Abstract: A brand new find out about in worms unearths a core set of insoluble proteins connected to each growing old and Alzheimer’s illness. Those proteins acquire all the way through standard growing old and are exacerbated by way of amyloid beta, an indicator of Alzheimer’s. Boosting mitochondrial well being with a herbal compound reversed the poisonous results of protein clumping, highlighting the significance of mitochondria in preventing age-related illnesses.Key Information:A core set of insoluble proteins is connected to each growing old and Alzheimer’s.Amyloid beta exacerbates protein clumping, making a vicious cycle of decline.Boosting mitochondrial well being can opposite the poisonous results of protein clumping.Supply: Dollar InstituteIt has lengthy been identified {that a} hallmark of Alzheimer’s illness, and maximum different neurodegenerative illnesses, is the clumping in combination of insoluble protein aggregates within the mind. All over standard disease-free growing old, there may be an accumulation of insoluble proteins.So far, approaches to remedies for Alzheimer’s illness have now not addressed the contribution of protein insolubility as a common phenomenon, as a substitute specializing in one or two insoluble proteins. 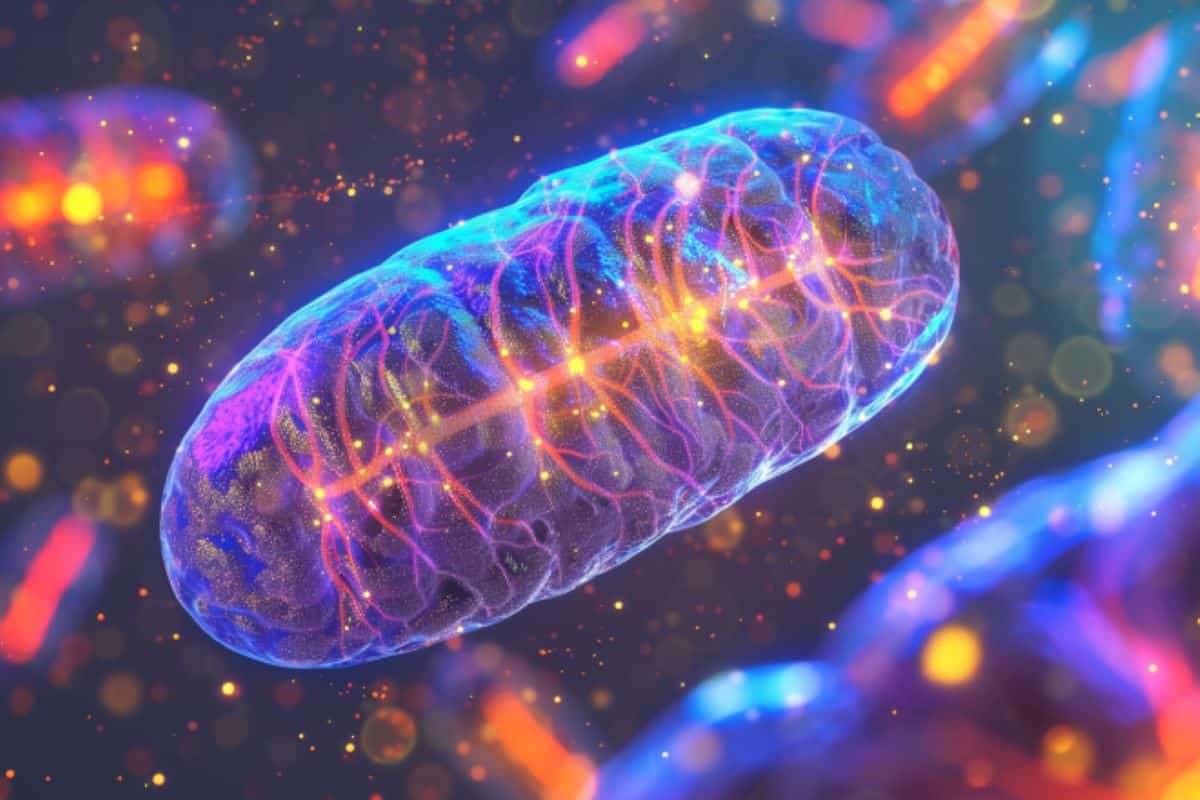 A takeaway, the authors say, is the reminder that the well being of mitochondria is significant to general well being. Credit score: Neuroscience NewsBuck researchers have lately finished a scientific find out about in worms that paints an intricate image of the connections between insoluble proteins in neurodegenerative illnesses and growing old.Moreover, the paintings demonstrated an intervention that might opposite the poisonous results of the aggregates by way of boosting mitochondrial well being.“In keeping with our discoveries, concentrated on insoluble proteins may supply a technique for the prevention and remedy of a number of age-related illnesses,” mentioned Edward Anderton, PhD, a postdoctoral fellow in Gordon Lithgow’s lab and co-first writer of a find out about that looks within the Might 16 factor of the magazine GeroScience.“Our find out about displays how keeping up wholesome mitochondria can battle protein clumping connected to each growing old and Alzheimer’s,” mentioned Manish Chamoli, PhD, a analysis scientist in Gordon Lithgow’s and Julie Andersen’s lab, and co-first writer of the find out about. “Through boosting mitochondrial well being, we will probably decelerate or opposite those destructive results, providing new techniques to regard each growing old and age-related illnesses.”Effects improve the geroscience hypothesisThe sturdy hyperlink between insoluble proteins selling standard growing old and illnesses additionally builds a case for the larger image of ways growing old and age-related illnesses happen. “We’d argue that this paintings truly helps the geroscience speculation that there’s a commonplace pathway to Alzheimer’s illness and growing old itself,” mentioned Dollar Professor Gordon Lithgow. PhD, Vice President of Instructional Affairs and the senior writer of the find out about.“Getting old is riding the illness, however the elements that put you at the monitor towards the illness if truth be told happen very early.”The truth that the workforce discovered a core insoluble proteome enriched with a large number of proteins that had now not been thought to be ahead of creates new goals for exploration, mentioned Lithgow. “In many ways it raises the flag about whether or not we must be occupied with what Alzheimer’s looks as if in very younger other folks,” he mentioned.Past amyloid and tauThe center of attention of maximum analysis on Alzheimer’s illness to this point has been concentrated on accumulations of 2 proteins: amyloid beta and tau. However there are if truth be told 1000’s of different proteins in those insoluble aggregations, mentioned Anderton, and their function in Alzheimer’s illness used to be unknown.Moreover, he added, their lab and others’ have seen that all the way through the standard disease-free growing old procedure there may be an accumulation of insoluble proteins. Those insoluble proteins from elderly animals, when blended with amyloid beta within the check tube, boost up the aggregation of the amyloid.What used to be the relationship between the buildup aggregates Alzheimer’s and disease-free growing old, the workforce questioned. That specialize in the amyloid beta protein, they used a pressure of the microscopic trojan horse Caenorhabditis elegans, lengthy been utilized in growing old research, that has been engineered to provide human amyloid protein.Anderton mentioned the workforce suspected they could see that amyloid beta is riding some stage of insolubility in different proteins.“What we discovered is that amyloid beta reasons an enormous quantity of insolubility, even in an excessively younger animal,” mentioned Anderton. They discovered that there’s a subset of proteins that appear to be very at risk of turning into insoluble, both by way of including amyloid beta or all the way through the standard growing old procedure. They known as that prone subset the “core insoluble proteome”.The workforce went directly to show that the core insoluble proteome is stuffed with proteins that experience already been connected to other neurodegenerative illnesses along with Alzheimer’s illness, together with Parkinson’s illness, Huntington’s illness and prion illness.“Our paper displays that amyloid may well be performing as a motive force of this standard growing old aggregation,” mentioned Anderton.“Now we’ve were given transparent proof, I feel for the primary time, that each amyloid and growing old are affecting the similar proteins in a similar fashion. It’s fairly perhaps a vicious cycle the place growing old is riding insolubility and amyloid beta may be riding insolubility, they usually’re simply making each and every different worse.”The amyloid protein may be very poisonous to the worms and the workforce sought after to have the ability to opposite that toxicity.“Since masses of mitochondrial proteins turn into insoluble each all the way through growing old and after expressing amyloid beta, we concept if we will spice up the mitochondrial protein high quality the use of a compound, then perhaps we will opposite one of the unwanted side effects of amyloid beta,” mentioned Anderton.That’s precisely what they discovered, the use of Urolithin A, a herbal intestine metabolite produced once we devour raspberries, walnuts, and pomegranates which is understood to support mitochondrial serve as: it considerably not on time the poisonous results of amyloid beta.“One thing that used to be obviously glaring from our dataset is that the significance of mitochondria assists in keeping arising,” mentioned Anderton. A takeaway, the authors say, is the reminder that the well being of mitochondria is significant to general well being. “Mitochondria have a powerful hyperlink with growing old. They’ve were given a powerful hyperlink with amyloid beta,” he mentioned. “I feel ours is likely one of the few research that displays that insolubility and aggregation of the ones proteins could be the hyperlink between the 2.”“For the reason that mitochondria are so central to all of this, one method to smash the vicious cycle of decline is to interchange broken mitochondria with new mitochondria,” mentioned Lithgow. “And the way do you do this? You workout and apply a nutritious diet.”Different Dollar researchers concerned within the find out about come with Dipa Bhaumik, Christina D. King, Xueshu Xie, Anna Foulger, Julie Okay. Andersen, and Birgit Schilling.Investment: This paintings used to be supported partly via price range from the Nationwide Institute on Getting old (NIA RF1AG057358 NIA U01AG045844), a Nationwide Institutes of Well being shared instrumentation grant, and the Larry L. Hillblom Scientific Basis.About this Alzheimer’s illness, genetics, and growing old analysis newsAuthor: Kris Rebillot
A takeaway, the authors say, is the reminder that the well being of mitochondria is significant to general well being. Credit score: Neuroscience NewsBuck researchers have lately finished a scientific find out about in worms that paints an intricate image of the connections between insoluble proteins in neurodegenerative illnesses and growing old.Moreover, the paintings demonstrated an intervention that might opposite the poisonous results of the aggregates by way of boosting mitochondrial well being.“In keeping with our discoveries, concentrated on insoluble proteins may supply a technique for the prevention and remedy of a number of age-related illnesses,” mentioned Edward Anderton, PhD, a postdoctoral fellow in Gordon Lithgow’s lab and co-first writer of a find out about that looks within the Might 16 factor of the magazine GeroScience.“Our find out about displays how keeping up wholesome mitochondria can battle protein clumping connected to each growing old and Alzheimer’s,” mentioned Manish Chamoli, PhD, a analysis scientist in Gordon Lithgow’s and Julie Andersen’s lab, and co-first writer of the find out about. “Through boosting mitochondrial well being, we will probably decelerate or opposite those destructive results, providing new techniques to regard each growing old and age-related illnesses.”Effects improve the geroscience hypothesisThe sturdy hyperlink between insoluble proteins selling standard growing old and illnesses additionally builds a case for the larger image of ways growing old and age-related illnesses happen. “We’d argue that this paintings truly helps the geroscience speculation that there’s a commonplace pathway to Alzheimer’s illness and growing old itself,” mentioned Dollar Professor Gordon Lithgow. PhD, Vice President of Instructional Affairs and the senior writer of the find out about.“Getting old is riding the illness, however the elements that put you at the monitor towards the illness if truth be told happen very early.”The truth that the workforce discovered a core insoluble proteome enriched with a large number of proteins that had now not been thought to be ahead of creates new goals for exploration, mentioned Lithgow. “In many ways it raises the flag about whether or not we must be occupied with what Alzheimer’s looks as if in very younger other folks,” he mentioned.Past amyloid and tauThe center of attention of maximum analysis on Alzheimer’s illness to this point has been concentrated on accumulations of 2 proteins: amyloid beta and tau. However there are if truth be told 1000’s of different proteins in those insoluble aggregations, mentioned Anderton, and their function in Alzheimer’s illness used to be unknown.Moreover, he added, their lab and others’ have seen that all the way through the standard disease-free growing old procedure there may be an accumulation of insoluble proteins. Those insoluble proteins from elderly animals, when blended with amyloid beta within the check tube, boost up the aggregation of the amyloid.What used to be the relationship between the buildup aggregates Alzheimer’s and disease-free growing old, the workforce questioned. That specialize in the amyloid beta protein, they used a pressure of the microscopic trojan horse Caenorhabditis elegans, lengthy been utilized in growing old research, that has been engineered to provide human amyloid protein.Anderton mentioned the workforce suspected they could see that amyloid beta is riding some stage of insolubility in different proteins.“What we discovered is that amyloid beta reasons an enormous quantity of insolubility, even in an excessively younger animal,” mentioned Anderton. They discovered that there’s a subset of proteins that appear to be very at risk of turning into insoluble, both by way of including amyloid beta or all the way through the standard growing old procedure. They known as that prone subset the “core insoluble proteome”.The workforce went directly to show that the core insoluble proteome is stuffed with proteins that experience already been connected to other neurodegenerative illnesses along with Alzheimer’s illness, together with Parkinson’s illness, Huntington’s illness and prion illness.“Our paper displays that amyloid may well be performing as a motive force of this standard growing old aggregation,” mentioned Anderton.“Now we’ve were given transparent proof, I feel for the primary time, that each amyloid and growing old are affecting the similar proteins in a similar fashion. It’s fairly perhaps a vicious cycle the place growing old is riding insolubility and amyloid beta may be riding insolubility, they usually’re simply making each and every different worse.”The amyloid protein may be very poisonous to the worms and the workforce sought after to have the ability to opposite that toxicity.“Since masses of mitochondrial proteins turn into insoluble each all the way through growing old and after expressing amyloid beta, we concept if we will spice up the mitochondrial protein high quality the use of a compound, then perhaps we will opposite one of the unwanted side effects of amyloid beta,” mentioned Anderton.That’s precisely what they discovered, the use of Urolithin A, a herbal intestine metabolite produced once we devour raspberries, walnuts, and pomegranates which is understood to support mitochondrial serve as: it considerably not on time the poisonous results of amyloid beta.“One thing that used to be obviously glaring from our dataset is that the significance of mitochondria assists in keeping arising,” mentioned Anderton. A takeaway, the authors say, is the reminder that the well being of mitochondria is significant to general well being. “Mitochondria have a powerful hyperlink with growing old. They’ve were given a powerful hyperlink with amyloid beta,” he mentioned. “I feel ours is likely one of the few research that displays that insolubility and aggregation of the ones proteins could be the hyperlink between the 2.”“For the reason that mitochondria are so central to all of this, one method to smash the vicious cycle of decline is to interchange broken mitochondria with new mitochondria,” mentioned Lithgow. “And the way do you do this? You workout and apply a nutritious diet.”Different Dollar researchers concerned within the find out about come with Dipa Bhaumik, Christina D. King, Xueshu Xie, Anna Foulger, Julie Okay. Andersen, and Birgit Schilling.Investment: This paintings used to be supported partly via price range from the Nationwide Institute on Getting old (NIA RF1AG057358 NIA U01AG045844), a Nationwide Institutes of Well being shared instrumentation grant, and the Larry L. Hillblom Scientific Basis.About this Alzheimer’s illness, genetics, and growing old analysis newsAuthor: Kris Rebillot
Supply: Beck Institute
Touch: Kris Rebillot – Beck Institute
Symbol: The picture is credited to Neuroscience NewsOriginal Analysis: Open get right of entry to.
“Amyloid β speeds up age-related proteome-wide protein insolubility” by way of Edward Anderton et al. GeroScienceAbstractAmyloid β speeds up age-related proteome-wide protein insolubilityLoss of proteostasis is a extremely conserved characteristic of growing old throughout style organisms and leads to the buildup of insoluble protein aggregates.Protein insolubility may be a unifying characteristic of primary age-related neurodegenerative illnesses, together with Alzheimer’s Illness (AD), during which masses of insoluble proteins go together with aggregated amyloid beta (Aβ) in senile plaques.In spite of the relationship between growing old and AD possibility, healing approaches to this point have lost sight of aging-driven generalized protein insolubility as a contributing issue. Alternatively, proteins that turn into insoluble all the way through growing old in style organisms are able to accelerating Aβ aggregation in vitro and lifespan in vivo.Right here, the use of an impartial proteomics way, we puzzled the connection between Aβ and age-related protein insolubility.In particular, we exposed that Aβ expression drives proteome-wide protein insolubility in C. elegans, even in younger animals, and this insoluble proteome is very very similar to the insoluble proteome pushed by way of standard growing old, this prone sub-proteome we time period the core insoluble proteome (CIP).We display that the CIP is enriched with proteins that fluctuate Aβ toxicity in vivo, suggesting the potential for a vicious feedforward cycle within the context of AD.Importantly, the use of human genome-wide affiliation research (GWAS), we display that the CIP is replete with organic processes implicated now not best in neurodegenerative illnesses but in addition throughout a large array of continual, age-related illnesses (CARDs).This offers suggestive proof that age-related lack of proteostasis may play a task typically CARD possibility.In the end, we display that the geroprotective, gut-derived metabolite, Urolithin A, relieves Aβ toxicity, supporting its use in scientific trials for dementia and age-related illnesses.
Mitochondrial Spice up Reverses Protein Clumping in Getting old and Alzheimer's – Neuroscience Information