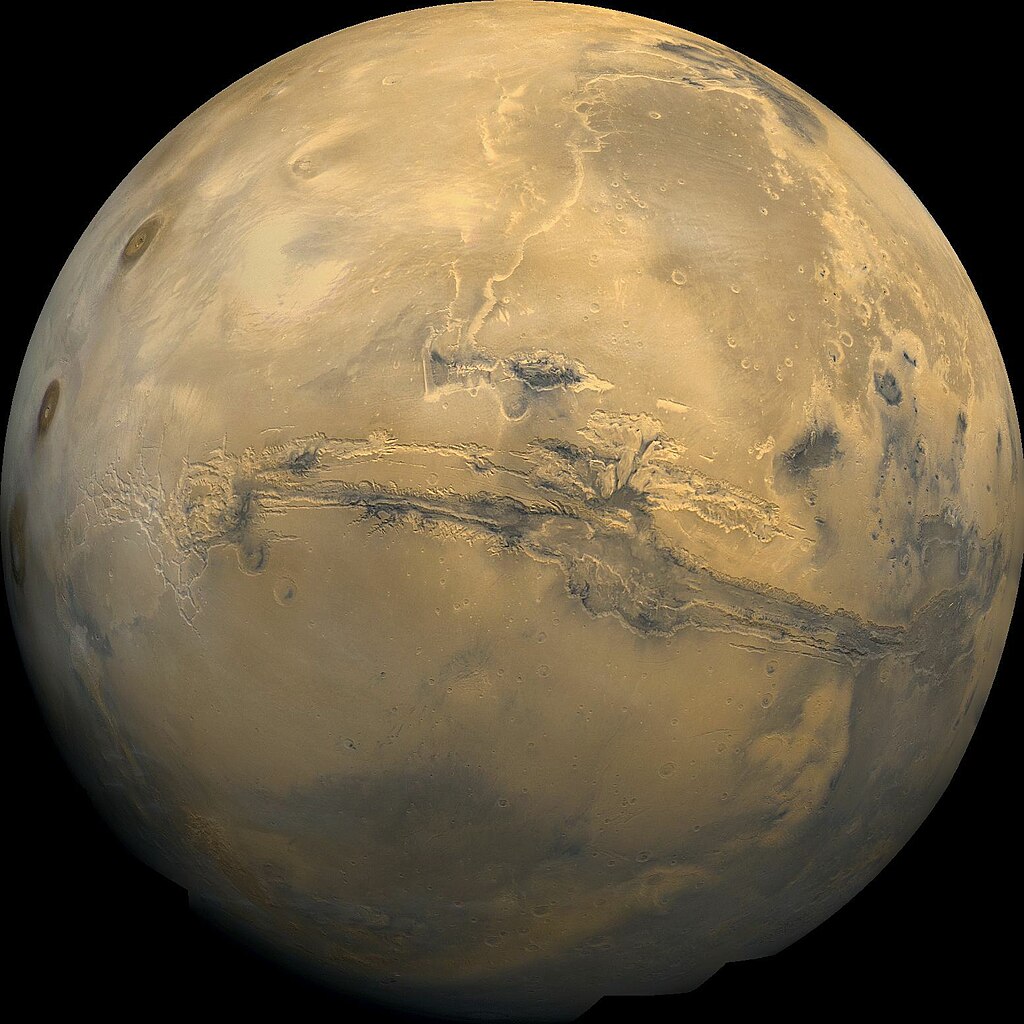
Mars, our neighboring crimson planet, possesses one of the most maximum excessive topographical options inside of our sun gadget. Its colossal volcanoes, canyons and have an effect on craters be offering clues into its geological previous spanning billions of years.
Believe Olympus Mons as an example, the most important volcano within the sun gadget that stands nearly thrice taller than Mount Everest. Or the Valles Marineris canyon gadget which stretches longer than the breadth of the United States.
Because of missions like Perseverance, Interest, and Alternative, extra of Mars’ geological options proceed to be printed. A few of which can be landmarks in relation to indicators of water and attainable Martian lifestyles. Fascinating Engineering (IE) walks you thru ten impressive geological options on Mars so you’ll be able to make a decision which one astounds you probably the most.
1. Olympus Mons: Tallest volcano within the sun gadget
 A satellite tv for pc symbol appearing Olympus Mons on Mars. Supply:Wikimedia Commons/ESA/DLR/FUBerlin/AndreaLuck
A satellite tv for pc symbol appearing Olympus Mons on Mars. Supply:Wikimedia Commons/ESA/DLR/FUBerlin/AndreaLuck
Dubbed the most important volcano within the sun gadget, Olympus Mons stands at a top of 72,000 toes (13.6 miles). Situated within the western hemisphere of Mars, between the Tharsis and Amazonis Planitia volcanic areas, Olympus Mons beats the Mount Everest by means of nearly thrice.
Olympus Mons is a protect volcano that shaped from a succession of lava flows over billions of years. Many scientists agree that the volcano started forming all the way through Mars’ Hesperian Duration—round 3.7 to a few billion years in the past.
In contrast to the volcanoes of Earth, Olympus Mons assists in keeping rising as a result of there aren’t any plate tectonics on Mars. This implies the lava does now not get displaced however accumulates in a single position.
The bottom of Olympus Mons measures just about 373 miles (600 kilometers)—that’s concerning the width of Italy or the Philippines! The construction itself means that Mars was once very energetic in its geological previous.
2. Valles Marineris: Biggest canyon gadget in our sun gadget
 Valles Marineris stretches over 2,500 miles throughout Mars. Supply: NASA/USGS
Valles Marineris stretches over 2,500 miles throughout Mars. Supply: NASA/USGS
Valles Marineris is a large canyon gadget—the most important in our sun gadget. It’s round 2,500 miles (4,000 kilometers) lengthy, which equates to being more or less ten instances longer than the Grand Canyon and 5 instances deeper than it. Higher but, if Valles Marineris existed on Earth, it will be longer than the United States.
Primarily based close to Mars’ Equator, Valles Marineris is thought to have shaped because of tectonic process on the earth. Through the years, landslides, erosion, and historic water glide could have widened and deepened the valley. The canyon options one of the most inner most sections plunging to nearly 4.3 miles (7 kilometers). With historic rock uncovered, those be offering clues concerning the planet’s geological historical past, previous local weather and water.
3. Tharsis Volcanoes: Ascraeus Mons, Pavonis Mons and Arsia Mons
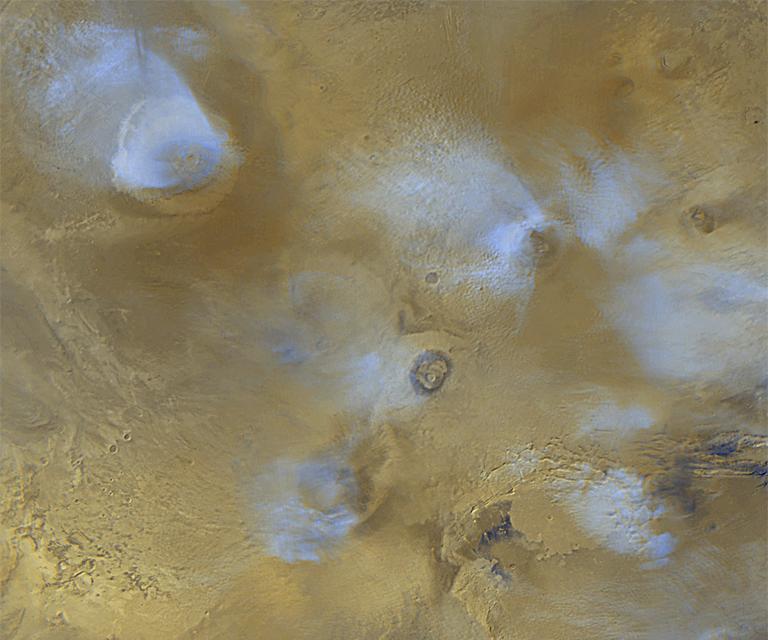 The Tharsis volcanoes. Arsia Mons on the backside, Pavonis Mons on the middle, and Ascraeus Mons on the most sensible. Supply: NASA/JPL-Caltech
The Tharsis volcanoes. Arsia Mons on the backside, Pavonis Mons on the middle, and Ascraeus Mons on the most sensible. Supply: NASA/JPL-Caltech
The Tharsis Volcanoes are a bunch of colossal protect volcanoes on Mars. They shape a part of our sun gadget’s greatest volcanic area—the Tharsis volcanic plateau.
This plateau covers round 25% of Mars’ floor and is house to Olympus Mons. The area additionally comprises the volcanoes Ascraeus Mons, Pavonis Mons, and Arsia Mons. From house, those 3 volcanoes are organized in a nearly instantly line alongside Mars’ equator. The formation of those volcanoes is remarkably other in comparison to Earth.
As discussed previous, Mars does now not have tectonic plates. This implies lava accumulates in the similar position time and again for billions of years, permitting volcanos to upward push to peculiar heights. Many scientists imagine the Tharsis area’s volcanic process influenced Mars’ local weather, air or even floor fractures.
4. Hellas Planitia: One of the crucial greatest have an effect on basins within the sun gadget
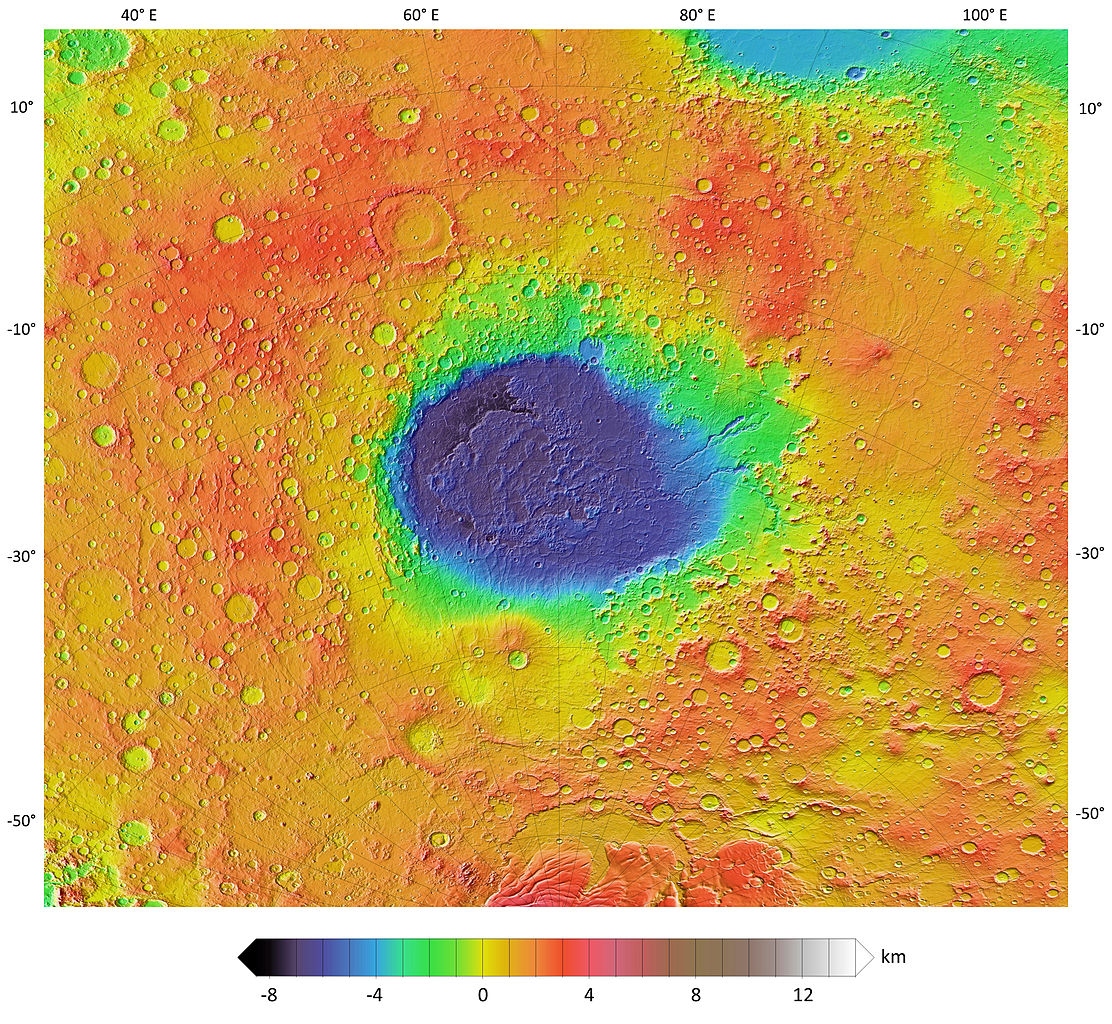 Topographic map of Hellas Planitia and its setting within the southern uplands. Supply: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Arizona State College
Topographic map of Hellas Planitia and its setting within the southern uplands. Supply: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Arizona State College
Hellas Planitia is likely one of the inner most and biggest have an effect on basins within the sun gadget. It’s situated within the southern hemisphere of Mars. It’s more or less 1,400 miles (2,300 kilometers) broad. It additionally marks the bottom level of Mars, because it plunges as much as 4.3 miles (7 kilometers) beneath its setting.
It’s idea that Hellas Planitia evolved about 4 billion years in the past—all the way through the Noachian Duration—when a colossal asteroid smashed into Mars.
It was once all the way through this time that Mars skilled the Past due Heavy Bombardment (LHB)—a length of intense asteroid bombardment within the early sun gadget. Scientists theorize that the Hellas Planitia was once then formed by means of volcanism, wind, ice, and in all probability historic water.
Apparently, because of its intensity, Hellas Planitia possesses a extra considerable environment than maximum websites on Mars. This leads to larger air power with frost or fog every now and then witnessed within the house.
5. Medusae Fossae Formation: Large wind-eroded deposits
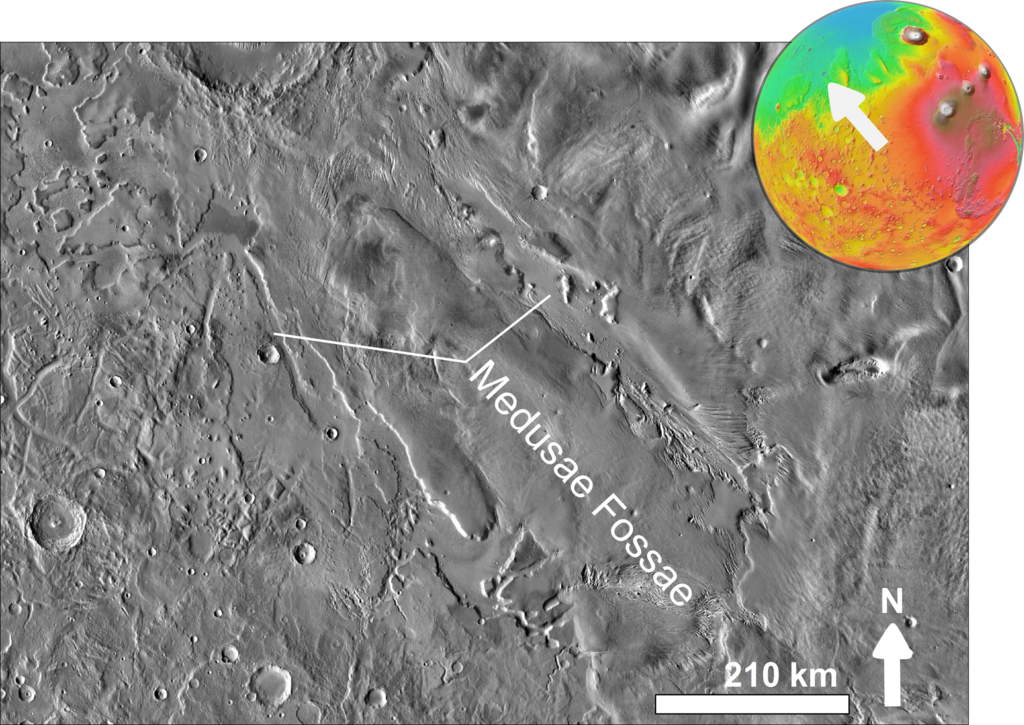 An infrared symbol mosaic of the Medusae Fossae Formation from the 2001 Mars Odyssey orbiter venture. Supply: Wikimedia Commons/NASA/Chmee2
An infrared symbol mosaic of the Medusae Fossae Formation from the 2001 Mars Odyssey orbiter venture. Supply: Wikimedia Commons/NASA/Chmee2
The Medusae Fossae Formation (MFF) is an enigmatic characteristic of Mars that spans over two million sq. miles (5 million sq. kilometers). It’s made up of big wind-eroded deposits and is close to the planet’s equator. MFF is considered more or less 3 billion years outdated which corresponds to Mars’ Hesperian length.
Scientists speculate that it’s composed of soppy, simply erodible subject material. This will have originated from volcanic ash, wind-deposited mud, or sediments from historic water our bodies. Radar scans counsel MFF is strangely porous, with deposits in all probability being one of the most least dense forged subject material on Mars.
MFF’s origins are nonetheless hotly contested, however a well-liked principle is that explosive volcanic eruptions from the close by Tharsis volcanic area spewed large amounts of ash that finally consolidated into rock. Robust Martian winds then sculpted the land into peculiar ‘yardangs’ (wind-carved rock formations), valleys, and ridges.
Accumulating additional wisdom of MFF can let us know extra about Mars’ climatic historical past and make clear its former volcanic process, and atmospheric stipulations. It’ll have contributed to the formation of the planet’s environment all the way through Mars’ earlier period when liquid water was once considered provide.
6. Gale Crater: 3.8 billion-year-old have an effect on crater
 NASA’s Interest rover (inexperienced dot) landed at the Gale Crater in 2012. Supply: NASA/JPL-Caltech/ESA/DLR/FU Berlin/MSSS
NASA’s Interest rover (inexperienced dot) landed at the Gale Crater in 2012. Supply: NASA/JPL-Caltech/ESA/DLR/FU Berlin/MSSS
Gale Crater is the identify of an enormous have an effect on crater on Mars with a diameter of roughly 96 miles (154 kilometers). Scientist estimate it to be between 3.5 and three.8 billion years outdated. One main principle suggests Gale Crater was once the results of a big comet or asteroid colluding towards Mars all the way through the Noachian or early Hesperian classes.
The middle of Gale Crater incorporates Mount Sharp (Aeolis Mons)—an 18,000-foot (5.5 kilometers) mountain composed of sedimentary rock. Scientists speculate that the presence of those sedimentary deposits is proof of historic lakes and rivers. Sulfate deposits and minerals counsel liquid water as soon as existed within the Gale Crater, probably developing liveable stipulations for microbial lifestyles.
NASA’s Interest rover has been actively exploring Gale Crater since 2012. Its venture comes to finding out the Gale Crater’s rock layers and in the hunt for natural compounds. Since its touchdown, the rover has aided scientists in working out the a couple of phases of ways Mars transitioned from a hotter and wetter planet to the chilly and dry global of as of late.
7. Utopia Planitia: A undeniable with the sun gadget’s greatest have an effect on crater
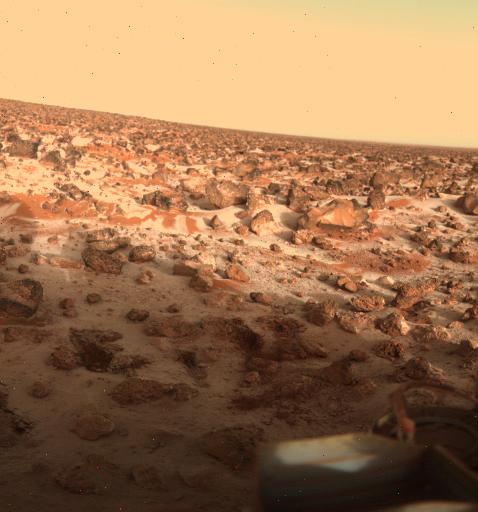 Frosted terrain on Utopia Planitia, taken by means of the Viking 2 lander in 1979. Supply: NASA/JPL
Frosted terrain on Utopia Planitia, taken by means of the Viking 2 lander in 1979. Supply: NASA/JPL
Utopia Planitia is a big undeniable inside of Utopia—the most important known have an effect on basin on Mars and within the sun gadget. Positioned on the earth’s northern hemisphere, it has an estimated diameter of two,100 miles (3,300 kilometers), which is more or less better than the blended spaces of Alaska and Texas.
Scientists estimate Utopia Planitia to be round 3.5 billion years outdated, comparable to the Noachian-Hesperian transition on Mars. After NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) detected buried water ice underneath its floor in 2016, scientists imagine Utopia Planitia could have as soon as contained a shallow ocean or huge glacial deposits.
As well as, the area is understood for being the touchdown web site of NASA’s Viking 2 lander in 1976, which did one of the most earliest checks for Martian lifestyles. Extra just lately, China’s Zhurong rover visited Utopia Planitia in 2021, generating new information about the planet’s local weather historical past and subsurface composition.
8. Noctis Labyrinthus: A 740-mile labyrinth
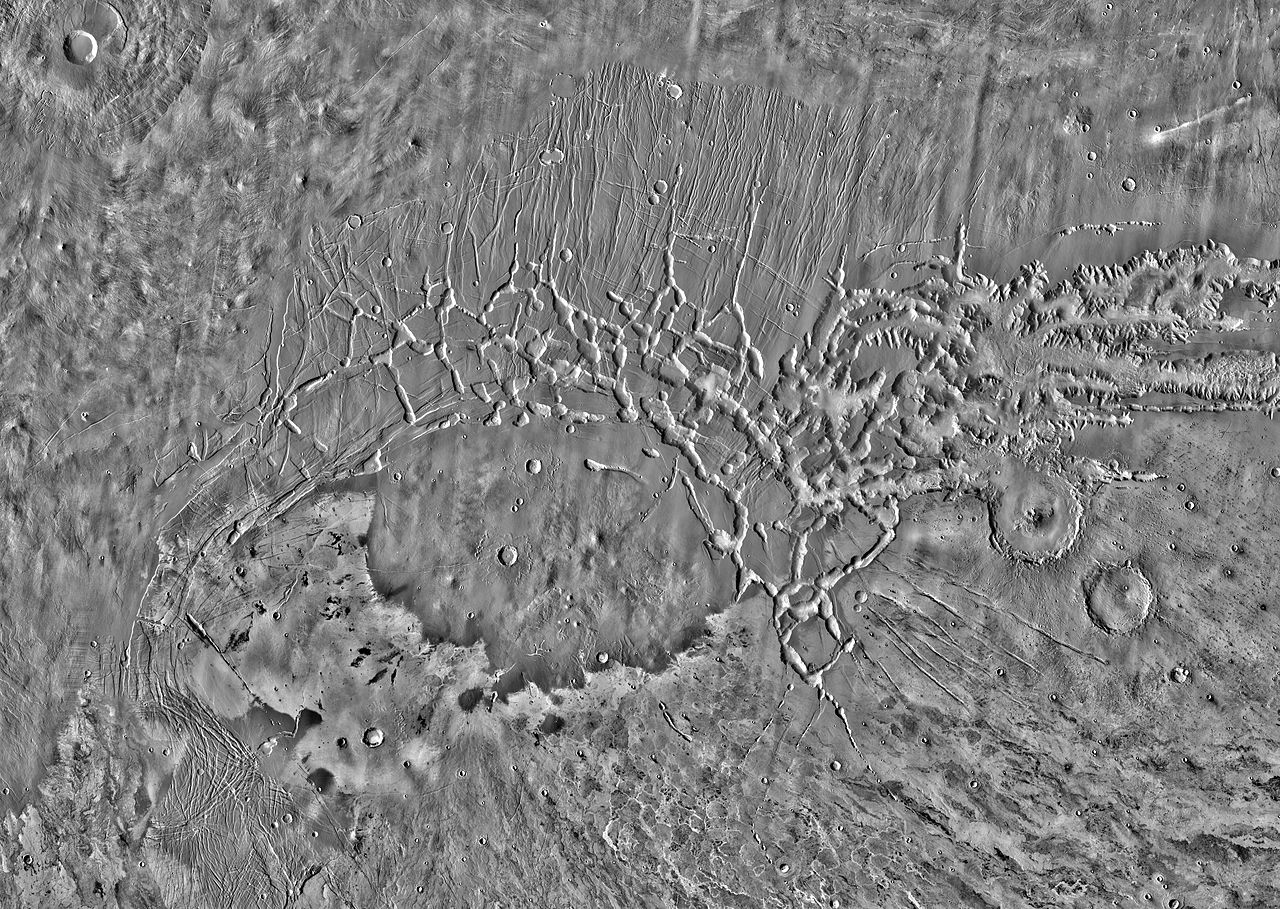 Top-resolution THEMIS sunlight hours infrared symbol mosaic of Noctis Labyrinthus and its setting. Supply: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Arizona State College
Top-resolution THEMIS sunlight hours infrared symbol mosaic of Noctis Labyrinthus and its setting. Supply: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Arizona State College
Noctis Labyrinthus is an unlimited community of canyons and valleys on Mars situated between Tharsis and the Valles Marineris. It extends 740 miles (1,190 kilometers) in period and resembles a labyrinth. The valleys of Noctis Labyrinthus have a intensity of as much as 3 miles (5 kilometers) and divulge historic Martian rock.
Scientists imagine that the panorama has additionally been formed by means of previous water process, wind erosion, and landslides. Hydrated minerals detected thru orbital statement counsel the presence of liquid water previously.
The complicated geology of Noctis Labyrinthus paired with the potential for historic water makes this a main goal house for long run exploration. Figuring out this house may just build up our working out of Martian tectonics and the potential for previous habitability.
9. Cerberus Fossae: Monumental 620-mile fissures
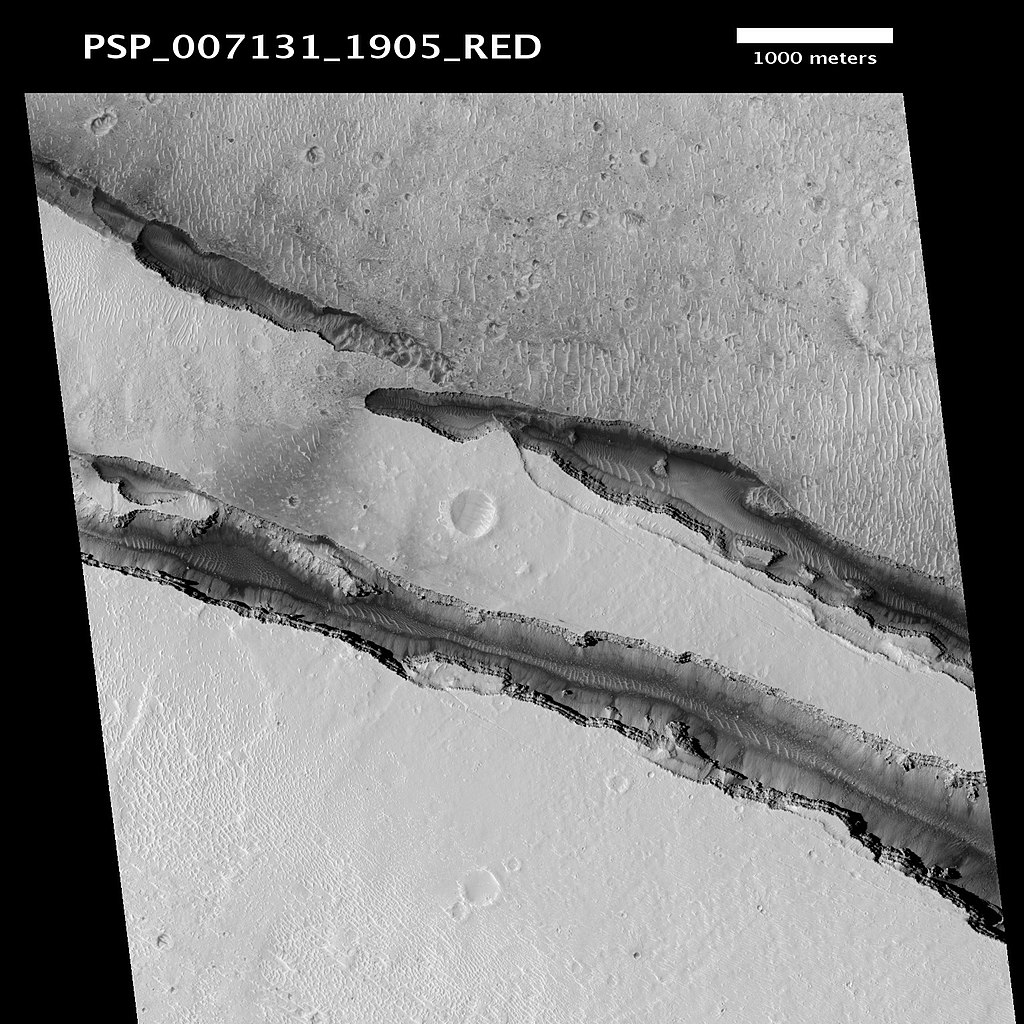 Closeup of a number of troughs within the Cerberus Fossae, as observed by means of the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter’s HiRISE digital camera. Supply: NASA/JPL-Caltech/College of Arizona
Closeup of a number of troughs within the Cerberus Fossae, as observed by means of the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter’s HiRISE digital camera. Supply: NASA/JPL-Caltech/College of Arizona
Cerberus Fossae is situated within the southeastern a part of Mars and is characterised by means of a collection of semi-parallel fissures that unfold 620 miles (1000 kilometers) around the planet. Some researchers imagine that the fissures generally is a supply of subsurface ice, or liquid water which brings up additional questions about habitability.
The fissures are estimated to be between 2 and 10 million years outdated, which is somewhat younger in geological phrases. Scientists hypothesize that those fissures are the manufactured from tectonic process similar to lava flows, and the possible presence of underground water.
The InSight lander, which stands for ‘Inner Exploration the use of Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Warmth Delivery,’ was once ready to hit upon marsquakes, suggesting that Mars remains to be seismically energetic.
10. Reull Vallis: An historic, dry riverbed
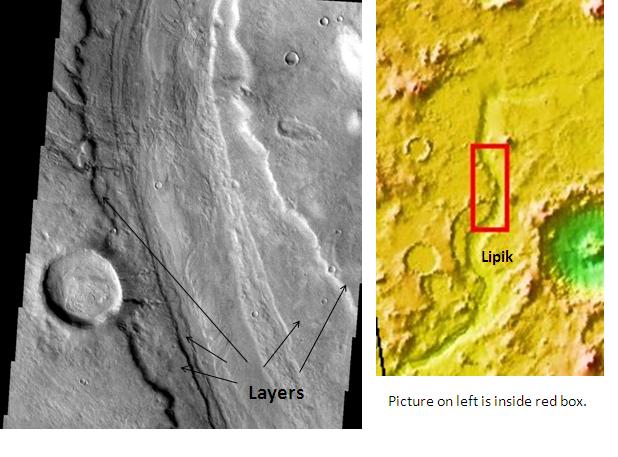 Layers in Reull Vallis, as observed by means of THEMIS. Supply: Wikimedia Commons/Jim Secosky/NASA
Layers in Reull Vallis, as observed by means of THEMIS. Supply: Wikimedia Commons/Jim Secosky/NASA
Reull Vallis is an historic, dry riverbed situated on Mars’ floor which stretches roughly 930 miles (1,500 kilometers) during the Promethei Terra area. Researchers imagine that liquid water carved it out of the skin billions of years in the past, making its location the most important within the exploration of Mars’ hydrologic historical past.
The valley’s steep partitions observe a winding path, such as meandering river channels discovered on Earth. Its ridged ground has tough, grooved patterns indicating that glacial motion possibly befell. One principle is that it was once carved by means of the glide of water which was once as soon as provide within the area.
Reull Vallis is among the distinguished options that finds clues concerning the climatic historical past of Mars. It additionally gives insights into the main stages of water and ice dominating the planet’s floor, serving to scientists identify the time through which Mars modified from a rainy global to the dry, chilly desolate tract we see as of late.