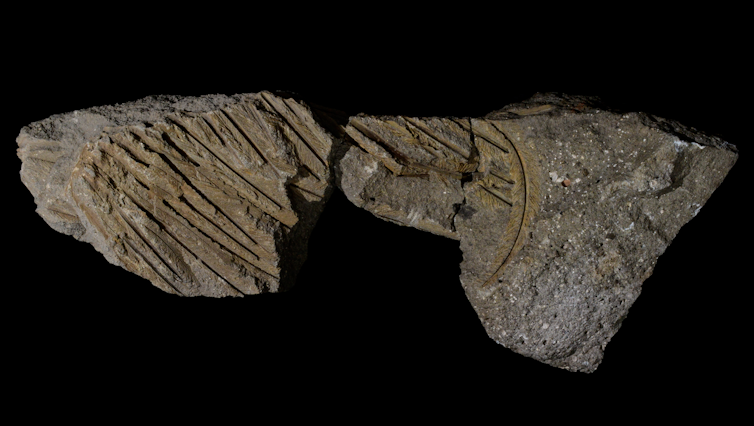
As bones encased in rock rotted away, water-borne silica seeped into the crevices, solidifying into opal and keeping treasured main points for 100 million years. The ensuing fossils now supply proof that there actually will have been an Age of Monotremes, prior to different mammals got here to dominate.
“It is like finding a complete new civilization,” says Australian Museum paleontologist Tim Flannery.
“Lately, Australia is referred to as a land of marsupials, however finding those new fossils is the primary indication that Australia used to be up to now house to a variety of monotremes.”
Simplest 5 of those uncommon mammals nonetheless hang to lifestyles: one platypus and 4 echidna species, shared between Australia and Papua New Guinea. However because of their reptilian-like egg-laying characteristic, it has lengthy been idea those animals developed prior to placental mammals like us and marsupials.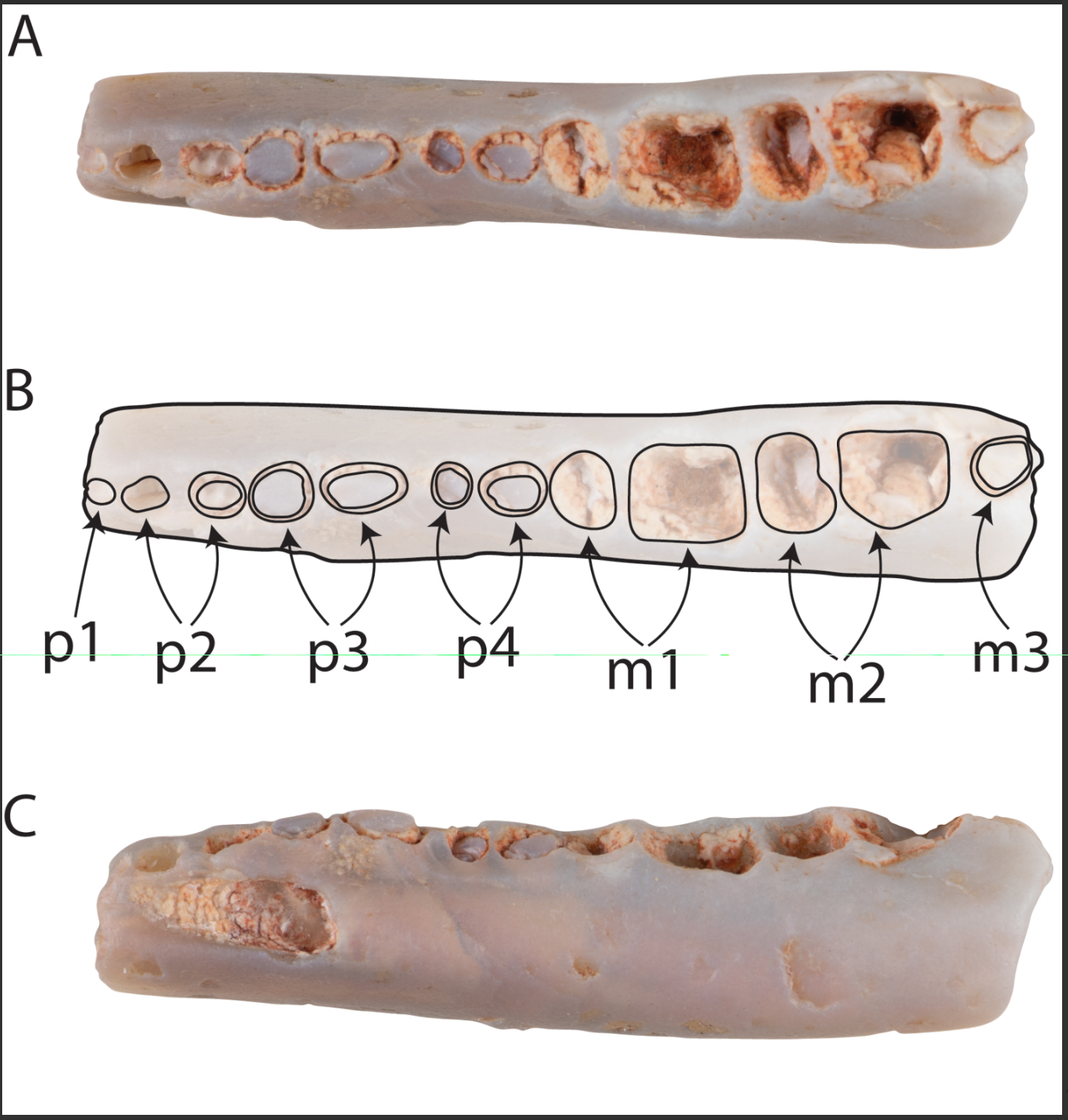 Opalized fossil of Dharragarra aurora. (Flannery, et al., Alcheringa: An Australasian Magazine of Palaeontology, 2024)”It can be guessed that, anywhere they originated, monotremes radiated in Australia prior to marsupials did, and that the outdated Australian monotreme fauna will have been a minimum of as various because the later marsupial fauna… ” naturalist Philip Jackson Darlington speculated again in 1957.
Opalized fossil of Dharragarra aurora. (Flannery, et al., Alcheringa: An Australasian Magazine of Palaeontology, 2024)”It can be guessed that, anywhere they originated, monotremes radiated in Australia prior to marsupials did, and that the outdated Australian monotreme fauna will have been a minimum of as various because the later marsupial fauna… ” naturalist Philip Jackson Darlington speculated again in 1957.
Whilst this concept is extensively authorised, fossil proof has remained scarce.
Now, 3 newly found out monotremes deliver the overall of fossil species recognized on this one position and time frame to 6, proving there actually used to be some variety amongst those hairy egg-layers. The brand new reveals vary from the scale of a small possum to that of a cat, Flannery advised James Woodford at New Scientist.
Australia’s Lightning Ridge in northeastern New South Wales, the place the fossils had been discovered, now has essentially the most various vary of monotreme fossils on document, all from the Cenomanian length between kind of 100 and 95 million years in the past.
“4 species are recognized from a unmarried specimen, suggesting that variety stays underrepresented. This discovery provides greater than 20 p.c to the up to now recognized variety of monotremes,” says Australian Museum paleontologist Matthew McCurry.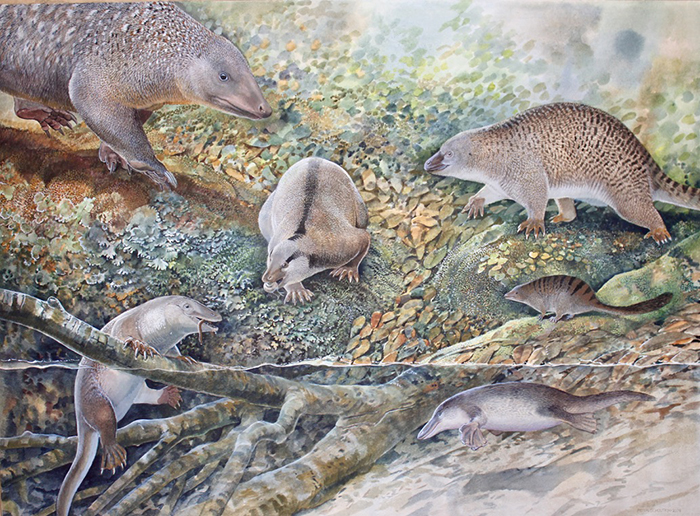 Clockwise from decrease left: Opalios splendens, Stirtodon elizabethae, Kollikodon ritchiei, Steropodon galmani, Parvopalus clytiei and Dharragarra aurora. (Peter Shouten)Some of the new fossils is the toothy ‘echidnapus’ (Opalios splendens), who, as its nickname suggests, stocks traits of each echidnas and platypuses. It has the lengthy slim snout of an echidna but in addition some options of a platypus, like advanced electroreception.
Clockwise from decrease left: Opalios splendens, Stirtodon elizabethae, Kollikodon ritchiei, Steropodon galmani, Parvopalus clytiei and Dharragarra aurora. (Peter Shouten)Some of the new fossils is the toothy ‘echidnapus’ (Opalios splendens), who, as its nickname suggests, stocks traits of each echidnas and platypuses. It has the lengthy slim snout of an echidna but in addition some options of a platypus, like advanced electroreception.
“The tale of ways our egg-laying mammals developed is ‘toothy to toothless’,” describes Australian Museum mammologist Kris Helgen.
“The oldest monotreme, Teinolophos trusleri, which dates again to Victoria 130 million years in the past, had 5 molars in each and every jaw. What we see at Lightning Ridge is that via 100 million years in the past, one of the vital monotremes nonetheless have 5 molars however a few of them are down to a few.”
Trendy echidnas haven’t any enamel and platypuses lose theirs prior to they totally mature.
Flannery and co-workers additionally describe the tiniest recognized monotreme, Parvopalus clytiei, and Dharragarra aurora, which has a identical jaw to trendy platypuses, of their new paper. Those sign up for the 3 up to now found out historic Lightning Ridge monotremes: Kollikodon ritchiei, Steropodon galmani, and Stirtodon elizabethae, the biggest recognized monotreme.
To this point researchers have discovered no different indicators of mammals from this era, suggesting that monotremes actually will have been on my own among the dinosaurs of that technology. Then again, a extra intensive fossil assemblage that comes with different websites shall be had to ascertain this concept.This analysis used to be revealed in Alcheringa: An Australasian Magazine of Palaeontology.
Misplaced Age of Monotremes Printed via Fossils From 100 Million Years In the past













