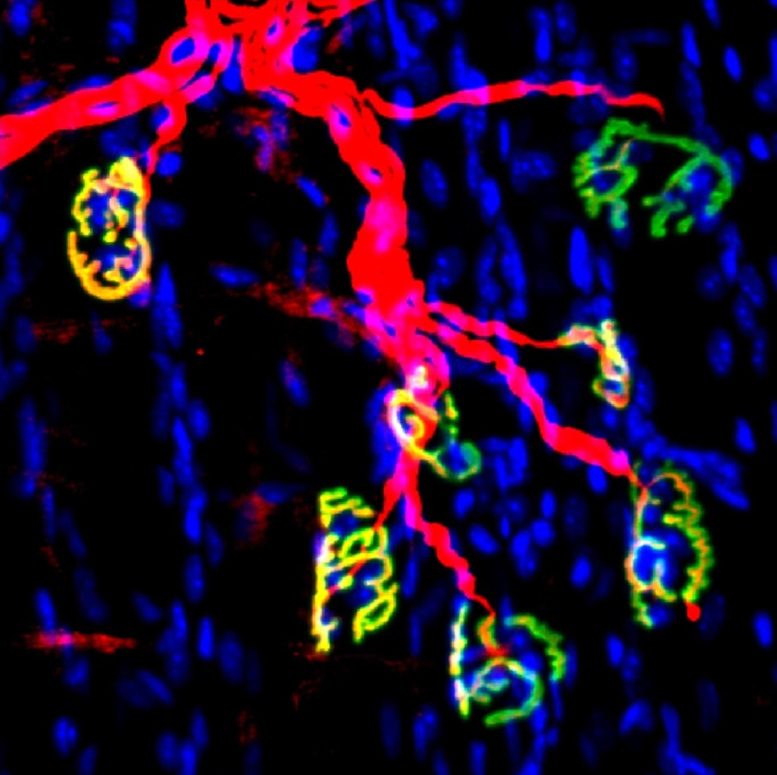
Mouse neuromuscular junctions: the motor nerve and synapses are in purple; the acetylcholine receptors of muscle fibers are in inexperienced. Credit score: Blau lab, Stanford College Faculty of MedicineScientists at Stanford College Faculty of Medication and Sanford Burnham Prebys have demonstrated a brand new technique to boost up restoration from peripheral nerve damage. They did this through focused on an enzyme that was once regarded as chargeable for muscle losing with growing old.Working out the Peripheral Anxious SystemDamage to the peripheral fearful device (the nerves that shape the communications community between the mind, spinal wire, and frame) is debilitating; the effectiveness of physiotherapy as remedy is proscribed. Whether or not from trauma, illness, or growing old, nerve serve as declines and/or is misplaced, leading to reduced energy or even paralysis.Fresh DiscoveriesIn the brand new learn about, just lately revealed within the magazine Science Translational Medication and co-authored through Helen M. Blau, Ph.D., the Donald E. and Delia B. Baxter Basis Professor at Stanford College Faculty of Medication, and Yu Xin Wang, Ph.D., assistant professor within the Construction, Getting old and Regeneration Program at Sanford Burnham Prebys, the analysis workforce discovered that an enzyme related to growing old is caused through the lack of innervation.Inhibiting this enzyme after nerve damage in a mouse fashion with a small molecule inhibitor promoted the regeneration of motor nerve and formation of neuromuscular synapses that led to sped up restoration of energy.“Our knowledge means that inhibiting the serve as of this actual enzyme, known as 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase or 15-PGDH, with a small molecule boosted a naturally going on compound (prostaglandin E2 or PGE2) in muscle mass that lend a hand repair nerve connectivity, serve as, and energy,” stated Wang.Results of DenervationWhen skeletal muscular tissues lose nerve serve as, a phenomenon known as denervation, they atrophy and weaken. Denervation may end up from bodily trauma, comparable to harm to nerves connecting muscular tissues to the spinal wire, or from heritable neuromuscular losing illnesses, comparable to amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Complex age too can result in critical muscle losing known as sarcopenia.Muscle denervation and its penalties impact as much as an estimated 5% of the U.S. inhabitants (roughly 17 million individuals) and lead to annual estimated nationwide healthcare prices of $380 billion.Significance of PGE2 and the Position of 15-PGDHWang was once part of Blau’s workforce at Stanford College, who had proven in earlier analysis that PGE2 in muscle mass is needed for muscle stem cells to proliferate and for muscular tissues to successfully regenerate and service after damage.The researchers have additionally discovered that 15-PGDH degrades PGE2 and that the enzyme accumulates with age. They have got dubbed 15-PGDH a gerozyme — an enzyme that determines muscle losing and which will increase with growing old.“We puzzled why this enzyme activates with age if it has this type of detrimental affect on muscle tissues and energy,” stated Wang.The brand new paintings concerned finding out younger mice the usage of surgical how one can fashion accidents to the sciatic nerve. Ranges of 15-PGDH rose within the denervated muscular tissues, however pharmacological inhibition of 15-PGDH promoted next motor axon enlargement, neuromuscular connectivity, and sooner restoration.In research of human tissues, the researchers detected aggregates of 15-PGDH in biopsies from a various vary of human neuromuscular illnesses, suggesting that inhibiting this enzyme might be really useful.“Restoring neuromuscular connectivity is a crucial step in treating those debilitating problems. This new way is sexy for the reason that remedy alerts the nerve to develop again,” stated Wang. “That’s why it has this type of profound impact at the muscle and energy.”Reference: “Regeneration of neuromuscular synapses after acute and protracted denervation through inhibiting the gerozyme 15-prostaglandin dehydrogenase” through Mohsen A. Bakooshli, Yu Xin Wang, Elena Monti, Shiqi Su, Peggy Kraft, Minas Nalbandian, Ludmila Alexandrova, Joshua R. Wheeler, Hannes Vogel and Helen M. Blau, 11 October 2023, Science Translational Medication.
Mouse neuromuscular junctions: the motor nerve and synapses are in purple; the acetylcholine receptors of muscle fibers are in inexperienced. Credit score: Blau lab, Stanford College Faculty of MedicineScientists at Stanford College Faculty of Medication and Sanford Burnham Prebys have demonstrated a brand new technique to boost up restoration from peripheral nerve damage. They did this through focused on an enzyme that was once regarded as chargeable for muscle losing with growing old.Working out the Peripheral Anxious SystemDamage to the peripheral fearful device (the nerves that shape the communications community between the mind, spinal wire, and frame) is debilitating; the effectiveness of physiotherapy as remedy is proscribed. Whether or not from trauma, illness, or growing old, nerve serve as declines and/or is misplaced, leading to reduced energy or even paralysis.Fresh DiscoveriesIn the brand new learn about, just lately revealed within the magazine Science Translational Medication and co-authored through Helen M. Blau, Ph.D., the Donald E. and Delia B. Baxter Basis Professor at Stanford College Faculty of Medication, and Yu Xin Wang, Ph.D., assistant professor within the Construction, Getting old and Regeneration Program at Sanford Burnham Prebys, the analysis workforce discovered that an enzyme related to growing old is caused through the lack of innervation.Inhibiting this enzyme after nerve damage in a mouse fashion with a small molecule inhibitor promoted the regeneration of motor nerve and formation of neuromuscular synapses that led to sped up restoration of energy.“Our knowledge means that inhibiting the serve as of this actual enzyme, known as 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase or 15-PGDH, with a small molecule boosted a naturally going on compound (prostaglandin E2 or PGE2) in muscle mass that lend a hand repair nerve connectivity, serve as, and energy,” stated Wang.Results of DenervationWhen skeletal muscular tissues lose nerve serve as, a phenomenon known as denervation, they atrophy and weaken. Denervation may end up from bodily trauma, comparable to harm to nerves connecting muscular tissues to the spinal wire, or from heritable neuromuscular losing illnesses, comparable to amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Complex age too can result in critical muscle losing known as sarcopenia.Muscle denervation and its penalties impact as much as an estimated 5% of the U.S. inhabitants (roughly 17 million individuals) and lead to annual estimated nationwide healthcare prices of $380 billion.Significance of PGE2 and the Position of 15-PGDHWang was once part of Blau’s workforce at Stanford College, who had proven in earlier analysis that PGE2 in muscle mass is needed for muscle stem cells to proliferate and for muscular tissues to successfully regenerate and service after damage.The researchers have additionally discovered that 15-PGDH degrades PGE2 and that the enzyme accumulates with age. They have got dubbed 15-PGDH a gerozyme — an enzyme that determines muscle losing and which will increase with growing old.“We puzzled why this enzyme activates with age if it has this type of detrimental affect on muscle tissues and energy,” stated Wang.The brand new paintings concerned finding out younger mice the usage of surgical how one can fashion accidents to the sciatic nerve. Ranges of 15-PGDH rose within the denervated muscular tissues, however pharmacological inhibition of 15-PGDH promoted next motor axon enlargement, neuromuscular connectivity, and sooner restoration.In research of human tissues, the researchers detected aggregates of 15-PGDH in biopsies from a various vary of human neuromuscular illnesses, suggesting that inhibiting this enzyme might be really useful.“Restoring neuromuscular connectivity is a crucial step in treating those debilitating problems. This new way is sexy for the reason that remedy alerts the nerve to develop again,” stated Wang. “That’s why it has this type of profound impact at the muscle and energy.”Reference: “Regeneration of neuromuscular synapses after acute and protracted denervation through inhibiting the gerozyme 15-prostaglandin dehydrogenase” through Mohsen A. Bakooshli, Yu Xin Wang, Elena Monti, Shiqi Su, Peggy Kraft, Minas Nalbandian, Ludmila Alexandrova, Joshua R. Wheeler, Hannes Vogel and Helen M. Blau, 11 October 2023, Science Translational Medication.
DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.adg1485Additional authors at the learn about come with Mohsen A. Bakooshli, Elena Monti, Shiqi Su, Peggy Kraft, Minas Nalbandian, Ludmila Alexandrova, Joshua R. Wheeler and Hannes Vogel, all at Stanford College.This learn about was once supported through the Nationwide Institutes of Well being Shared Instrumentation Grant (S100D026962); the Canadian Institutes of Well being (MFE-152457); Stanford Translational Analysis and Implemented Medication Pilot grant; Nationwide Institutes of Well being (K99NS120278, R00NS120278, R01-AG020961, R01-AG069858, R01-G009674), Stanford Dean of Analysis—SUMS Seed Grant Program; Donald E. and Delia B. Baxter Basis; the Li Ka Shing Basis; Milky Manner Analysis Basis (MWRF-21664), California Institute for Regenerative Medication (DISC2-10604).
Miracle Regrowth: How Preventing an Getting old Enzyme Can Restore Nerve Injury