Astronomers could have discovered an extraordinary “lacking hyperlink” black hollow within the Milky Manner after recognizing a gaggle of improbably fast-moving stars on the center of a close-by stellar cluster. If showed, the cosmic juggernaut, referred to as an intermediate-mass black hollow (IMBH), will be the second-largest black hollow ever present in our galaxy. IMBHs are a particularly uncommon subset of black holes which are better than stellar-mass black holes however smaller than supermassive black holes. This implies they may be able to be anyplace between 100 and 100,000 occasions the mass of the solar, in keeping with NASA.In idea, IMBHs will have to be simply as commonplace as different black hollow sorts. On the other hand, astronomers have struggled to find doable IMBHs or verify their lifestyles — and they don’t seem to be positive why. In consequence, IMBHs are regularly known as lacking hyperlink black holes. Whilst a number of promising applicants were detected, none were confirmed to be the actual deal.Now, in a up to date find out about uploaded April 4 to the preprint server arXiv, researchers could have exposed proof of a big IMBH within the globular cluster Omega Centauri — a compact staff of round 10 million stars within the Milky Manner positioned round 17,000 light-years from Earth.The crew when put next 500 images of Omega Centauri taken by means of the Hubble House Telescope and mapped the actions of round 1.4 million stars on the cluster’s heart. This published no less than seven stars that “will have to no longer be there,” researchers wrote in a observation.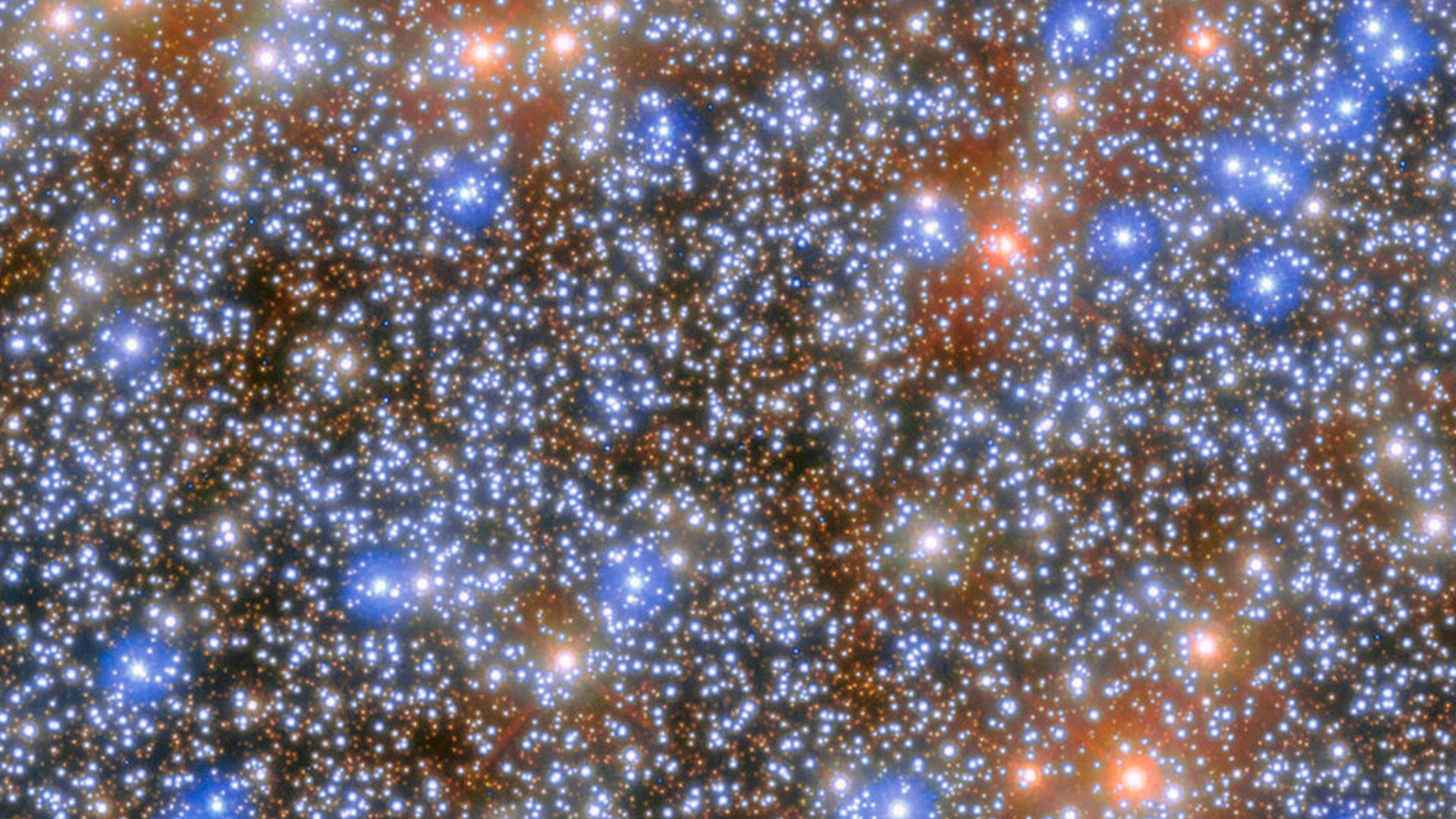 Omega Centauri is the most important globular cluster within the Milky Manner. (Symbol credit score: ESA/Hubble & NASA, M. Häberle)It’s because those stars had been noticed whizzing round quick sufficient to flee the cluster’s gravity and fly off into intergalactic area. However in spite of this, the celebs proceed to orbit at breakneck velocity close to the cluster’s heart.”The perhaps rationalization [for this] is {that a} very large object is gravitationally pulling on those stars and maintaining them with reference to the [cluster’s] centre,” find out about lead writer Maximilian Häberle, a doctoral candidate on the Max Planck Institute for Astronomy (MPIA) in Germany, stated within the observation. “The one object that may be so large is a black hollow, with a mass no less than 8,200 occasions that of our solar.”Get the sector’s most enticing discoveries delivered directly on your inbox.Comparable: Essentially the most elusive black holes within the universe may lurk on the Milky Manner’s centerThe Milky Manner’s second-biggest black hollow?
Omega Centauri is the most important globular cluster within the Milky Manner. (Symbol credit score: ESA/Hubble & NASA, M. Häberle)It’s because those stars had been noticed whizzing round quick sufficient to flee the cluster’s gravity and fly off into intergalactic area. However in spite of this, the celebs proceed to orbit at breakneck velocity close to the cluster’s heart.”The perhaps rationalization [for this] is {that a} very large object is gravitationally pulling on those stars and maintaining them with reference to the [cluster’s] centre,” find out about lead writer Maximilian Häberle, a doctoral candidate on the Max Planck Institute for Astronomy (MPIA) in Germany, stated within the observation. “The one object that may be so large is a black hollow, with a mass no less than 8,200 occasions that of our solar.”Get the sector’s most enticing discoveries delivered directly on your inbox.Comparable: Essentially the most elusive black holes within the universe may lurk on the Milky Manner’s centerThe Milky Manner’s second-biggest black hollow? Researchers have narrowed down a most likely location for the IMBH. (Symbol credit score: ESA/Hubble & NASA, M. Häberle)Omega Centauri is an odd entity: It’s round 10 occasions better than maximum different globular clusters and is unusually flat. It’s so large that you’ll even see it with the bare eye on darkish, transparent nights, when it takes up nearly as a lot of the night time sky because the moon when seen from Earth.Researchers suspect that the cluster most likely was a dwarf galaxy that orbited the Milky Manner, ahead of being pulled into the galaxy’s center. In consequence, scientists have regularly puzzled if there can have been a large black hollow at its center.Researchers first proposed the theory of an IMBH in Omega Centauri in 2008, when Hubble published how tightly the cluster’s stars are bunched at its heart. On the other hand, on the time, different researchers argued that this may well be brought about by means of a swarm of a number of smaller, stellar-mass black holes.However the superfast stars highlighted within the new find out about point out the lifestyles of an IMBH, the find out about authors argue.”This discovery is probably the most direct proof thus far of an IMBH in Omega Centauri,” find out about co-author Nadine Neumayer, an astronomer at MPIA, stated within the observation. If showed, it will be the Milky Manner’s second-largest recognized black hollow in the back of Sagittarius A* — the supermassive black hollow on the center of our galaxy, she added. “That is thrilling as a result of there are simplest only a few different black holes recognized with a equivalent mass.”On the other hand, the presence of an IMBH in Omega Centauri isn’t showed, and extra knowledge is had to know for sure whether it is truly there. Additionally it is unclear precisely how massive the cosmic entity may well be and the place it’s.The researchers were granted time one day to make use of the robust James Webb House Telescope to look deeper into the cluster, this means that we would possibly not have to attend too lengthy for extra proof of the black hollow’s lifestyles.
Researchers have narrowed down a most likely location for the IMBH. (Symbol credit score: ESA/Hubble & NASA, M. Häberle)Omega Centauri is an odd entity: It’s round 10 occasions better than maximum different globular clusters and is unusually flat. It’s so large that you’ll even see it with the bare eye on darkish, transparent nights, when it takes up nearly as a lot of the night time sky because the moon when seen from Earth.Researchers suspect that the cluster most likely was a dwarf galaxy that orbited the Milky Manner, ahead of being pulled into the galaxy’s center. In consequence, scientists have regularly puzzled if there can have been a large black hollow at its center.Researchers first proposed the theory of an IMBH in Omega Centauri in 2008, when Hubble published how tightly the cluster’s stars are bunched at its heart. On the other hand, on the time, different researchers argued that this may well be brought about by means of a swarm of a number of smaller, stellar-mass black holes.However the superfast stars highlighted within the new find out about point out the lifestyles of an IMBH, the find out about authors argue.”This discovery is probably the most direct proof thus far of an IMBH in Omega Centauri,” find out about co-author Nadine Neumayer, an astronomer at MPIA, stated within the observation. If showed, it will be the Milky Manner’s second-largest recognized black hollow in the back of Sagittarius A* — the supermassive black hollow on the center of our galaxy, she added. “That is thrilling as a result of there are simplest only a few different black holes recognized with a equivalent mass.”On the other hand, the presence of an IMBH in Omega Centauri isn’t showed, and extra knowledge is had to know for sure whether it is truly there. Additionally it is unclear precisely how massive the cosmic entity may well be and the place it’s.The researchers were granted time one day to make use of the robust James Webb House Telescope to look deeper into the cluster, this means that we would possibly not have to attend too lengthy for extra proof of the black hollow’s lifestyles.