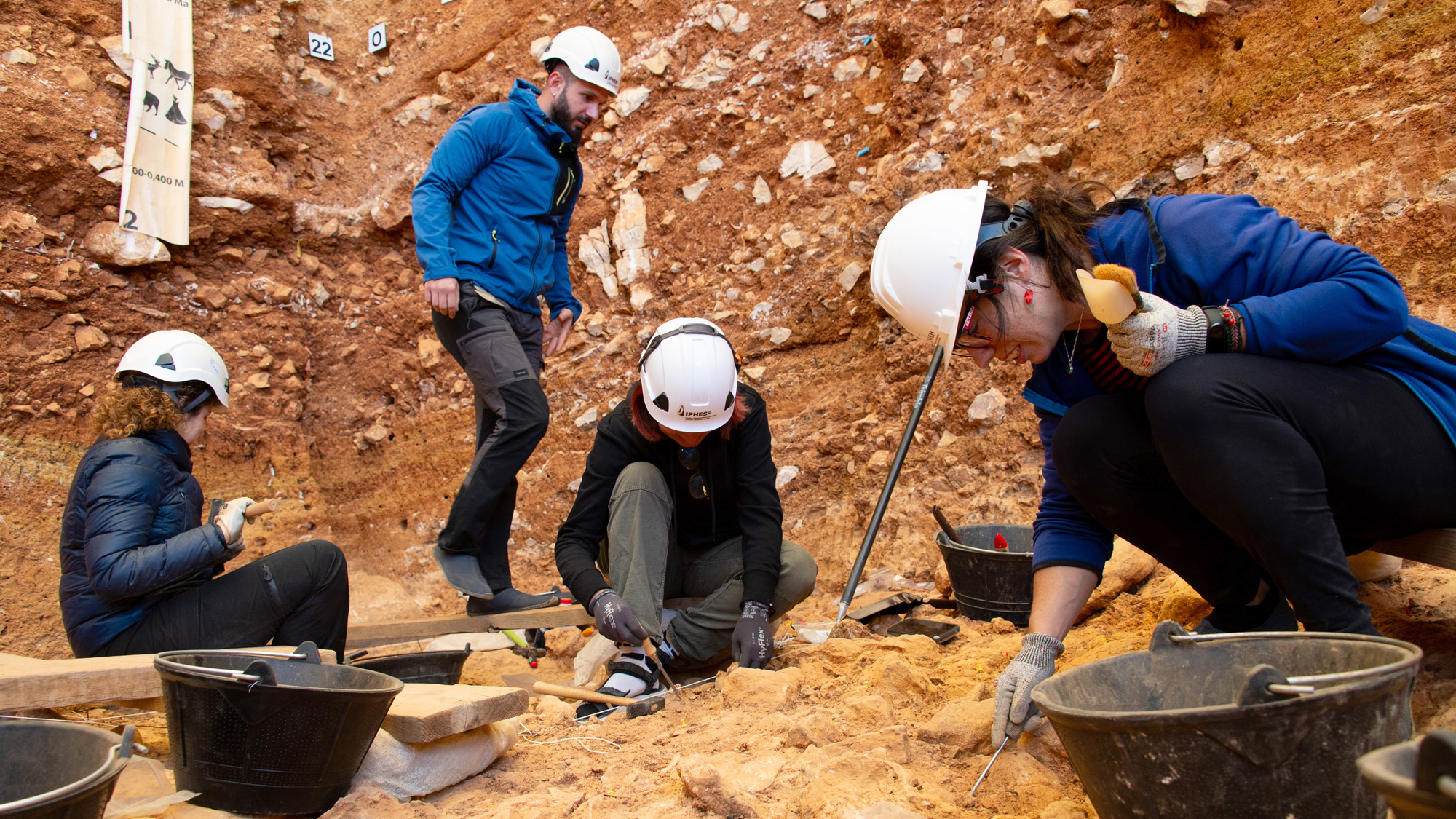
Tiny fragments of plastic don’t seem to be best discovering their means into animals, far flung ice caps, oceans, or even the depths of our our bodies. They are additionally seeping thru layers of rock, making the emergence of plastics within the geological document a deficient marker for the morning time of the human age.In a brand new find out about, sediment samples from 3 other lakes in Latvia – Seksu, Pinku, and Usmas – have been analyzed to look how deep microplastics had sunk. The effects confirmed that smaller debris may commute deeper into the dust, achieving layers laid down ahead of plastic manufacturing sped up at first of the Fifties.That makes the presence of plastics in rock strata an unreliable indicator of plastics’ proliferation in society, ecologist Inta Dimante-Deimantovica from the Latvian Institute of Aquatic Ecology and a global workforce of researchers say.Some geologists have proposed this presence of plastic as an acceptable geological start line to outline the reliable starting of human’s shaping of the planet’s floor, referred to as the Anthropocene.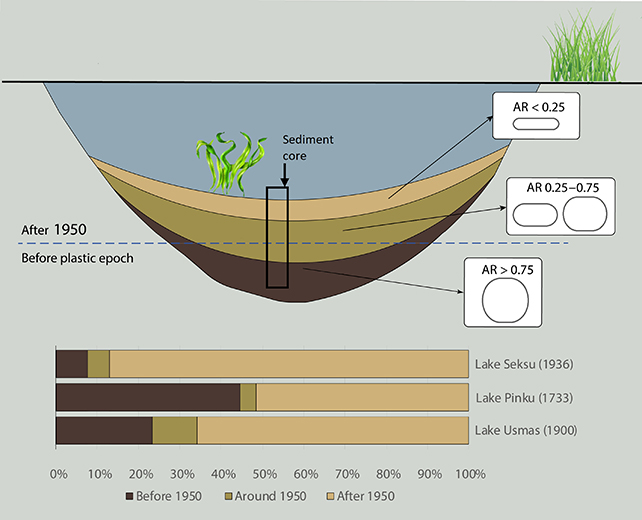 Sediment from 3 lakes was once analyzed. (Dimante-Deimantovica et al., Science Advances, 2024)”We conclude that interpretation of microplastics distribution within the studied sediment profiles is ambiguous and does now not strictly point out the start of the Anthropocene Epoch,” write the researchers of their revealed paper.The effects have been slightly constant around the lakes, regardless of diversifications relating to how a ways away they have been from urbanized spaces, and the extent of get right of entry to to the general public they presented – but extra proof of the way pervasive microplastics have turn out to be.Every pattern was once dated from fashionable instances again to the early 1700s the use of unbiased proxies, offering a competent measure in their ages. Microplastic debris have been discovered during the samples from all websites, with a complete of 14 several types of plastic known by means of the analysis time period.Sorts of microplastic debris incorporated polyamide (utilized in nylon), polyethylene (ceaselessly present in packaging), polyurethane (utilized in foams and fibers), and polyvinyl acetate (present in glues).The 3 lakes have been selected for the reason that sediments they sit down on have all been widely studied and dated – this means that the workforce might be positive that smaller plastic debris have been achieving older layers of dust.”We propose that those findings display a real herbal phenomenon, unambiguous downward motion of microplastics in sediment profiles,” the researchers write .A wide variety of things may affect this motion, the researchers say – from the kind of the sediment subject matter, to the kind of microplastic, to the encircling environmental stipulations – which makes it difficult to review.What does appear transparent is that we are on the degree the place we will’t escape from microplastics. Professionals are nonetheless looking to perceive what that is doing to our well being, however it is turning into transparent that the tiny debris are way more pervasive than we ever idea imaginable.”It’s estimated that best about 9 p.c of all plastic ever produced is recycled and 12 p.c is incinerated, resulting in the realization that over 6,000 million metric heaps of waste plastic has the prospective to leak into the surroundings and turn out to be integrated in herbal cycles and meals chains,” write the researchers.The analysis has been revealed in Science Advances.
Sediment from 3 lakes was once analyzed. (Dimante-Deimantovica et al., Science Advances, 2024)”We conclude that interpretation of microplastics distribution within the studied sediment profiles is ambiguous and does now not strictly point out the start of the Anthropocene Epoch,” write the researchers of their revealed paper.The effects have been slightly constant around the lakes, regardless of diversifications relating to how a ways away they have been from urbanized spaces, and the extent of get right of entry to to the general public they presented – but extra proof of the way pervasive microplastics have turn out to be.Every pattern was once dated from fashionable instances again to the early 1700s the use of unbiased proxies, offering a competent measure in their ages. Microplastic debris have been discovered during the samples from all websites, with a complete of 14 several types of plastic known by means of the analysis time period.Sorts of microplastic debris incorporated polyamide (utilized in nylon), polyethylene (ceaselessly present in packaging), polyurethane (utilized in foams and fibers), and polyvinyl acetate (present in glues).The 3 lakes have been selected for the reason that sediments they sit down on have all been widely studied and dated – this means that the workforce might be positive that smaller plastic debris have been achieving older layers of dust.”We propose that those findings display a real herbal phenomenon, unambiguous downward motion of microplastics in sediment profiles,” the researchers write .A wide variety of things may affect this motion, the researchers say – from the kind of the sediment subject matter, to the kind of microplastic, to the encircling environmental stipulations – which makes it difficult to review.What does appear transparent is that we are on the degree the place we will’t escape from microplastics. Professionals are nonetheless looking to perceive what that is doing to our well being, however it is turning into transparent that the tiny debris are way more pervasive than we ever idea imaginable.”It’s estimated that best about 9 p.c of all plastic ever produced is recycled and 12 p.c is incinerated, resulting in the realization that over 6,000 million metric heaps of waste plastic has the prospective to leak into the surroundings and turn out to be integrated in herbal cycles and meals chains,” write the researchers.The analysis has been revealed in Science Advances.
Microplastics Invade Historical Rock, And That's a Giant Drawback For Age Markers














