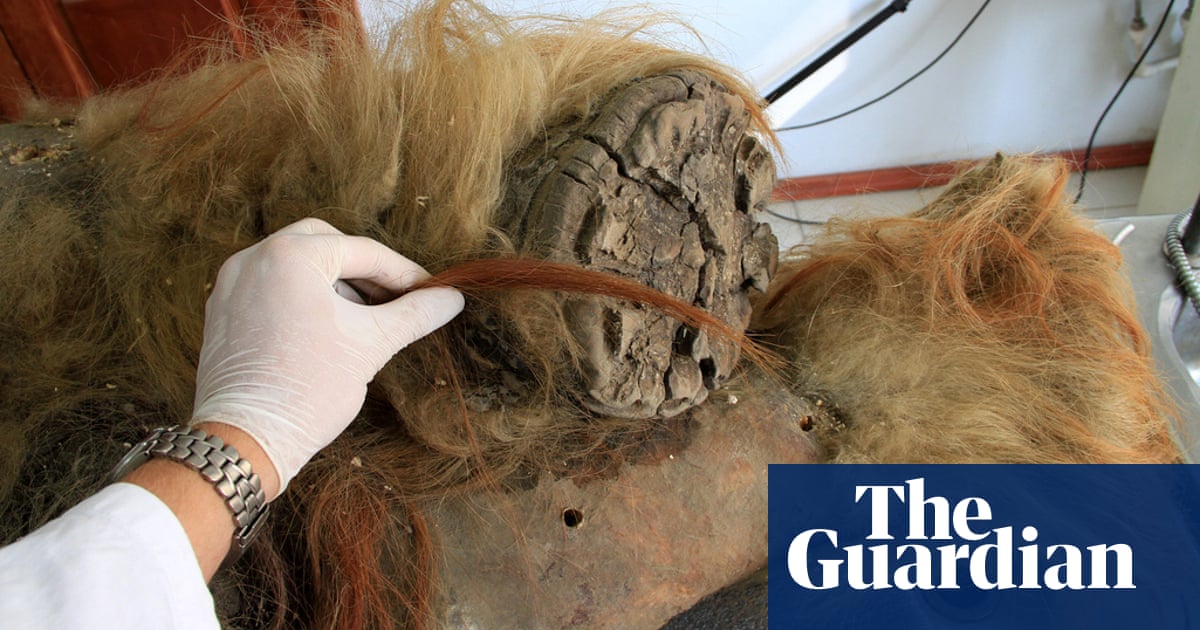
Researchers have reconstructed the genetic code of the woolly mammoth in exceptional element after finding fossilised chromosomes within the pores and skin of a 52,000-year-old carcass preserved within the Siberian permafrost.The mammoth’s lavish mane led researchers to call it after Chris Waddle, the mulleted former England footballer. It turned into freeze-dried on dying, a procedure that preserved the 3-d construction of the chromosomes within the animal’s pores and skin.Armed with the traditional genetic subject matter, scientists had been in a position to collect the mammoth genome, decide that it had 28 pairs of chromosomes, and notice genes that had been switched on or off, main points which might be the most important for figuring out what it intended to be a mammoth.Prof Erez Lieberman Aiden, the director of the Middle for Genome Structure at Baylor School of Drugs in Houston, mentioned the samples had been “a brand new roughly fossil” that “preserved biomolecules for huge sessions of time” and contained way more knowledge than the ones studied prior to.Dr Olga Dudchenko, additionally at Baylor, mentioned the invention of fossil chromosomes used to be a “gamechanger” as a result of understanding the form of an organism’s chromosomes made it conceivable to collect all of the DNA series of an extinct creature, offering insights into their biology that had been up to now out of succeed in.The scientists consider the animal’s pores and skin spontaneously freeze-dried in a while after dying. {Photograph}: Love Dalén/Stockholm UniversityThe world crew of researchers examined dozens of samples over 5 years prior to putting gold with a work of pores and skin taken from at the back of the ear of a mammoth excavated in northern Siberia in 2018. They consider the animal’s pores and skin spontaneously freeze-dried in a while after dying, keeping the tissue thru a an identical procedure used to make red meat jerky.The mammoth used to be referred to as Chris Waddle when scientists getting better the carcass spotted its spectacular mane. “It’s now not transparent that it’s precisely the hairdo the mammoth had whilst it used to be alive,” mentioned Dudchenko. “And it later grew to become out that the mammoth used to be feminine.”Research of the outside published the 3-d construction of the mammoth’s chromosomes used to be preserved within the dehydrated cells after being became a powerful glass-like subject matter. As soon as shaped the fossil samples, labelled chromoglass, may bear for thousands and thousands of years, the researchers wrote within the magazine Mobile. In a sequence of ordinary exams, the researchers confirmed that the DNA may live on in tissues run over through a automobile, hit with a baseball or blasted from a shot gun.Till now, historical DNA recovered from extinct species has been extremely fragmented. The snippets permit scientists to identify small-scale genetic variations between extinct animals and their dwelling kin, however little extra. In contrast, the brand new samples comprise loads of thousands and thousands of letters of code, revealing the large-scale construction of the genome.Past having the ability to compile the mammoth’s genome and rely its chromosomes, the scientists discovered that the association of chromosomes within the cells confirmed which genes had been activated, together with genes connected to woolliness and chilly tolerance.The paintings boosts plans to convey again the woolly mammoth, a feat researchers hope to reach through rewriting the genome of an Asian elephant to compare that of a mammoth. “Is it enough for de-extinction? Most probably now not,” mentioned Prof Marc Marti-Renom on the Nationwide Centre for Genomic Research in Barcelona. “There’s reasonably a bit of of labor nonetheless to be finished if somebody needs to grow to be a contemporary elephant right into a mammoth. It’s one step ahead in that path.”The researchers are hoping to search out extra fossil chromosomes in different extinct animals and in Egyptian mummies, lots of which might exist already in museum collections.Prof Adrian Lister, a mammoth professional on the Herbal Historical past Museum who used to be now not concerned within the find out about, referred to as the analysis “astonishing”.“Historical DNA analysis has, till now, trusted a ‘soup’ of small fragments of DNA extracted from historical tissues,” he mentioned. “The researchers were in a position, relating to this mammoth carcass preserved in arctic permafrost, to retrieve intact chromosomes with their DNA, and the chromatin protein crucial to their serve as, intact.”He added: “This new paintings opens up main new chances of exploring the biology of extinct species. This outstanding preservation may well be present in fossils a lot older than the 51,000-year-old mammoth, again to two million years in the past, opening the chance to analyze the biology of a lot older extinct species and their dating to and variations from dwelling kin.”
Mulleted mammoth referred to as Chris Waddle is helping scientists crack creatures’ genetic code











)