New analysis means that temperatures on historical Mars can have fluctuated between cold and warm sessions via a rather quick length right through its life of billions of years. However those cold and warm spells can have been unfavorable to existence if it existed at the Purple Planet.Mars could also be a dry and arid planet these days, however scientists know that Earth’s neighbor used to be a lot wetter and a lot more like our planet in its historical previous.Those new findings from a group of researchers on the Harvard John A. Paulson College of Engineering and Carried out Sciences (SEAS) recommend how Mars can have sustained its heat and held directly to its water billions of years in the past.”It is been the sort of puzzle that there used to be liquid water on Mars, as a result of Mars is farther from the solar, and in addition, the solar used to be fainter early on,” group chief Danica Adams, NASA Sagan Postdoctoral Fellow, stated in a remark. “It makes a truly nice case learn about for a way planets can evolve through the years.”The group’s analysis used to be revealed new paper in Nature Geoscience.The Martian hydrogen paradoxScientists had prior to now theorized that Mars used to be in a position to carry directly to its liquid water with out it freezing regardless of its distance from the solar because of an far more than hydrogen in its environment. This component, the universe’s lightest, would bond with carbon atoms to shape carbon dioxide within the Martian environment. As we all know all too neatly on Earth, carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gasoline that traps warmth, inflicting a greenhouse impact. This may have saved Mars temperate sufficient to host liquid water on its floor.The issue is that atmospheric hydrogen will have to’ve been short-lived round Mars. This triggered the group to use a an identical procedure to Mars as is used on Earth to trace pollution, letting them type how the hydrogen content material of the Martian environment modified through the years.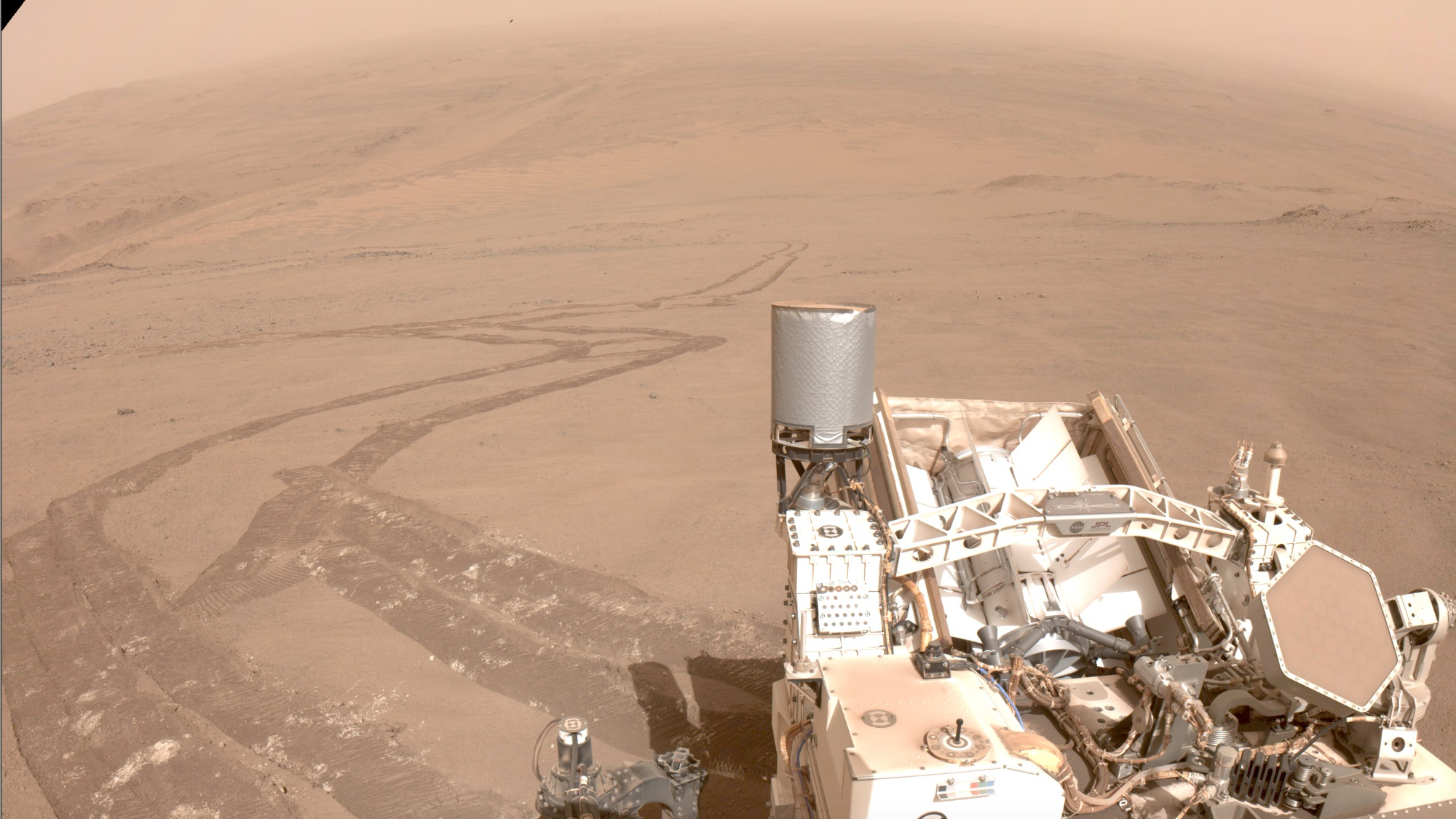 A picture of the dry and arid floor of Mars seize by means of the Perseverance rover because it hunts historical waterways for indicators of now extingushed microbial existence. (Symbol credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech)Adams and co-workers simulated how hydrogen would have blended and reacted with different gases in Mars’s environment and with chemical substances on its floor. They discovered that Mars skilled episodic heat sessions round 4 to three billion years in the past. Those fluctuations happened over the process 40 million years, with every person episode lasting no less than 100,000 years.Those heat, rainy sessions would had been pushed by means of Mars shedding water from its environment to the bottom, which mockingly refilled the hydrogen content material of the ambience, thus maintaining the greenhouse impact.Breaking area information, the most recent updates on rocket launches, skywatching occasions and extra!The adjustments in Mars’ temperature have been mirrored by means of chemical adjustments, too, the group theorizes. Carbon dioxide would had been repeatedly reacting with daylight to supply carbon monoxide. Alternatively, right through heat sessions the carbon monoxide would have modified again to carbon dioxide. This recycling procedure would stall if Mars remained frigid for lengthy sufficient, resulting in a build-up of carbon monoxide and oxygen.”We have now recognized time scales for all of those alternations,” Adams stated. “And we now have described the entire items in the similar photochemical type.”What everybody truly desires to understand is that if Mars may have ever supported existence, albeit easy and microbial, in its historical historical past. The life of existence can have been challenged right through sessions wherein the temperatures dropped and oxygen ranges climbed.At some point, the group in the back of this learn about intends to match their fashions to exact rock and soil accumulated from the Purple Planet and returned to Earth by means of NASA’s proposed Mars Pattern Go back Challenge.”Early Mars is a misplaced global, however it may be reconstructed in nice element if we ask the suitable questions,” SEAS researcher and group member Robin Wordsworth stated. “This learn about synthesizes atmospheric chemistry and local weather for the primary time to make some placing new predictions – which can be testable when we carry Mars rocks again to Earth.”
A picture of the dry and arid floor of Mars seize by means of the Perseverance rover because it hunts historical waterways for indicators of now extingushed microbial existence. (Symbol credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech)Adams and co-workers simulated how hydrogen would have blended and reacted with different gases in Mars’s environment and with chemical substances on its floor. They discovered that Mars skilled episodic heat sessions round 4 to three billion years in the past. Those fluctuations happened over the process 40 million years, with every person episode lasting no less than 100,000 years.Those heat, rainy sessions would had been pushed by means of Mars shedding water from its environment to the bottom, which mockingly refilled the hydrogen content material of the ambience, thus maintaining the greenhouse impact.Breaking area information, the most recent updates on rocket launches, skywatching occasions and extra!The adjustments in Mars’ temperature have been mirrored by means of chemical adjustments, too, the group theorizes. Carbon dioxide would had been repeatedly reacting with daylight to supply carbon monoxide. Alternatively, right through heat sessions the carbon monoxide would have modified again to carbon dioxide. This recycling procedure would stall if Mars remained frigid for lengthy sufficient, resulting in a build-up of carbon monoxide and oxygen.”We have now recognized time scales for all of those alternations,” Adams stated. “And we now have described the entire items in the similar photochemical type.”What everybody truly desires to understand is that if Mars may have ever supported existence, albeit easy and microbial, in its historical historical past. The life of existence can have been challenged right through sessions wherein the temperatures dropped and oxygen ranges climbed.At some point, the group in the back of this learn about intends to match their fashions to exact rock and soil accumulated from the Purple Planet and returned to Earth by means of NASA’s proposed Mars Pattern Go back Challenge.”Early Mars is a misplaced global, however it may be reconstructed in nice element if we ask the suitable questions,” SEAS researcher and group member Robin Wordsworth stated. “This learn about synthesizes atmospheric chemistry and local weather for the primary time to make some placing new predictions – which can be testable when we carry Mars rocks again to Earth.”
Mars used to be sizzling then chilly then sizzling once more. May existence have truly survived there?