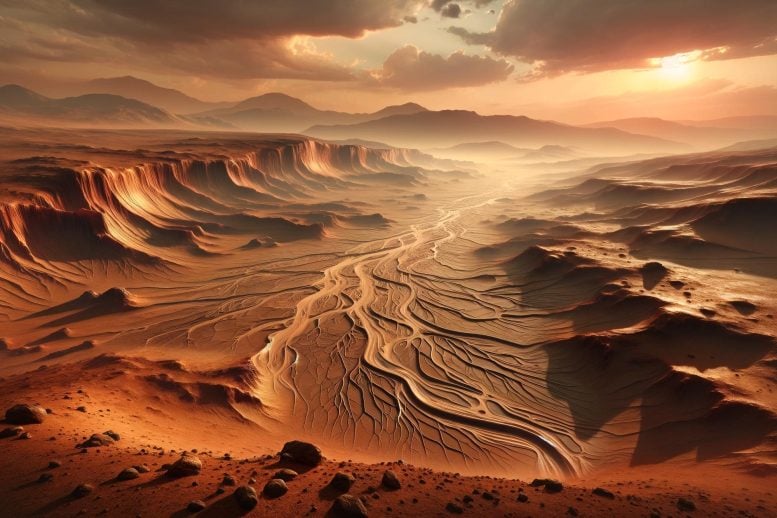
 A find out about finds that historical Mars had a considerably low groundwater recharge charge, suggesting that in spite of proof of water on its floor, the planet’s water regime used to be massively other from Earth’s. This discovering, derived from more than a few modeling strategies, highlights the demanding situations in figuring out Mars’ hydrological previous and has implications for long term exploration and the seek for water sources. (Artist’s thought.) Credit score: SciTechDaily.comResearch signifies historical Mars had minimum groundwater recharge, massively differing from Earth’s water dynamics, affecting our figuring out of its local weather and helping long term Mars missions.Mars used to be as soon as a rainy global. The geological report of the Pink Planet displays proof for water flowing at the floor – from river deltas to valleys carved via huge flash floods.However a brand new find out about displays that regardless of how a lot rainfall fell at the floor of historical Mars, little or no of it seeped into an aquifer within the planet’s southern highlands.A graduate pupil at The College of Texas at Austin made the invention via modeling groundwater recharge dynamics for the aquifer the use of a spread of strategies – from laptop fashions to easy back-of-the-envelope calculations.
A find out about finds that historical Mars had a considerably low groundwater recharge charge, suggesting that in spite of proof of water on its floor, the planet’s water regime used to be massively other from Earth’s. This discovering, derived from more than a few modeling strategies, highlights the demanding situations in figuring out Mars’ hydrological previous and has implications for long term exploration and the seek for water sources. (Artist’s thought.) Credit score: SciTechDaily.comResearch signifies historical Mars had minimum groundwater recharge, massively differing from Earth’s water dynamics, affecting our figuring out of its local weather and helping long term Mars missions.Mars used to be as soon as a rainy global. The geological report of the Pink Planet displays proof for water flowing at the floor – from river deltas to valleys carved via huge flash floods.However a brand new find out about displays that regardless of how a lot rainfall fell at the floor of historical Mars, little or no of it seeped into an aquifer within the planet’s southern highlands.A graduate pupil at The College of Texas at Austin made the invention via modeling groundwater recharge dynamics for the aquifer the use of a spread of strategies – from laptop fashions to easy back-of-the-envelope calculations.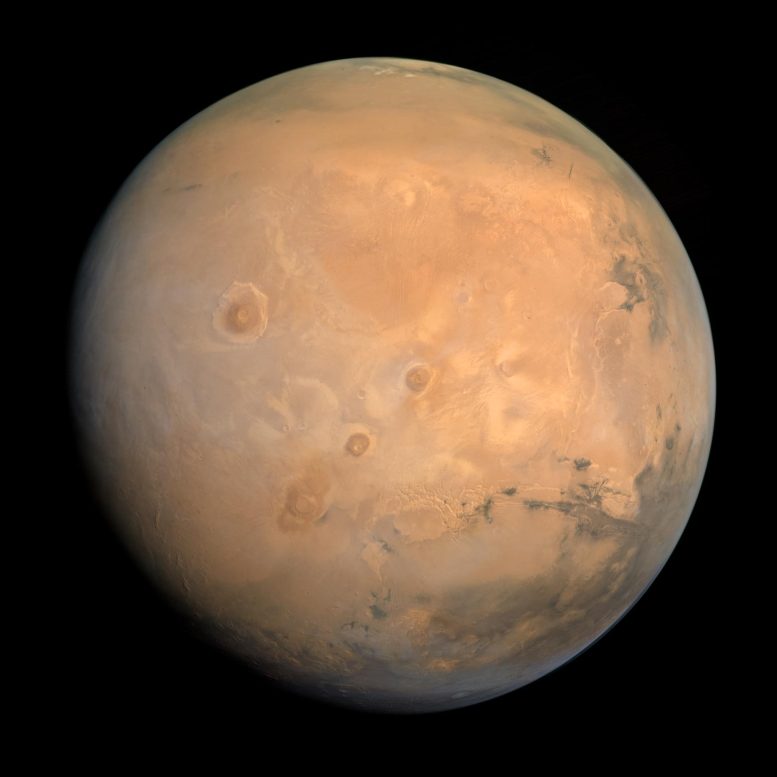 Mars in true colour, taken via the Emirates Mars Venture in August 2021. Credit score: Kevin M. GillGroundwater Recharge on MarsNo subject the stage of complexity, the effects converged at the identical solution – a minuscule .03 millimeters of groundwater recharge in line with 12 months on moderate. That implies that anywhere rain fell within the type, handiest a median of .03 millimeters in line with 12 months can have entered the aquifer and nonetheless produced the landforms ultimate in the world nowadays.For comparability, the once a year charge of groundwater recharge for the Trinity and Edwards-Trinity Plateau aquifers that offer water to San Antonio in most cases levels from 2.5 to 50 millimeters in line with 12 months, or about 80 to one,600 instances the Martian aquifer recharge charge calculated via the researchers.There are a selection of doable causes for such low groundwater glide charges, stated lead creator Eric Hiatt, a doctoral pupil on the Jackson College of Geosciences. When it rained, the water can have most commonly washed around the Martian panorama as runoff. Or it will have simply no longer rained very a lot in any respect.Implications for Martian Local weather and ExplorationThese findings can assist scientists constrain the climatic stipulations able to generating rainfall on early Mars. In addition they counsel an excessively other water regime at the Pink Planet than what exists on Earth nowadays.“The truth that the groundwater isn’t as giant of a procedure may just imply that different issues are,” Hiatt stated. “It could amplify the significance of runoff, or it will imply that it simply didn’t rain as a lot on Mars. But it surely’s simply basically other from how we take into consideration [water] on Earth.”The consequences had been revealed within the magazine Icarus. The paper’s co-authors are Mohammad Afzal Shadab, a doctoral pupil on the Jackson College and school participants Sean Gulick, Timothy Goudge, and Marc Hesse.
Mars in true colour, taken via the Emirates Mars Venture in August 2021. Credit score: Kevin M. GillGroundwater Recharge on MarsNo subject the stage of complexity, the effects converged at the identical solution – a minuscule .03 millimeters of groundwater recharge in line with 12 months on moderate. That implies that anywhere rain fell within the type, handiest a median of .03 millimeters in line with 12 months can have entered the aquifer and nonetheless produced the landforms ultimate in the world nowadays.For comparability, the once a year charge of groundwater recharge for the Trinity and Edwards-Trinity Plateau aquifers that offer water to San Antonio in most cases levels from 2.5 to 50 millimeters in line with 12 months, or about 80 to one,600 instances the Martian aquifer recharge charge calculated via the researchers.There are a selection of doable causes for such low groundwater glide charges, stated lead creator Eric Hiatt, a doctoral pupil on the Jackson College of Geosciences. When it rained, the water can have most commonly washed around the Martian panorama as runoff. Or it will have simply no longer rained very a lot in any respect.Implications for Martian Local weather and ExplorationThese findings can assist scientists constrain the climatic stipulations able to generating rainfall on early Mars. In addition they counsel an excessively other water regime at the Pink Planet than what exists on Earth nowadays.“The truth that the groundwater isn’t as giant of a procedure may just imply that different issues are,” Hiatt stated. “It could amplify the significance of runoff, or it will imply that it simply didn’t rain as a lot on Mars. But it surely’s simply basically other from how we take into consideration [water] on Earth.”The consequences had been revealed within the magazine Icarus. The paper’s co-authors are Mohammad Afzal Shadab, a doctoral pupil on the Jackson College and school participants Sean Gulick, Timothy Goudge, and Marc Hesse.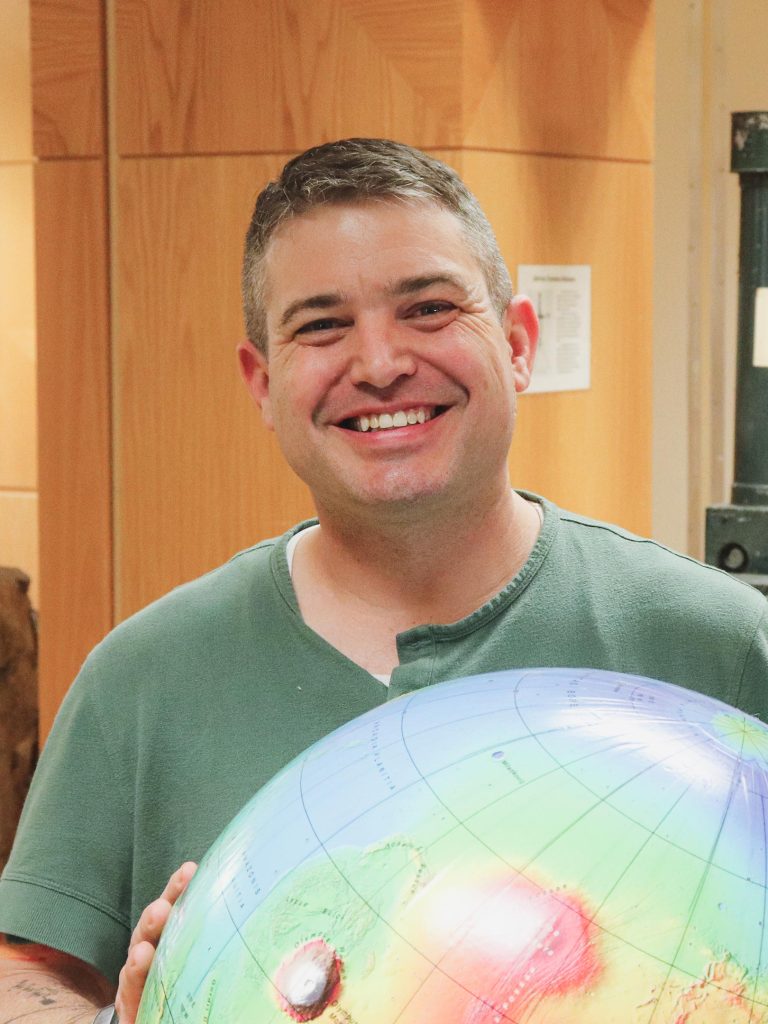 Lead creator Eric Hiatt, a doctoral pupil on the UT Austin Jackson College of Geosciences, with a globe of Mars. Credit score: The College of Texas at Austin / Jackson College of GeosciencesThe fashions used within the find out about paintings via simulating groundwater glide in a “stable state” surroundings the place influx and outflow of water into the aquifer is balanced. Scientists then modified the parameters affecting the glide – as an example, the place rain falls or the common porosity of the rock – and noticed what different variables must exchange to handle the stable state and the way believable the ones fees are.Whilst different researchers have simulated groundwater glide on Mars the use of an identical tactics, this type is the primary to include the affect of the oceans that existed at the floor of Mars greater than 3 billion years in the past within the Hellas, Argyre, and Borealis basins.The find out about additionally comprises fashionable topographical knowledge gathered via satellites. The trendy panorama, Hiatt stated, nonetheless preserves one of the vital planet’s oldest and maximum influential topographical options – an excessive distinction in elevation between the northern hemisphere – the lowlands – and the southern hemisphere – the highlands – referred to as the “nice dichotomy.” The dichotomy preserves indicators of previous groundwater upwelling wherein groundwater rose up from the aquifer to the outside. The researchers used geological markers of those previous upwelling occasions to guage other type outputs.Throughout other fashions, the researchers discovered the imply groundwater recharge charge of .03 millimeters in line with 12 months to compare maximum intently with what’s identified concerning the geologic report.The analysis isn’t as regards to figuring out the Pink Planet’s previous. It has implications for long term Mars exploration too. Working out groundwater glide can assist tell the place to seek out water nowadays, Hiatt stated. Whether or not you’re on the lookout for indicators of historical lifestyles, looking to maintain human explorers, or making rocket gas to get again house to Earth, it’s very important to understand the place the water would perhaps be.Reference: “Restricted recharge of the southern highlands aquifer on early Mars” via Eric Hiatt, Mohammad Afzal Shadab, Sean P.S. Gulick, Timothy A. Goudge and Marc A. Hesse, 9 September 2023, Icarus.
Lead creator Eric Hiatt, a doctoral pupil on the UT Austin Jackson College of Geosciences, with a globe of Mars. Credit score: The College of Texas at Austin / Jackson College of GeosciencesThe fashions used within the find out about paintings via simulating groundwater glide in a “stable state” surroundings the place influx and outflow of water into the aquifer is balanced. Scientists then modified the parameters affecting the glide – as an example, the place rain falls or the common porosity of the rock – and noticed what different variables must exchange to handle the stable state and the way believable the ones fees are.Whilst different researchers have simulated groundwater glide on Mars the use of an identical tactics, this type is the primary to include the affect of the oceans that existed at the floor of Mars greater than 3 billion years in the past within the Hellas, Argyre, and Borealis basins.The find out about additionally comprises fashionable topographical knowledge gathered via satellites. The trendy panorama, Hiatt stated, nonetheless preserves one of the vital planet’s oldest and maximum influential topographical options – an excessive distinction in elevation between the northern hemisphere – the lowlands – and the southern hemisphere – the highlands – referred to as the “nice dichotomy.” The dichotomy preserves indicators of previous groundwater upwelling wherein groundwater rose up from the aquifer to the outside. The researchers used geological markers of those previous upwelling occasions to guage other type outputs.Throughout other fashions, the researchers discovered the imply groundwater recharge charge of .03 millimeters in line with 12 months to compare maximum intently with what’s identified concerning the geologic report.The analysis isn’t as regards to figuring out the Pink Planet’s previous. It has implications for long term Mars exploration too. Working out groundwater glide can assist tell the place to seek out water nowadays, Hiatt stated. Whether or not you’re on the lookout for indicators of historical lifestyles, looking to maintain human explorers, or making rocket gas to get again house to Earth, it’s very important to understand the place the water would perhaps be.Reference: “Restricted recharge of the southern highlands aquifer on early Mars” via Eric Hiatt, Mohammad Afzal Shadab, Sean P.S. Gulick, Timothy A. Goudge and Marc A. Hesse, 9 September 2023, Icarus.
DOI: 10.1016/j.icarus.2023.115774The analysis used to be funded via NASA, the College of Texas Institute for Geophysics, and the UT Middle for Planetary Habitability.
Mars Water Thriller Deepens With Newest Groundwater Findings












