Entanglement, a shocking physics prediction, hyperlinks far-off items as although they’re attached.
Historically noticed in photons and coffee energies, this phenomenon has now been came upon in pairs of peak quarks, the heaviest debris identified.
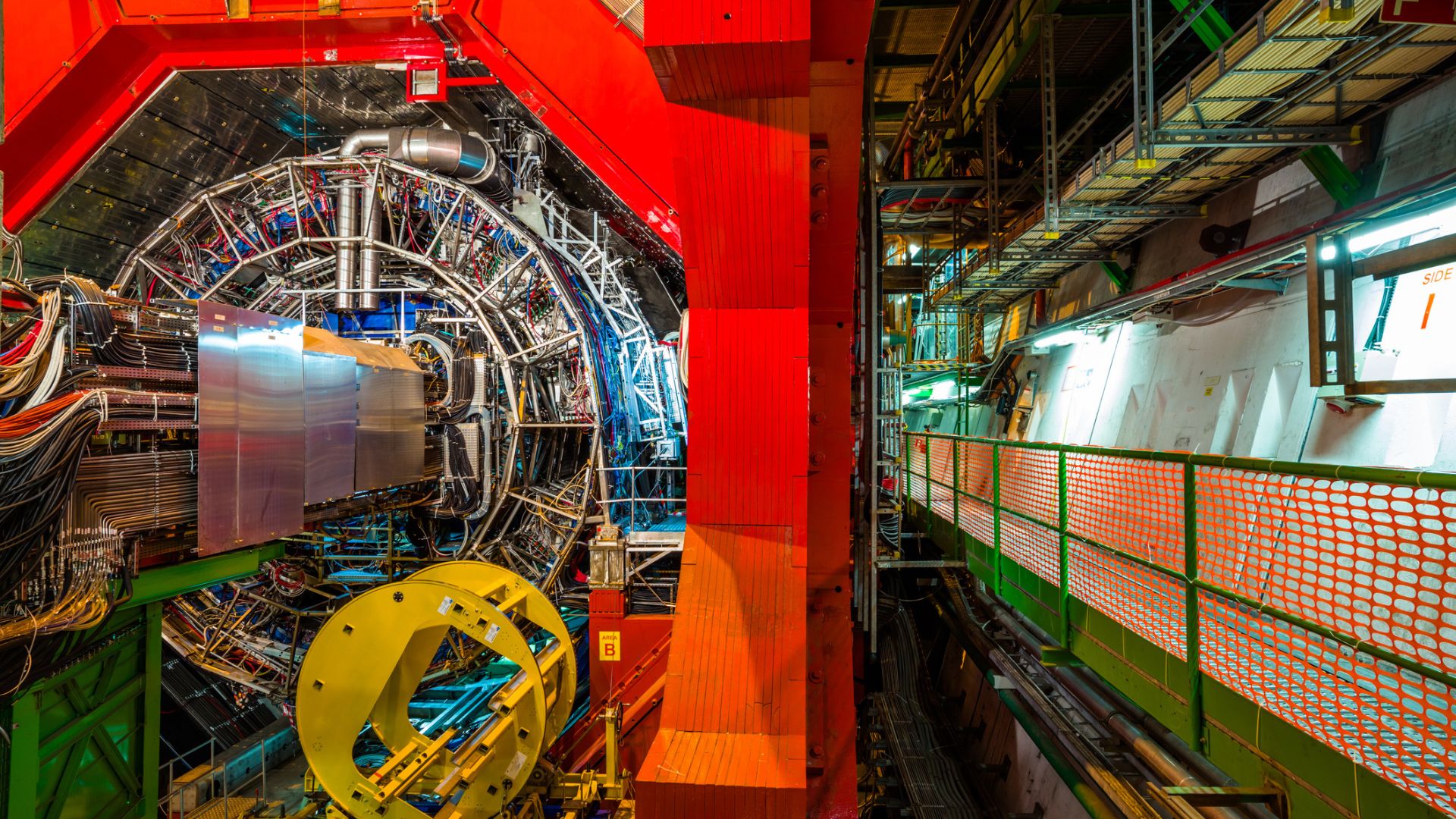
Now, the ATLAS experiment on the Massive Hadron Collider in Geneva has made this groundbreaking discovery, increasing the scope of entanglement past its earlier examples.
Researchers say they’ve measured spin entanglement with nice precision the usage of knowledge from high-energy proton collisions. This marks the primary statement of such entanglement in quarks and on the perfect calories scale but.
Best quark discovery
In on a regular basis phrases, we call to mind items as both separate or attached. Entangled items, alternatively, are neither in point of fact separate nor bodily attached; measuring one object immediately unearths details about the opposite, even though they’re some distance aside.
Researchers have demonstrated this phenomenon with photons, and this can be a key thought in quantum physics. In keeping with the group, although in style sci-fi like The 3-Frame Downside imagines the usage of entanglement for faster-than-light communique, in step with quantum concept, this isn’t conceivable.
Entanglement, first proven with photons within the Eighties, is now utilized in applied sciences like quantum computing. Fresh developments from Geneva have prolonged this to high-energy peak quarks, marking the primary statement of entanglement at such excessive calories ranges.
Subject consists of molecules, which might be fabricated from atoms, with electrons orbiting a dense nucleus, an idea established in 1911. The nucleus incorporates protons and neutrons, and via the Seventies, it was once came upon that those are fabricated from quarks—six varieties in general.
Amongst them, the “peak” quark is the heaviest, weighing about 184 instances greater than a proton or even heavier than a tungsten atom. Its huge measurement stays unexplained and is the point of interest of intense learn about on the Massive Hadron Collider.
Researchers, together with the ones operating at the ATLAS experiment in Sydney, are investigating whether or not this massive mass may well be because of unknown forces or divulge new physics, as present bodily rules appear incomplete.
Prime-energy entanglement
The ATLAS experiment on the Massive Hadron Collider, which research peak and antitop quarks produced in proton collisions at 13 TeV, has made the highest-energy statement of entanglement up to now.
Researchers had been in a position to spot spin entanglement via measuring a specific perspective between charged leptons from the quark pairs. By means of focusing on strong debris to reduce errors from simulation fashions, this dimension, which was once made close to the top-antitop quark manufacturing barrier, is helping to make sure precision.With a excessive level of self belief, the end result published a considerable entanglement marker price of D = -0.537. That is the primary time quark entanglement at such excessive energies has been observed.
The gang claims that entanglement isn’t particular to peak quarks however reasonably a fashionable incidence in quantum physics. Despite the fact that entanglement can occur in a number of methods, this can be a delicate procedure this is ceaselessly researched in extraordinarily chilly temperatures to keep away from disruptions.Since the peak quark has an important mass, it can be used to inspect entanglement extra successfully than the opposite 5 quark varieties. Alternatively, on account of the magnitude of the Massive Hadron Collider, peak quark pairs don’t seem to be helpful for on a regular basis applied sciences.Regardless of this, scientists declare that high quarks supply an invaluable experimental software and that entanglement analysis continues to be interesting, encouraging further analysis to make new findings.
The main points of the group’s analysis had been revealed within the magazine Nature.