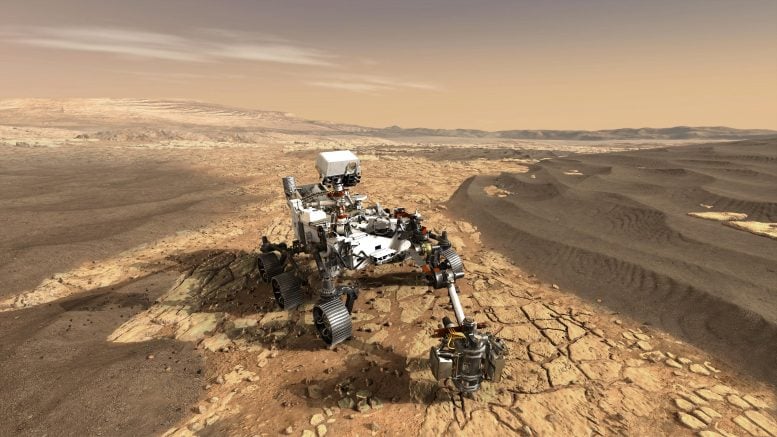
 NASA’s Perseverance rover has amassed Mars samples that would divulge the planet’s watery historical past and attainable previous lifestyles. Those rocks, a very powerful for working out Martian biology, will have to be analyzed on Earth, necessitating a long term project. Whilst some natural molecules had been detected, extra delicate research is wanted. Credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech
NASA’s Perseverance rover has amassed Mars samples that would divulge the planet’s watery historical past and attainable previous lifestyles. Those rocks, a very powerful for working out Martian biology, will have to be analyzed on Earth, necessitating a long term project. Whilst some natural molecules had been detected, extra delicate research is wanted. Credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech
NASA’s Perseverance rover has amassed rock samples from Mars that would adjust our working out of water’s historical past on the earth and doubtlessly divulge previous lifestyles.
Those samples, gathered over 5 months in 2022 from Jezero Crater, are a very powerful as a result of they had been transported and deposited by way of water, in all probability keeping proof of previous microbial lifestyles. On the other hand, detailed research will have to happen on Earth, which would require a long term project to retrieve them.
Over the process just about 5 months in 2022, NASA’s Perseverance rover gathered rock samples from Mars that would rewrite the historical past of water at the Purple Planet. They might even include proof of previous lifestyles on Mars.
However the knowledge they include can’t be extracted with out extra detailed research on Earth, which calls for a brand new project to the planet to retrieve the samples and produce them again. Scientists hope to have the samples on Earth by way of 2033, even though NASA’s pattern go back project is also behind schedule.
The Significance of Sedimentary Rock Samples
“Those samples are the explanation why our project used to be flown,” stated paper co-author David Shuster, professor of earth and planetary science on the College of California, Berkeley, and a member of NASA’s science staff for pattern assortment. “That is precisely what everybody used to be hoping to perform. And we’ve completed it. Those are what we went on the lookout for.”
The vital significance of those rocks, sampled from river deposits in a dried-up lake that when crammed a crater referred to as Jezero, is detailed in a find out about to be printed nowadays (August 14) in AGU Advances, a magazine of the American Geophysical Union.
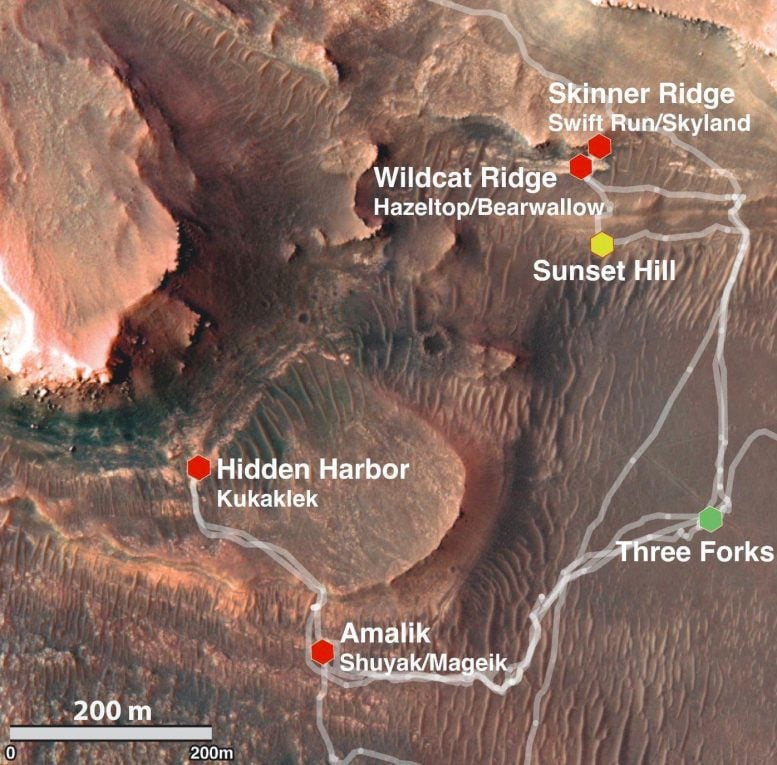 Purple hexagons mark the 4 websites the place the Perseverance rover gathered rock samples across the sediment fan in Jezero crater in 2022. Credit score: NASA
Purple hexagons mark the 4 websites the place the Perseverance rover gathered rock samples across the sediment fan in Jezero crater in 2022. Credit score: NASA
“Those are the primary and best sedimentary rocks which were studied and picked up from a planet rather than Earth,” stated paper co-author David Shuster, professor of earth and planetary science on the College of California, Berkeley, and a member of NASA’s science staff for pattern assortment. “Sedimentary rocks are vital as a result of they had been transported by way of water, deposited into a status frame of water, and therefore changed by way of chemistry that concerned liquid water at the floor of Mars someday prior to now. The entire reason why that we got here to Jezero used to be to check this kind of rock kind. Those are completely incredible samples for the overarching targets of the project.”
Possible for Previous Existence on Mars
Shuster is co-author of the paper with first writer Tanja Bosak, a geobiologist on the Massachusetts Institute of Era (MIT) in Cambridge.
“Those rock cores are most likely the oldest fabrics sampled from any identified surroundings that can have supported lifestyles,” Bosak stated. “Once we convey them again to Earth, they may be able to let us know such a lot about when, why and for the way lengthy Mars contained liquid water, and whether or not some natural, prebiotic, and doubtlessly even organic evolution can have taken position on that planet.”
Importance of Advantageous-Grained Sediments
Considerably, one of the samples include very fine-grained sediments which can be the perhaps form of rock to retain proof of previous microbial lifestyles on Mars — if there ever used to be or is lifestyles on the earth.
“Liquid water is a key component in all of this as a result of it’s the key aspect for organic process, so far as we realize it,” stated Shuster, a geochemist. “Advantageous-grained sedimentary rocks on Earth are the ones which can be perhaps to maintain signatures of previous organic process, together with natural molecules. That’s why those samples are so vital.”
Contemporary Discoveries From Cheyava Falls
NASA introduced on July 25 that Perseverance had gathered new rock samples from an outcrop named Cheyava Falls that still would possibly include indicators of previous lifestyles on Mars. The rover’s medical tools detected proof of natural molecules, whilst “leopard spot” inclusions within the rocks are very similar to options that on Earth are regularly related to fossilized microbial lifestyles.
In a observation, Ken Farley, Perseverance undertaking scientist at Caltech, stated, “Scientifically, Perseverance has not anything extra to offer. To completely perceive what in point of fact took place in that Martian river valley at Jezero crater billions of years in the past, we’d wish to convey the Cheyava Falls pattern again to Earth, so it may be studied with the robust tools to be had in laboratories.”
Unanswered Questions About Natural Compounds
Shuster famous that Jezero and the fan of sediments left at the back of by way of the river that when flowed into it most likely shaped 3.5 billion years in the past. That considerable water is now long past, both trapped underground or misplaced to house. However Mars used to be rainy at a time when lifestyles on Earth — within the type of microbes — used to be already in all places.
“Existence used to be doing its factor on Earth at that cut-off date, 3.5 billion years in the past,” he stated. “The elemental query is: Was once lifestyles additionally doing its factor on Mars at that cut-off date?”
“Anyplace on Earth over the past 3.5 billion years, if you happen to give me the state of affairs of a river flowing right into a crater transporting fabrics to a status frame of water, biology would have taken hang there and left its mark, in a method or every other,” Shuster stated. “And within the fine-grained sediment, in particular, we’d have an excellent likelihood of recording that biology within the laboratory observations that we will make on that subject matter on Earth.”
Shuster and Bosak recognize that the natural research apparatus aboard the rover didn’t hit upon natural molecules within the 4 samples from the sedimentary fan. Natural molecules are used and produced by way of the kind of lifestyles we’re conversant in on Earth, even though their presence isn’t unequivocal proof of lifestyles.
“We didn’t obviously follow natural compounds in those key samples,” Shuster stated. “However simply because that device didn’t hit upon natural compounds does now not imply that they don’t seem to be in those samples. It simply manner they weren’t at a focus detectable by way of the rover instrumentation in the ones explicit rocks.”
Perseverance’s Pattern Assortment Milestones
To this point, Perseverance has gathered a complete of 25 samples, together with duplicates and atmospheric samples, plus 3 “witness tubes” that seize conceivable contaminants across the rover. 8 replica rock samples plus an atmospheric pattern and witness tube had been deposited within the so-called 3 Forks cache at the floor of Jezero as a backup in case the rover suffers issues and the onboard samples can’t be retrieved. The opposite 15 samples — together with the Cheyava Falls pattern gathered July 21 — stay aboard the rover waiting for restoration.
Inspecting Mars’ Historic River Deposits
Shuster used to be a part of a staff that analyzed the primary 8 rock samples gathered, two from each and every website online at the crater flooring, all of that have been igneous rocks most likely created when a meteor have an effect on smashed into the outside and excavated the crater. The ones effects had been reported in a 2023 paper, in accordance with analyses by way of the tools aboard Perseverance.
The brand new paper is an research of 7 extra samples, 3 of them duplicates now cached on Mars’ floor, gathered between July 7 and November 29 of 2022 from the entrance of the western sediment fan in Jezero. Bosak, Shuster, and their colleagues discovered the rocks to be composed most commonly of sandstone and mudstone, all created by way of fluvial processes.
Unlocking Mars’ Water Historical past
“Perseverance encountered aqueously deposited sedimentary rocks on the entrance, most sensible, and margin of the western Jezero fan and picked up a pattern suite composed of 8 carbonate-bearing sandstones, a sulfate-rich mudstone, a sulfate-rich sandstone, a sand-pebble conglomerate,” Bosak stated. “The rocks gathered on the fan entrance are the oldest, while the rocks gathered on the fan most sensible are most likely the youngest rocks produced all over aqueous process and sediment deposition within the western fan.”
Whilst Bosak is maximum desirous about conceivable biosignatures within the fine-grained sediments, the coarse-grained sediments additionally include key details about water on Mars, Shuster stated. Despite the fact that much less prone to maintain natural subject or attainable organic fabrics, they include carbonate fabrics and detritus washed from upstream by way of the now-vanished river. They thus may just assist resolve when water in truth flowed on Mars, the primary emphasis of Shuster’s personal analysis.
“With lab research of the ones detrital minerals, shall we make quantitative statements about when the sediments had been deposited and the chemistry of that water. What used to be the pH (acidity) of that water when the ones secondary levels prompted? At what cut-off date used to be that chemical alteration going down?” he stated. “We’ve this mix of samples now within the pattern suite which can be going to allow us to know the environmental prerequisites when the liquid water used to be flowing into the crater. When used to be that liquid water flowing into the crater? Was once it intermittent?”
Long run Missions and Laboratory Research
Solutions to those questions rely on analyses of the returned fabrics in terrestrial laboratories to discover the natural, isotopic, chemical, morphological, geochronological, and paleomagnetic knowledge they report, the researchers emphasised.
“One of the vital planetary science targets is to convey those samples again,” Shuster stated.
Reference: “Astrobiological attainable of rocks got by way of the Perseverance rover at a sedimentary fan entrance in Jezero crater, Mars” 14 August 2024, AGU Advances.
May just Perseverance’s Mars Samples Cling the Secret to Historic Existence?














