 ESA’s Mars Specific has equipped new insights into Mars’s Medusae Fossae Formation, revealing deep layers of water ice, the biggest such discovery within the area. This ice may considerably affect our figuring out of Mars’s local weather historical past and is an important for long run human exploration. Credit score: Planetary Science Institute/Smithsonian InstitutionRecent Mars Specific knowledge unearths the Medusae Fossae Formation accommodates intensive water ice layers, providing new clues about Mars’s previous and supporting long run exploration.Windswept piles of mud, or layers of ice? ESA’s Mars Specific has revisited one among Mars’s maximum mysterious options to elucidate its composition. Its findings counsel layers of water ice stretching a number of kilometers beneath flooring – essentially the most water ever discovered on this a part of the planet.Over 15 years in the past, Mars Specific studied the Medusae Fossae Formation (MFF), revealing large deposits as much as 2.5 km deep. From those early observations, it was once unclear what the deposits have been product of – however new analysis now has a solution.
ESA’s Mars Specific has equipped new insights into Mars’s Medusae Fossae Formation, revealing deep layers of water ice, the biggest such discovery within the area. This ice may considerably affect our figuring out of Mars’s local weather historical past and is an important for long run human exploration. Credit score: Planetary Science Institute/Smithsonian InstitutionRecent Mars Specific knowledge unearths the Medusae Fossae Formation accommodates intensive water ice layers, providing new clues about Mars’s previous and supporting long run exploration.Windswept piles of mud, or layers of ice? ESA’s Mars Specific has revisited one among Mars’s maximum mysterious options to elucidate its composition. Its findings counsel layers of water ice stretching a number of kilometers beneath flooring – essentially the most water ever discovered on this a part of the planet.Over 15 years in the past, Mars Specific studied the Medusae Fossae Formation (MFF), revealing large deposits as much as 2.5 km deep. From those early observations, it was once unclear what the deposits have been product of – however new analysis now has a solution.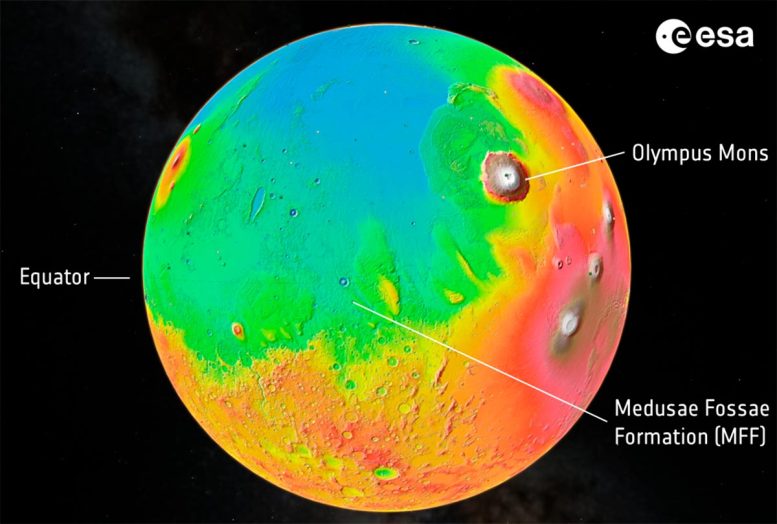 This symbol presentations a top map of the Martian floor, with lowest land in blue and perfect in white. Status at an excellent 22 km, Olympus Mons is the tallest volcano in all the Sun Machine.
This symbol presentations a top map of the Martian floor, with lowest land in blue and perfect in white. Status at an excellent 22 km, Olympus Mons is the tallest volcano in all the Sun Machine.
The Medusae Fossae Formation (MFF) is a fascinating area on the subject of the equator. It is composed of a sequence of huge wind-sculpted deposits measuring masses of kilometers throughout and a number of other kilometers excessive. Discovered on the boundary between Mars’s highlands and lowlands, the MFF is most likely the largest unmarried supply of mud on Mars, and one of the vital intensive deposits on this planet.
Credit score: ESA“We’ve explored the MFF once more the use of more moderen knowledge from Mars Specific’s MARSIS radar, and located the deposits to be even thicker than we idea: as much as 3.7 km thick,” says Thomas Watters of the Smithsonian Establishment, USA, lead writer of each the brand new analysis and the preliminary 2007 find out about. “Excitingly, the radar alerts fit what we’d be expecting to peer from layered ice, and are very similar to the alerts we see from Mars’s polar caps, which we all know to be very ice wealthy.”If melted, the ice locked up within the MFF would duvet all the planet in a layer of water 1.5 to two.7 m deep: essentially the most water ever discovered on this a part of Mars, and sufficient to fill Earth’s Crimson Sea. Mars’s Medusae Fossae Formation (MFF) is composed of a sequence of wind-sculpted deposits measuring masses of kilometers throughout and a number of other kilometers excessive. Discovered on the boundary between Mars’s highlands and lowlands, the options are most likely the largest unmarried supply of mud on Mars, and one of the vital intensive deposits on this planet.
Mars’s Medusae Fossae Formation (MFF) is composed of a sequence of wind-sculpted deposits measuring masses of kilometers throughout and a number of other kilometers excessive. Discovered on the boundary between Mars’s highlands and lowlands, the options are most likely the largest unmarried supply of mud on Mars, and one of the vital intensive deposits on this planet.
However this dry layer turns out to cover a secret. A crew of researchers used Mars Specific radar knowledge to look beneath the outside. What they discovered was once a most sensible layer of mud that covers what appears to be a thick layer of deposits wealthy in water ice. This map presentations the estimated quantity of ice inside the mounds that shape the MFF, indicating that the ice-rich deposits are as much as 3000 m thick.
The researchers estimate that the layer of dry subject matter (most likely mud or volcanic ash) protecting the ice is 300–600 m thick. This map presentations the ice thickness if we suppose that the mud is 300 m thick. On this case, the full quantity of water ice contained inside the MFF deposits could be 400,000 km3, or if it melted, sufficient to hide Mars in an ocean of water 2.7 m deep.
If the mud layer is as an alternative 600 m thick, the water ice layer could be thinner, and the full quantity of water ice contained inside the MFF deposits could be 220,000 km3, or if it melted, sufficient to hide Mars in an ocean of water 1.5 m deep.
Credit score: Planetary Science Institute/Smithsonian InstitutionAlternating Layers of IceThe MFF is composed of a number of wind-sculpted options measuring masses of kilometers throughout and a number of other kilometers excessive. Discovered on the boundary between Mars’s highlands and lowlands, the options are most likely the largest unmarried supply of mud on Mars, and one of the vital intensive deposits on this planet.Preliminary observations from Mars Specific confirmed the MFF to be slightly clear to radar and occasional in density, each traits we’d see from icy deposits. On the other hand, scientists couldn’t rule out a drier risk: that the options are in reality large accumulations of windblown mud, volcanic ash, or sediment.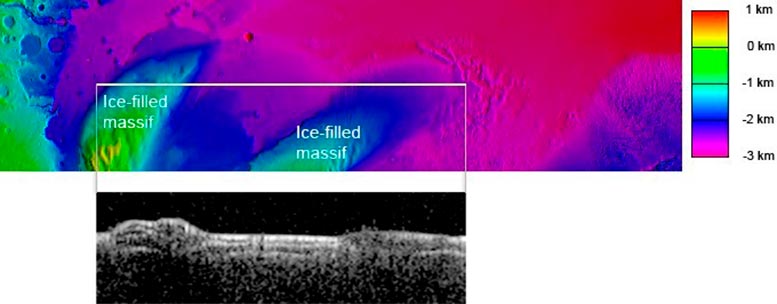 With reference to Mars’s equator lies the Medusae Fossae Formation (MFF), an interesting wind-sculpted area that can be the largest unmarried supply of mud on Mars.
With reference to Mars’s equator lies the Medusae Fossae Formation (MFF), an interesting wind-sculpted area that can be the largest unmarried supply of mud on Mars.
When Mars Specific became its MARSIS radar sounder tool against the MFF, it published a marvel. The radar alerts that echoed again matched what we’d be expecting to peer from layered deposits wealthy in water ice.
On this symbol, the white horizontal line at the coloured top map of Mars’s floor (most sensible) presentations a slim stretch of land that was once scanned by way of MARSIS. The pop-out beneath presentations the radar knowledge amassed by way of the tool that unearths the subsurface; the brighter the world, the more potent the radar echo won from that house.
The white line covers two mounds separated by way of a valley. Those mounds are obviously visual within the radar knowledge beneath. Research of the radar knowledge means that underneath a thick layer of dry subject matter (most likely mud or volcanic ash), the mounds are stuffed with water ice.
Credit score: CReSIS/KU/Smithsonian Establishment“Right here’s the place the brand new radar knowledge is available in! Given how deep it’s, if the MFF was once merely an enormous pile of mud, we’d be expecting it to transform compacted underneath its personal weight,” says co-author Andrea Cicchetti of the Nationwide Institute for Astrophysics, Italy. “This might create one thing some distance denser than what we in reality see with MARSIS. And after we modeled how other ice-free fabrics would behave, not anything reproduced the houses of the MFF – we’d like ice.”The brand new effects as an alternative counsel layers of mud and ice, all crowned by way of a protecting layer of dry mud or ash a number of hundred meters thick.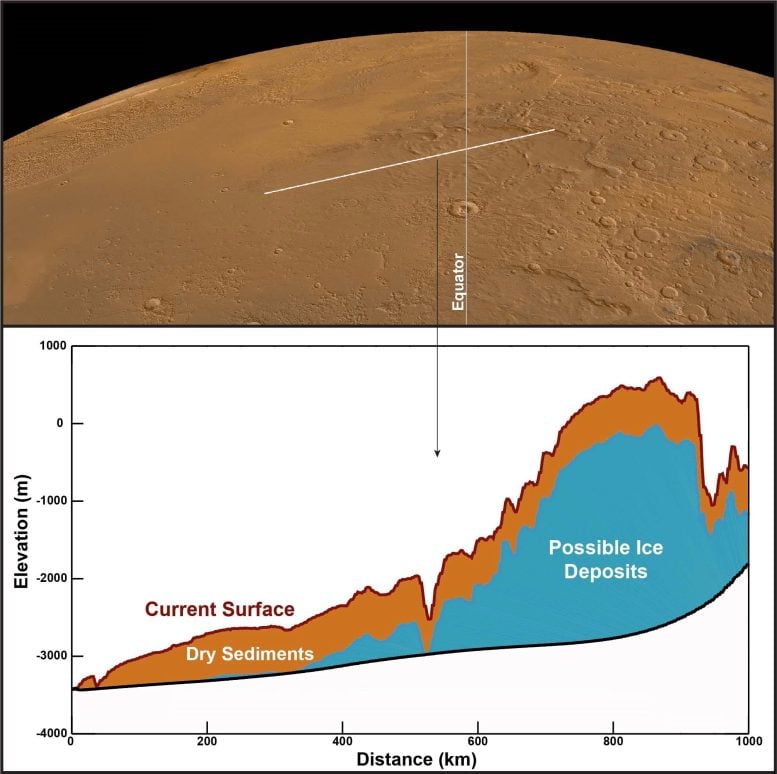 With reference to Mars’s equator lies the Medusae Fossae Formation (MFF), an interesting collection of wind-sculpted deposits that can be the largest unmarried supply of mud on Mars.
With reference to Mars’s equator lies the Medusae Fossae Formation (MFF), an interesting collection of wind-sculpted deposits that can be the largest unmarried supply of mud on Mars.
When Mars Specific became its MARSIS radar sounder tool against the MFF, it published a marvel. The radar alerts that echoed again from beneath the outside fit what we’d be expecting to peer from layered deposits wealthy in water ice.
On this symbol, the white line on Mars’s floor (most sensible) presentations a stretch of land that was once scanned by way of MARSIS. The graph beneath presentations the form of the land and the construction of the subsurface, with the layer of dry sediments (most likely mud or volcanic ash) in brown and the layer of suspected ice-rich deposits in blue. The graph presentations that the ice deposit is 1000’s of meters excessive and masses of kilometers huge.
If the entire suspected water ice within the MFF melted, it will duvet Mars in an ocean of water as much as 2.7 m deep.
Credit score: CReSIS/KU/Smithsonian InstitutionFuture Exploration and CollaborationAlthough Mars now seems to be an arid international, the planet’s floor is filled with indicators that water was once as soon as ample, together with dried-up river channels, historical ocean and lake beds, and water-carved valleys. We’ve additionally discovered important retail outlets of water ice on Mars, similar to the giant polar caps, buried glaciers closer the equator, and near-surface ice laced thru Martian soil.Large retail outlets of ice close to the equator – similar to the ones suspected to lurk beneath the dry floor of the MFF – couldn’t have shaped within the planet’s provide local weather. They will have to have shaped in a prior local weather epoch.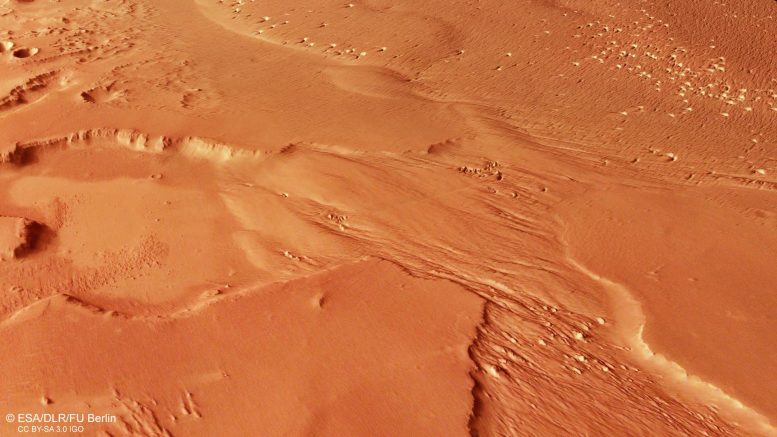 This indirect standpoint view of Medusae Fossae on Mars was once generated from the virtual terrain style and the nadir and colour channels of the Top Answer Stereo Digital camera on ESA’s Mars Specific. Credit score: ESA/DLR/FU Berlin, CC BY-SA 3.0 IGO“This newest research demanding situations our figuring out of the Medusae Fossae Formation, and raises as many questions as solutions,” says Colin Wilson, ESA undertaking scientist for Mars Specific and the ESA ExoMars Hint Fuel Orbiter (TGO). “How way back did those ice deposits shape, and what was once Mars-like at the moment? If showed to be water ice, those large deposits would trade our figuring out of Mars local weather historical past. Any reservoir of historical water could be an interesting goal for human or robot exploration.”The level and placement of those icy MFF deposits would additionally cause them to doubtlessly very treasured for our long run exploration of Mars. Missions to Mars will wish to land close to the planet’s equator, some distance from the ice-rich polar caps or high-latitude glaciers. And so they’ll want water as a useful resource – so discovering ice on this area is nearly a need for human missions to the planet.
This indirect standpoint view of Medusae Fossae on Mars was once generated from the virtual terrain style and the nadir and colour channels of the Top Answer Stereo Digital camera on ESA’s Mars Specific. Credit score: ESA/DLR/FU Berlin, CC BY-SA 3.0 IGO“This newest research demanding situations our figuring out of the Medusae Fossae Formation, and raises as many questions as solutions,” says Colin Wilson, ESA undertaking scientist for Mars Specific and the ESA ExoMars Hint Fuel Orbiter (TGO). “How way back did those ice deposits shape, and what was once Mars-like at the moment? If showed to be water ice, those large deposits would trade our figuring out of Mars local weather historical past. Any reservoir of historical water could be an interesting goal for human or robot exploration.”The level and placement of those icy MFF deposits would additionally cause them to doubtlessly very treasured for our long run exploration of Mars. Missions to Mars will wish to land close to the planet’s equator, some distance from the ice-rich polar caps or high-latitude glaciers. And so they’ll want water as a useful resource – so discovering ice on this area is nearly a need for human missions to the planet.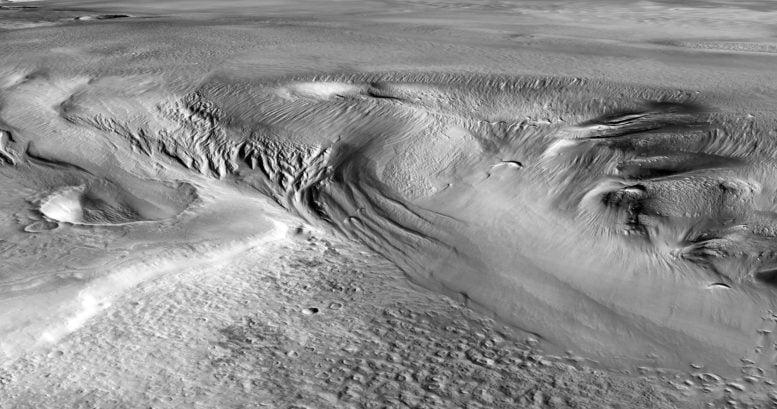 This standpoint view presentations Eumenides Dorsum, a part of Mars’s Medusae Fossae Formation (MFF). The MFF is composed of a sequence of wind-sculpted deposits measuring masses of kilometers throughout and a number of other kilometers excessive. Discovered on the boundary between Mars’s highlands and lowlands, the deposits are most likely the largest unmarried supply of mud on Mars, and one of the vital intensive deposits on this planet.
This standpoint view presentations Eumenides Dorsum, a part of Mars’s Medusae Fossae Formation (MFF). The MFF is composed of a sequence of wind-sculpted deposits measuring masses of kilometers throughout and a number of other kilometers excessive. Discovered on the boundary between Mars’s highlands and lowlands, the deposits are most likely the largest unmarried supply of mud on Mars, and one of the vital intensive deposits on this planet.
However this mud turns out to cover a secret. Over 15 years in the past, ESA’s Mars Specific studied the MFF, revealing that the mud coated large deposits as much as 2.5 km deep. From those early observations, it was once unclear what the deposits have been product of. A crew of researchers has now explored the MFF once more the use of more moderen Mars Specific radar knowledge and located the deposits to be even thicker than prior to now idea: as much as 3.7 km thick. And now it’s transparent that those radar alerts fit what we’d be expecting to peer from layered deposits wealthy in water ice.
If melted, the ice locked up within the MFF would duvet all the planet in a layer of water 1.5 to two.7 m deep: essentially the most water ever discovered on this a part of Mars, and sufficient to fill Earth’s Crimson Sea.
Credit score: Caltech/JPL International CTX Mosaic of Mars/Smithsonian Establishment“Sadly, those MFF deposits are coated by way of masses of meters of mud, making them inaccessible for no less than the following couple of many years. On the other hand, each little bit of ice we discover is helping us construct a greater image of the place Mars’s water has flowed ahead of, and the place it may be discovered these days.”Whilst Mars Specific maps water ice to a intensity of a couple of kilometers, a view of near-surface water is supplied by way of Mars orbiter TGO. This orbiter is sporting the FREND tool, which is mapping hydrogen – a trademark of water ice – within the topmost meter of Martian soil. FREND noticed a hydrogen-rich house the dimensions of the Netherlands inside of Mars’s Valles Marineris in 2021, and is these days mapping how shallow water deposits are dispensed around the Crimson Planet.“In combination, our Mars explorers are revealing increasingly more about our planetary neighbor,” provides Colin.
Mars Specific Unearths Hidden Ice Reserves at Mars’s Equator














:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-2208881545-47ded6f6c7164dacabf37396b531ccfd.jpg)