A brand new learn about from researchers on the California Institute of Era (CIT) suggests the Lengthy Valley Caldera in jap California is restlessly tossing and turning as its deep magma chamber cools down for a large, lengthy sleep.The final time the volcano blew used to be more or less 100,000 years in the past. Lengthy earlier than that, it spewed up sufficient ash to bury the fashionable town of Los Angeles underneath a kilometer of sediment.Nowadays, the Lengthy Valley volcano exists in a rather gradual state. However all isn’t quiet on California’s jap entrance. Within the past due Nineteen Seventies, a swarm of earthquakes started to emanate from the caldera – a melancholy that sits atop the buried volcano.For many years thereafter, the volcano produced common sessions of “pronounced unrest”, which inflated and deflated the bottom.Fortunately, that is not essentially an indication of imminent doom. Researchers at CIT have now discovered proof that each one this fussy process is because of the supervolcano cooling down, now not heating up.”We do not suppose the area is gearing up for every other supervolcanic eruption, however the cooling procedure would possibly free up sufficient gasoline and liquid to reason earthquakes and small eruptions,” says geophysicist Zhongwen Zhan.”For instance, in Might 1980, there have been 4 magnitude 6 earthquakes within the area on my own.”The group’s findings are in keeping with knowledge gathered from a 100-kilometer stretch of fiber optic cable, the usage of disbursed acoustic sensing.Over the process a 12 months and a part, researchers at Caltech used this interconnected gadget – which is similar to ten,000 person seismometers – to catalog greater than 2,000 seismic occasions, lots of which don’t have been felt by way of people at the floor.This information used to be then plugged right into a system finding out set of rules, which became the measurements right into a high-resolution map of the caldera and the volcano that lies underneath.Ettore Biondi, a seismologist from Caltech and primary creator at the learn about, says that is the primary time {that a} community of deeply disbursed acoustic sensors has published Earth’s inside dynamics.The photographs produced are of “remarkable lateral decision” in depths as much as 8 kilometers, the group says. Even photographs of deeper parts, as much as 30 kilometers down, had been accomplished with a “exceptional stage of element”.The findings display a certain separation between the massive magma chamber of the volcano, sitting 12 kilometers beneath the outside, and the shallow hydrothermal gadget that sits above.It sort of feels that because the deeper chamber cools off, gasses and liquids bubble up towards the outside, perhaps inflicting the quakes and inflated floor.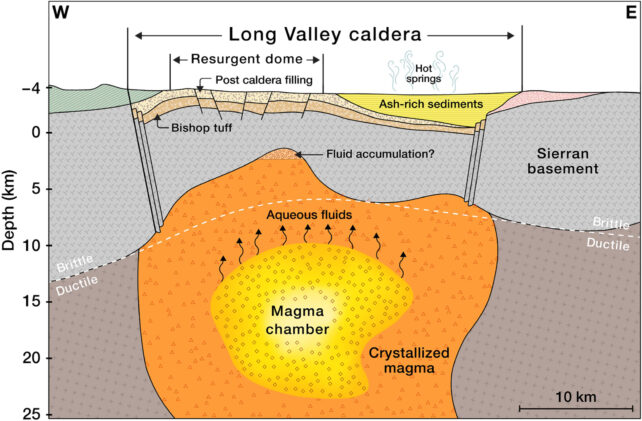 A diagram depicting the magma chamber underneath the Lengthy Valley Caldera. The diagram used to be evolved from tomographic imaging the usage of seismic waves. (Biondi et al. Science Advances, 2023)This boiling impact may “induce the noticed floor deformation and seismicity,” researchers write.That is other and a ways much less hazardous than what occurs all over an lively volcanic eruption when magma within the chamber of the volcano forces itself up into the higher crust and out into the arena.The best way seismic process travels via those layers suggests the highest of the magma chamber has a hardened lid of crystallized rock, which has cooled through the years.Because the supervolcano’s process winds down, researchers say its “beating center” is step by step slowing.The group plans to measure the ones final beats at 20 kilometers deep with a 200-kilometer-long cable of seismic sensors.The learn about used to be printed in Science Advances.
A diagram depicting the magma chamber underneath the Lengthy Valley Caldera. The diagram used to be evolved from tomographic imaging the usage of seismic waves. (Biondi et al. Science Advances, 2023)This boiling impact may “induce the noticed floor deformation and seismicity,” researchers write.That is other and a ways much less hazardous than what occurs all over an lively volcanic eruption when magma within the chamber of the volcano forces itself up into the higher crust and out into the arena.The best way seismic process travels via those layers suggests the highest of the magma chamber has a hardened lid of crystallized rock, which has cooled through the years.Because the supervolcano’s process winds down, researchers say its “beating center” is step by step slowing.The group plans to measure the ones final beats at 20 kilometers deep with a 200-kilometer-long cable of seismic sensors.The learn about used to be printed in Science Advances.
Massive Supervolcano in California Is Sleepy, However Scientists Say It is Stressed