Muscle fibers are multiscale cushy, rainy, energetic engines. Credit score: Nature Physics (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41567-024-02540-x
The go with the flow of water inside of a muscle fiber might dictate how temporarily muscle can contract, in line with a College of Michigan find out about.
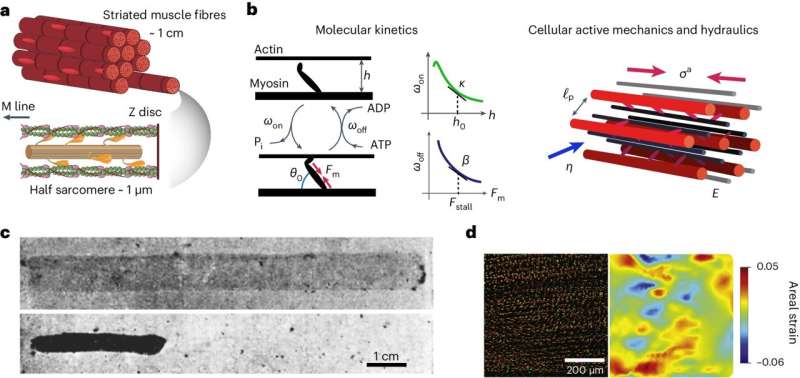
Just about all animals use muscle to transport, and it is been identified for a very long time that muscle, like every different cells, consists of about 70% water. However researchers have no idea what units the variety and higher limits of muscle efficiency. Earlier analysis into how muscle works centered simplest on the way it labored on a molecular degree reasonably than how muscle fibers are formed, that they’re three-d and are stuffed with fluid.
U-M physicist Suraj Shankar along side L. Mahadevan, a professor of physics at Harvard College, created a theoretical style of water’s function in muscle contraction and located that how fluid strikes thru a muscle fiber determines how temporarily a muscle fiber can contract.
In addition they discovered that muscle reveals a brand new more or less elasticity referred to as ordinary elasticity that permits muscle to generate energy the use of 3 dimensional deformations, proven in a commonplace commentary that after a muscle fiber contracts lengthwise, it additionally bulges perpendicularly. Their effects are printed within the magazine Nature Physics.
“Our effects counsel that even such fundamental questions as how temporarily muscle can contract or what number of techniques muscle can generate energy have new and surprising solutions when one takes a extra built-in and holistic view of muscle as a posh and hierarchically arranged subject material reasonably than only a bag of molecules,” Shankar mentioned. “Muscle is greater than the sum of its portions.”
The researchers envision every muscle fiber as a self-squeezing energetic sponge, a water-filled, sponge-like subject material that may contract and squeeze itself throughout the motion of molecular motors, he says.
“Muscle fibers are composed of many parts, akin to quite a lot of proteins, cellular nuclei, organelles akin to mitochondria, and molecular motors akin to myosin that convert chemical gas into movement and force muscle contraction,” Shankar mentioned. “All of those parts shape a porous community this is bathed in water. So a suitable, coarse-grained description for muscle is that of an energetic sponge.”
However the squeezing procedure takes time to transport water round, so the researchers suspected that this motion of water throughout the muscle fiber set an higher prohibit on how impulsively a muscle fiber can twitch.
To check their idea, they modeled muscle actions in more than one organisms throughout mammals, bugs, birds, fish and reptiles, that specialize in animals that use muscle tissues for terribly rapid motions. They discovered that muscle tissues that produce sound, such because the rattle in a rattlesnake’s tail, that may contract ten to masses of occasions according to 2d generally do not depend on fluid flows. As an alternative, those contractions are managed by means of the fearful device and are extra strongly dictated by means of molecular houses, or the time it takes for molecular motors inside of cells to bind and generate forces.
However in smaller organisms, akin to flying bugs who’re beating their wings a couple of hundred to one thousand occasions according to 2d, those contractions are too rapid for neurons to at once keep watch over. Right here fluid flows are extra necessary.
“In those instances, we discovered that fluid flows inside the muscle fiber are necessary and our mechanism of energetic hydraulics is prone to prohibit the quickest charges of contraction,” Shankar mentioned. “Some bugs akin to mosquitos appear to be with reference to our theoretically predicted prohibit, however direct experimental trying out is had to take a look at and problem our predictions.”
The researchers additionally discovered that after muscle fibers act as an energetic sponge, the method additionally reasons the muscle tissues to behave as an energetic elastic engine. When one thing is elastic, akin to a rubber band, it shops power because it tries to withstand deformation. Consider maintaining a rubber band between two arms and pulling it again.
While you unlock the rubber band, the band additionally releases the power saved when it used to be being stretched. On this case, power is conserved—a fundamental legislation of physics that dictates that the quantity of power inside of a closed device must stay the similar through the years.
But if muscle converts chemical gas into mechanical paintings, it could possibly produce power like an engine, violating the legislation of the conservation of power. On this case, muscle displays a brand new belongings referred to as “ordinary elasticity,” the place its reaction when squashed in a single course as opposed to some other isn’t mutual.
In contrast to the rubber band, when muscle contracts and relaxes alongside its period, it additionally bulges out perpendicularly, and its power does now not keep the similar. This permits muscle fibers to generate energy from repetitive deformations, behaving as a cushy engine.
“Those effects are by contrast to prevailing concept, which specializes in molecular main points and neglects the truth that muscle tissues are lengthy and filamentous, are hydrated, and feature processes on more than one scales,” Shankar mentioned.
“All in combination, our effects counsel a revised view of the way muscle purposes is very important to know its body structure. This could also be a very powerful to working out the origins, extent and bounds that underlie the various sorts of animal motion.”
Additional information:
Suraj Shankar et al, Energetic hydraulics and ordinary elasticity of muscle fibres, Nature Physics (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41567-024-02540-x
Equipped by means of
College of Michigan
Quotation:
Muscle device: How water controls the rate of muscle contraction (2024, July 11)
retrieved 11 July 2024
from
This record is topic to copyright. Except for any truthful dealing for the aim of personal find out about or analysis, no
section is also reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is equipped for info functions simplest.













