The neurons firing within the mind’s reminiscence middle as we sleep would possibly no longer simplest be revisiting previous reports. In keeping with a brand new find out about, they may be having a look in opposition to the longer term, rehearsing task that hasn’t took place but.
A workforce led through researchers from the College of Michigan analyzed mind wave readings from rats throughout occasions of wakefulness and occasions of sleep. Readings have been taken sooner than, throughout, and after the animals tackled maze demanding situations with a view to assessment the personal tastes of nerve cells whilst outdoor of the maze, reminiscent of throughout classes of relaxation.
“We addressed this problem through bearing on the task of every particular person neuron to the task of all of the different neurons,” says anesthesiologist Kamran Diba, from the College of Michigan.
“The power to trace the personal tastes of neurons even with out a stimulus used to be a very powerful step forward for us.”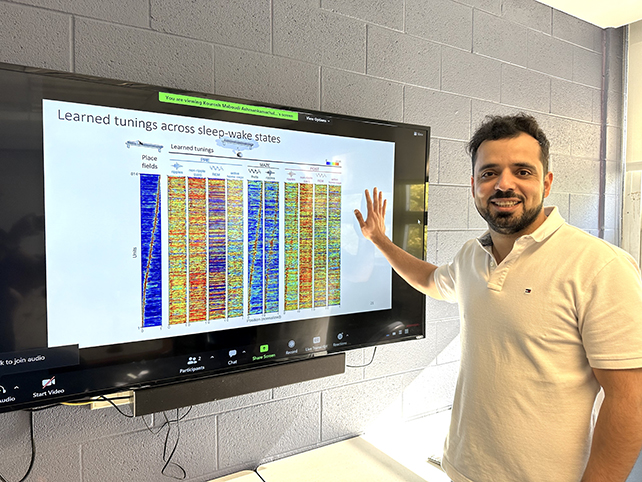 The researchers evolved a brand new solution to inspecting neuron task. (Kamran Diba)The brand new manner supposed that in addition to linking bodily areas within the maze with explicit neuron task in actual time, the workforce may just additionally paintings backwards and map neuron task to issues within the maze whilst the rats have been drowsing.
The researchers evolved a brand new solution to inspecting neuron task. (Kamran Diba)The brand new manner supposed that in addition to linking bodily areas within the maze with explicit neuron task in actual time, the workforce may just additionally paintings backwards and map neuron task to issues within the maze whilst the rats have been drowsing.
This used to be made imaginable via a system finding out procedure, weighing up the relationships of neurons with every different somewhat than taking into consideration them in isolation. In accordance with the neurons firing throughout sleep and alternatively throughout the following maze strive, the rats weren’t simply dreaming about puts they might already visited within the maze, but in addition operating on doable new routes.
Those are vital findings within the find out about of spatial tuning, the best way the task of explicit neurons pertains to explicit puts. This tuning is a dynamic procedure, and it sounds as if the sound asleep mind is concerned.
When the rats have been reintroduced to the maze after sound asleep, the neural task measured throughout their shut eye used to be to a point predictive of the brand new tactics they explored their setting. The suits were not actual, however they have been shut sufficient to trace at a courting between goals and long term intentions.
“We will be able to see those different adjustments going on throughout sleep, and after we put the animals again within the surroundings a 2d time, we will validate that those adjustments in reality do mirror one thing that used to be realized whilst the animals have been asleep,” says neuroscientist Caleb Kemere, from Rice College in the USA.
“It is as though the second one publicity to the gap in reality occurs whilst the animal is sound asleep.”
It is been neatly established that sleep is helping us shape reminiscences, and whilst this find out about simplest checked out rats, it is most likely that one thing an identical is occurring in human brains: a type of practice session for long term adventures.
The goings-on inside of our sound asleep brains proceed to fascinate – affecting the whole lot from the best way we learn how to how the mind is stored protected – and this newest find out about supplies a bit extra perception.
“It is not essentially the case that throughout sleep the one factor those neurons do is to stabilize a reminiscence of the enjoy,” says Kemere. “It seems some neurons finally end up doing one thing else.”The analysis has been printed in Nature.
Mind Cells Might If truth be told Attempt to Are expecting The Long term All the way through Sleep











/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25750031/STKS487_Antitrust_STK093_Google_D_1.jpg)
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25646628/STK485_STK414_AI_SAFETY_D.jpg)