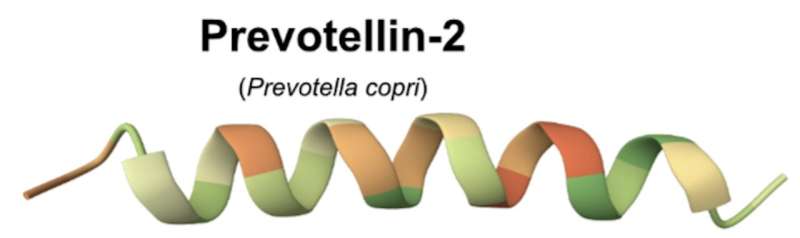
Prevotellin-2, an antibiotic came upon within the human intestine microbiome, demonstrated anti-infective functions on par with polymyxin B, an FDA-approved antibiotic used these days to regard multidrug-resistant infections, suggesting that the human intestine microbiome would possibly include antibiotics that may at some point to find scientific software. Credit score: Cesar de los angeles Fuente, Ami S. Bhatt
The common human intestine accommodates kind of 100 trillion microbes, lots of which can be continuously competing for restricted assets. “It is the sort of harsh atmosphere,” says César de los angeles Fuente, Presidential Assistant Professor in Bioengineering and in Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering inside the College of Engineering and Implemented Science, in Psychiatry and Microbiology inside the Perelman College of Drugs, and in Chemistry inside the College of Arts & Sciences.
“You will have these kinds of micro organism coexisting, but additionally preventing each and every different. Such an atmosphere would possibly foster innovation.”
In that war, de los angeles Fuente’s lab sees possible for brand spanking new antibiotics, which would possibly someday give a contribution to humanity’s personal defensive stockpile towards drug-resistant micro organism. Finally, if the micro organism within the human intestine must increase new gear within the struggle towards one every other to live on, why no longer use their very own guns towards them?
In a paper in Mobile, the labs of de los angeles Fuente and Ami S. Bhatt, Professor of Drugs (Hematology) and Genetics at Stanford, surveyed the intestine microbiomes of just about 2,000 folks, finding dozens of possible new antibiotics.
“We bring to mind biology as a knowledge supply,” says de los angeles Fuente. “The whole thing is solely code. And if we will get a hold of algorithms that may type via that code, we will dramatically boost up antibiotic discovery.”
In recent times, de los angeles Fuente’s lab has made headlines for locating antibiotic applicants all over, from the genetic knowledge of extinct creatures like Neanderthals and woolly mammoths to plenty of micro organism whose genetic subject material the lab analyzed the use of synthetic intelligence.
“One among our number one targets is to mine the sector’s organic knowledge as a supply of antibiotics and different helpful molecules,” says de los angeles Fuente.
“Quite than depending on conventional, painstaking strategies that contain amassing soil or water samples and purifying lively compounds, we harness the huge array of organic knowledge present in genomes, metagenomes and proteomes. This permits us to discover new antibiotics at virtual velocity.”
For the reason that micro organism evolve briefly, de los angeles Fuente and his co-authors hypothesized that an atmosphere that encourages pageant—just like the human intestine—may well be house to a large number of undiscovered antimicrobial compounds. “When there’s a loss of assets,” de los angeles Fuente issues out, “that is when biology in reality comes up with leading edge answers.”
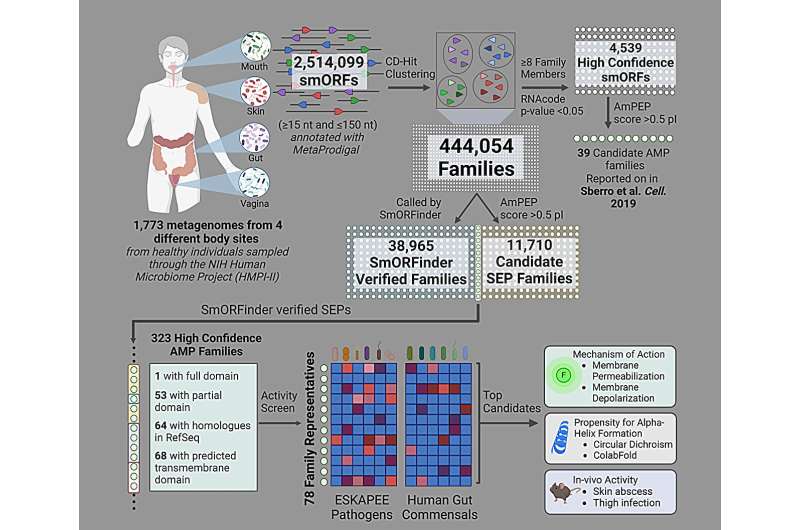
Penn Engineering and Stanford researchers used AI to lend a hand determine dozens of possible antibiotic applicants, via examining the genetic sequences in just about 2,000 other human intestine microbiomes. Credit score: Cesar de los angeles Fuente, Ami S. Bhatt
The gang all in favour of peptides, quick chains of amino acids, that have up to now proven promise as novel antibiotics.
“We computationally mined over 400,000 proteins,” de los angeles Fuente says, regarding the method wherein AI reads the letters of genetic code and, having been skilled on a collection of recognized antibiotics, predicts which genetic sequences would possibly have antimicrobial houses.
“Apparently, those molecules have a special composition from what has historically been regarded as antimicrobial,” says Marcelo D.T. Torres, a analysis affiliate within the de los angeles Fuente lab, and the paper’s first creator. “The compounds we now have came upon represent a brand new magnificence, and their distinctive houses will lend a hand us perceive and enlarge the collection house of antimicrobials.”
After all, the ones predictions will have to then be experimentally validated; after discovering a couple of hundred antibiotic applicants, the researchers decided on 78 to check towards precise micro organism.
After synthesizing those peptides, the researchers uncovered bacterial cultures to each and every peptide and waited 20 hours to look which peptides effectively inhibited bacterial enlargement. As well as, the crew later examined the antibiotic applicants in animal fashions.
Over part of the peptides examined labored—this is, they inhibited bacterial enlargement of both pleasant or pathogenic micro organism—and the lead candidate, prevotellin-2, demonstrated anti-infective functions on par with polymyxin B, an FDA-approved antibiotic used these days to regard multidrug-resistant infections, suggesting that the human intestine microbiome would possibly include antibiotics that may at some point to find scientific software.
“Figuring out prevotellin-2, which has actions on par with certainly one of our antibiotics of ultimate lodge, polymyxin B, used to be very sudden to me,” says Bhatt.
“This implies that mining the human microbiome for brand spanking new and thrilling categories of antimicrobial peptides is a promising trail ahead for researchers and docs, and maximum particularly for sufferers.”
Additional info:
Mining human microbiomes finds an untapped supply of peptide antibiotics, Mobile (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.mobile.2024.07.027. www.mobile.com/mobile/fulltext/S0092-8674(24)00802-X
Magazine knowledge:
Mobile
Supplied via
College of Pennsylvania
Quotation:
Mining the microbiome: Uncovering new antibiotics throughout the human intestine (2024, August 19)
retrieved 20 August 2024
from
This file is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal learn about or analysis, no
phase could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions handiest.










/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25750031/STKS487_Antitrust_STK093_Google_D_1.jpg)
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25646628/STK485_STK414_AI_SAFETY_D.jpg)