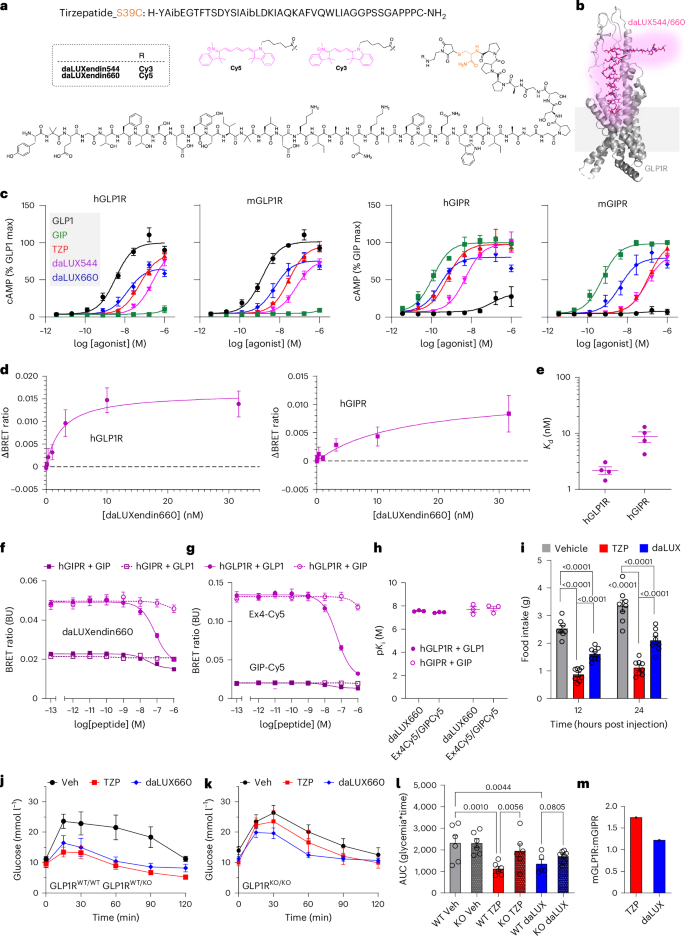
Clouds shape when water vapor – an invisible gasoline within the surroundings – sticks to tiny floating debris, corresponding to mud, and becomes liquid water droplets or ice crystals. In a newly printed learn about, we display that microplastic debris may have the similar results, generating ice crystals at temperatures 5 to ten levels Celsius (9 to 18 levels Fahrenheit) hotter than droplets with out microplastics.
This means that microplastics within the air would possibly impact climate and local weather via generating clouds in prerequisites the place they wouldn’t shape another way.
We’re atmospheric chemists who learn about how various kinds of debris shape ice after they come into touch with liquid water. This procedure, which happens repeatedly within the surroundings, is known as nucleation.
READ MORE: Research: How ornamental glitter contributes to microplastic air pollution
Clouds within the surroundings can also be made up of liquid water droplets, ice debris or a mix of the 2. In clouds within the mid- to higher surroundings the place temperatures are between 32 and minus 36 F (0 to minus 38 C), ice crystals typically shape round mineral mud debris from dry soils or organic debris, corresponding to pollen or micro organism.
Microplastics are lower than 5 millimeters huge – in regards to the measurement of a pencil eraser. Some are microscopic. Scientists have discovered them in Antarctic deep seas, the summit of Mount Everest and recent Antarctic snow. As a result of those fragments are so small, they may be able to be simply transported within the air.
Clouds are essential portions of Earth’s advanced climate machine, with results on precipitation, temperature and local weather.
Why it issues
Ice in clouds has essential results on climate and local weather as a result of maximum precipitation most often begins as ice debris.
Many cloud tops in nontropical zones around the globe prolong top sufficient into the ambience that chilly air reasons a few of their moisture to freeze. Then, as soon as ice paperwork, it attracts water vapor from the liquid droplets round it, and the crystals develop heavy sufficient to fall. If ice doesn’t expand, clouds generally tend to evaporate relatively than inflicting rain or snow fall.
Whilst youngsters be informed in grade college that water freezes at 32 F (0 C), that’s no longer all the time true. With out one thing to nucleate onto, corresponding to mud debris, water can also be supercooled to temperatures as little as minus 36 F (minus 38 C) prior to it freezes.
READ MORE: Why clouds are key to new local weather trade projections
For freezing to happen at hotter temperatures, some more or less subject matter that received’t dissolve in water must be provide within the droplet. This particle supplies a floor the place the primary ice crystal can shape. If microplastics are provide, they may motive ice crystals to shape, probably expanding rain or snow fall.
Clouds additionally impact climate and local weather in numerous techniques. They mirror incoming daylight clear of Earth’s floor, which has a cooling impact, and soak up some radiation this is emitted from Earth’s floor, which has a warming impact.
The quantity of daylight mirrored is determined by how a lot liquid water vs. ice a cloud comprises. If microplastics building up the presence of ice debris in clouds when put next with liquid water droplets, this moving ratio may trade clouds’ impact on Earth’s power stability.
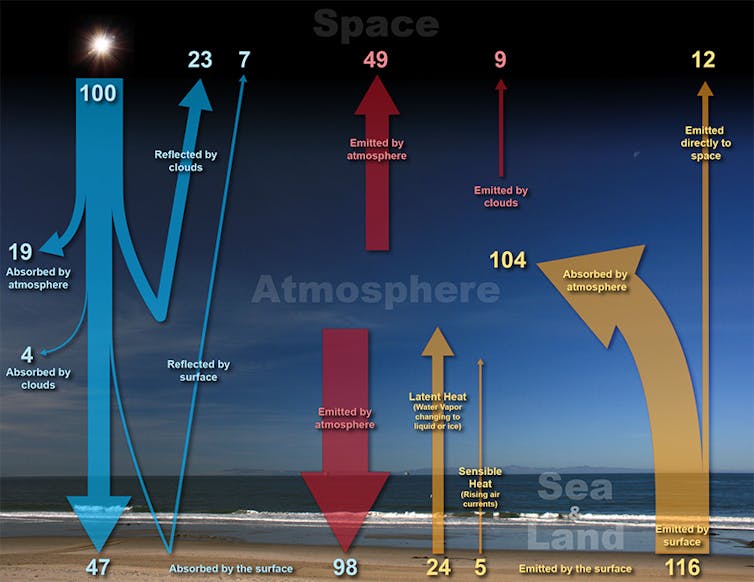 The Earth repeatedly receives power from the Solar and displays it again into area. Clouds have each warming and cooling results on this procedure.
The Earth repeatedly receives power from the Solar and displays it again into area. Clouds have each warming and cooling results on this procedure.
NOAA
How we did our paintings
To look whether or not microplastic fragments may function nuclei for water droplets, we used 4 of probably the most prevalent forms of plastics within the surroundings: low density polyethylene, polypropylene, polyvinyl chloride and polyethylene terephthalate. Every used to be examined each in a pristine state and after publicity to ultraviolet gentle, ozone and acids. All of those are provide within the surroundings and may impact the composition of the microplastics.
We suspended the microplastics in small water droplets and slowly cooled the droplets to look at after they iced up. We additionally analyzed the plastic fragments’ surfaces to decide their molecular construction, since ice nucleation may rely at the microplastics’ floor chemistry.
READ MORE: The sector is generating 57 million heaps of plastic air pollution in keeping with 12 months, new learn about unearths
For lots of the plastics we studied, 50 % of the droplets had been frozen by the point they cooled to minus 8 F (minus 22 C). Those effects parallel the ones from any other contemporary learn about via Canadian scientists, who additionally discovered that some forms of microplastics nucleate ice at hotter temperatures than droplets with out microplastics.
Publicity to ultraviolet radiation, ozone and acids tended to lower ice nucleation task at the debris. This means that ice nucleation is delicate to small chemical adjustments at the floor of microplastic debris. On the other hand, those plastics nonetheless nucleated ice, so they may nonetheless impact the quantity of ice in clouds.
What nonetheless isn’t identified
To know the way microplastics impact climate and local weather, we wish to know their concentrations on the altitudes the place clouds shape. We additionally wish to perceive the focus of microplastics when put next with different debris that might nucleate ice, corresponding to mineral mud and organic debris, to peer whether or not microplastics are provide at related ranges. Those measurements would let us style the affect of microplastics on cloud formation.
Plastic fragments are available many sizes and compositions. In long term analysis, we plan to paintings with plastics that include components, corresponding to plasticizers and colorants, in addition to with smaller plastic debris.
This text is republished from The Dialog below a Ingenious Commons license. Learn the unique article.