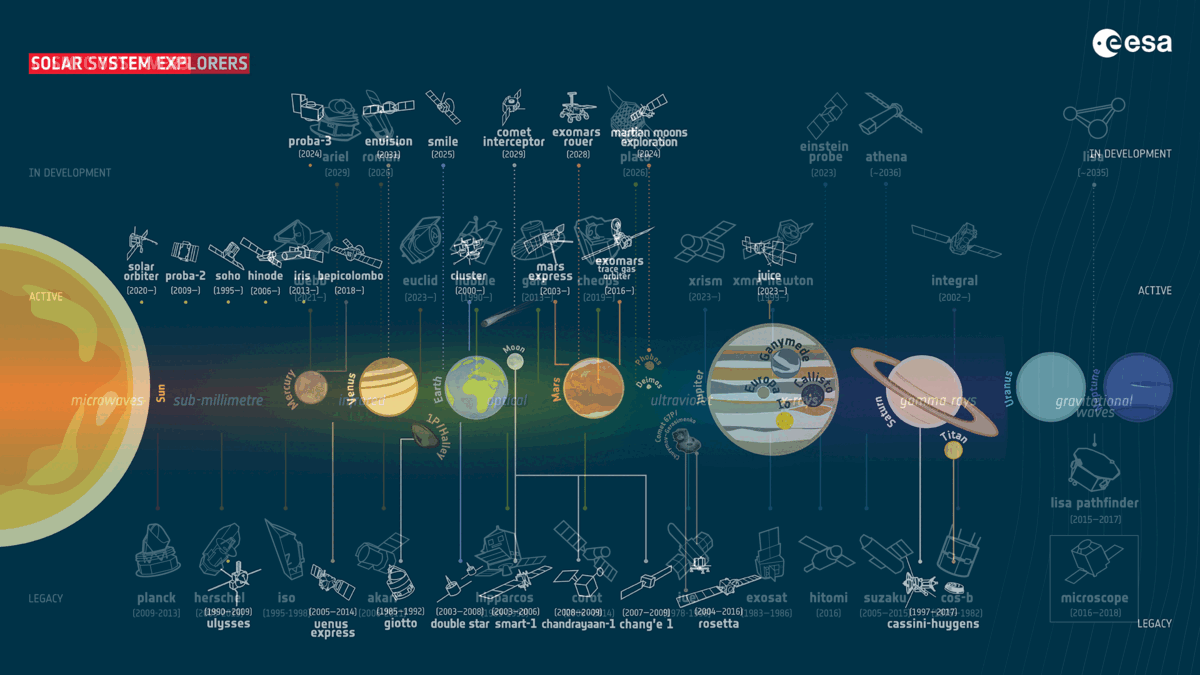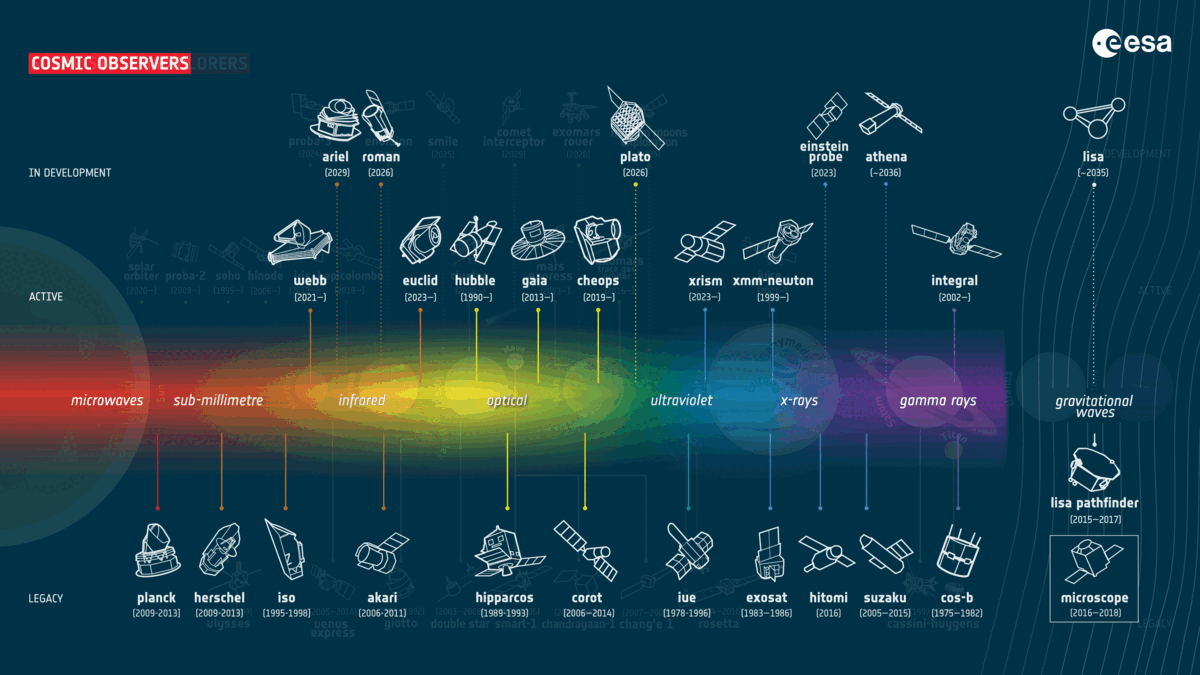 A GIF appearing present and long run ESA missions that the winner of undertaking seek will sign up for (Symbol credit score: ESA)A stereo view of Mars with M-Matisse The M-Matisse undertaking proposes the use of two spacecraft with an identical clinical tools to check Mars concurrently from two other places. The purpose of that is to decide how the sun wind — streams of shared debris from the solar — impact the ambience of the Crimson Planet in addition to its ionosphere and magnetosphere. Working out the affect of the sun wind on Mars’ decrease surroundings and floor is essential to figuring out how the Crimson Planet could have misplaced maximum of its surroundings and water way back. Such data may lend a hand us know how Mars used to be as soon as reworked from a rainy and heat global like Earth to the chilly, barren, and arid panorama we see lately.As such, M-Matisse may make clear whether or not Mars used to be ever liveable — and, if this is the case, when this habitability vanished all through the planet’s 4.5-billion-year historical past.Learning house round Earth with Plasma Observatory Plasma Observatory is a suggestion that will see seven spacecraft round Earth learning our planet’s fast house setting. If a success, this undertaking will in particular have a look at charged debris referred to as plasma that encompass our global.This is able to permit operators of Plasma Observatory, and others within the clinical group, to respond to two remarkable questions. In the beginning, how are debris energized in house plasmas? And secondly, what processes decide how calories is stunted round Earth’s magnetic bubble, the magnetosphere? An offshoot of the latter would even be: How do layers of the magnetosphere have interaction with each and every different? As such, Plasma Observatory would sign up for present ESA missions that have a look at how the sun wind impacts the Earth, which might lend a hand give protection to era, or even house missions, keep secure from its harsher results.A view at the cosmic expanse with TheseusThe ultimate candidate for a long run M-class ESA undertaking units its attractions past Earth and Mars to pay attention to occasions outdoor the sun gadget. Theseus will center of attention on learning short-lived blasts of high-energy mild, in particular what are referred to as “gamma-ray bursts.”This will likely come with the investigation of short-duration gamma-ray bursts believed to be introduced when ultra-dense stellar corpses, referred to as neutron stars, collide and merge. Theseus may also find out about longer-lasting gamma-ray bursts that may be attached to the emergence of the primary galaxies within the cosmos.Informing a variety of fields like astrophysics, stellar job, and the physics of subject in essentially the most turbulent and violent cosmic environments, Theseus may lend a hand solution lingering but basic questions concerning the universe. M-class winner will sign up for a bigger undertaking: NewAthena
A GIF appearing present and long run ESA missions that the winner of undertaking seek will sign up for (Symbol credit score: ESA)A stereo view of Mars with M-Matisse The M-Matisse undertaking proposes the use of two spacecraft with an identical clinical tools to check Mars concurrently from two other places. The purpose of that is to decide how the sun wind — streams of shared debris from the solar — impact the ambience of the Crimson Planet in addition to its ionosphere and magnetosphere. Working out the affect of the sun wind on Mars’ decrease surroundings and floor is essential to figuring out how the Crimson Planet could have misplaced maximum of its surroundings and water way back. Such data may lend a hand us know how Mars used to be as soon as reworked from a rainy and heat global like Earth to the chilly, barren, and arid panorama we see lately.As such, M-Matisse may make clear whether or not Mars used to be ever liveable — and, if this is the case, when this habitability vanished all through the planet’s 4.5-billion-year historical past.Learning house round Earth with Plasma Observatory Plasma Observatory is a suggestion that will see seven spacecraft round Earth learning our planet’s fast house setting. If a success, this undertaking will in particular have a look at charged debris referred to as plasma that encompass our global.This is able to permit operators of Plasma Observatory, and others within the clinical group, to respond to two remarkable questions. In the beginning, how are debris energized in house plasmas? And secondly, what processes decide how calories is stunted round Earth’s magnetic bubble, the magnetosphere? An offshoot of the latter would even be: How do layers of the magnetosphere have interaction with each and every different? As such, Plasma Observatory would sign up for present ESA missions that have a look at how the sun wind impacts the Earth, which might lend a hand give protection to era, or even house missions, keep secure from its harsher results.A view at the cosmic expanse with TheseusThe ultimate candidate for a long run M-class ESA undertaking units its attractions past Earth and Mars to pay attention to occasions outdoor the sun gadget. Theseus will center of attention on learning short-lived blasts of high-energy mild, in particular what are referred to as “gamma-ray bursts.”This will likely come with the investigation of short-duration gamma-ray bursts believed to be introduced when ultra-dense stellar corpses, referred to as neutron stars, collide and merge. Theseus may also find out about longer-lasting gamma-ray bursts that may be attached to the emergence of the primary galaxies within the cosmos.Informing a variety of fields like astrophysics, stellar job, and the physics of subject in essentially the most turbulent and violent cosmic environments, Theseus may lend a hand solution lingering but basic questions concerning the universe. M-class winner will sign up for a bigger undertaking: NewAthena  A diagram appearing the ESA’s M-class variety procedure. (Symbol credit score: ESA)To choose which of the above missions will adventure to house, the ESA’s Science Programme Committee now passes them to “Segment A,” which can contain a length of detailed find out about to additional assess the finalists’ doable advantages. The chosen undertaking will sign up for present M-class ESA tasks together with the Sun Orbiter, the “darkish universe detective” Euclid Telescope and the Mars Categorical. It is going to additionally perform along some coming near near mid-sized missions set to release throughout the subsequent six years, Plato and Ariel.Along with narrowing down the proposed M-class missions to fee, on Wednesday (Nov. 8) the ESA additionally counseled a transformed large-class (L-class) undertaking. The Athena undertaking used to be decided on as a long run ESA L-class undertaking in 2014; its rescoped model, NewAthena, will follow the universe in X-rays to check the recent, lively universe. This will likely have a big affect on high-energy astrophysics. Paintings is about to start out on NewAthena in 2027, with the undertaking’s release deliberate for 2037. Quickly, we will be able to see which M-class undertaking will sign up for NewAthena in building.”We wish to congratulate all 5 proposals, each and every of which confirmed very good promise to make clear unanswered house science questions,” Chair of the Science Programme Committee Cecilia Hernández of Agencia Espacial Española in Spain stated. “We sit up for the various discoveries that will probably be made by way of the overall decided on undertaking.”
A diagram appearing the ESA’s M-class variety procedure. (Symbol credit score: ESA)To choose which of the above missions will adventure to house, the ESA’s Science Programme Committee now passes them to “Segment A,” which can contain a length of detailed find out about to additional assess the finalists’ doable advantages. The chosen undertaking will sign up for present M-class ESA tasks together with the Sun Orbiter, the “darkish universe detective” Euclid Telescope and the Mars Categorical. It is going to additionally perform along some coming near near mid-sized missions set to release throughout the subsequent six years, Plato and Ariel.Along with narrowing down the proposed M-class missions to fee, on Wednesday (Nov. 8) the ESA additionally counseled a transformed large-class (L-class) undertaking. The Athena undertaking used to be decided on as a long run ESA L-class undertaking in 2014; its rescoped model, NewAthena, will follow the universe in X-rays to check the recent, lively universe. This will likely have a big affect on high-energy astrophysics. Paintings is about to start out on NewAthena in 2027, with the undertaking’s release deliberate for 2037. Quickly, we will be able to see which M-class undertaking will sign up for NewAthena in building.”We wish to congratulate all 5 proposals, each and every of which confirmed very good promise to make clear unanswered house science questions,” Chair of the Science Programme Committee Cecilia Hernández of Agencia Espacial Española in Spain stated. “We sit up for the various discoveries that will probably be made by way of the overall decided on undertaking.”
Mars, Earth, or deep house? ESA narrows down finalists for a long run house undertaking






:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/20210814_171303-4947aeb853b7494ba9f67537baae0cc2.jpg)





