A mysterious and fast upward push in Legionnaires’ illness, a serious bacterial lung an infection, has been connected to cleaner air, in a US learn about of traits in sulfur dioxide air pollution.At a loss for words through the long world upsurge in Legionnaires’ illness, an strange type of pneumonia led to through Legionella micro organism, researchers at two US universities and the New York State Division of Well being investigated conceivable environmental elements that might provide an explanation for the fad of their neck of the woods.During the last 20 years, the prevalence of Legionnaires’ illness in america has higher nine-fold, from round 1,100 instances reported in 2000 to almost 10,000 in 2018. Europe and portions of Canada have reported equivalent will increase, with instances up five- to seven-fold.Whilst main outbreaks of Legionnaires’ illness courting again to 1976 had been traced to air conditioners, industrial air flow techniques, and cooling towers – which use fanatics to burn up warmth from factories – within the overwhelming majority of sporadic instances, no major supply is understood.Airflow techniques and cooling towers, if infected, unfold Legionella micro organism over really extensive distances through dispersing water vapor; the micro organism hold to airborne water droplets that individuals inhale. Then again, this may range relying on environmental stipulations.”Figuring out how converting environmental stipulations affect Legionella proliferation is important to mitigating this necessary public well being chance,” says atmospheric scientist Fangqun Yu of the College of Albany in New York, who co-led the learn about.The researchers all for New York state, after figuring out it as the number 1 state for Legionnaires’ illness in an research of instances reported to america Facilities for Illness Keep an eye on and Prevention between 1992 and 2019.Then again, not one of the environmental elements the staff first of all studied – relative humidity, temperature, precipitation, and UV radiation – defined the long-term development in Legionnaires’ illness.Having a look additional, they spotted that ranges of sulfur dioxide (SO2) within the air had diminished over the past 20 years at a equivalent fee to the will increase in Legionnaires’ illness.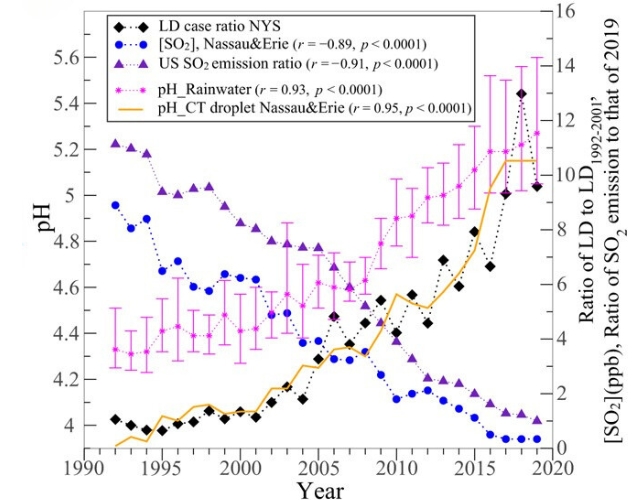 Legionnaires’ instances in New York state (black diamonds) higher whilst SO2 ranges at two websites in New York state (blue dots) and throughout america (red triangles) diminished over the similar length. Modeling displays the pH of rainwater (crimson stars) and water droplets (yellow line) has additionally higher, making the ones droplets much less acidic. (Yu et al., PNAS Nexus, 2024)The usage of a type of water-based chemistry, they confirmed how atmospheric SO2 may also be absorbed into water droplets, and transformed into sulfuric acid, making the droplets extra acidic and no more hospitable to Legionella micro organism.Conversely, the type confirmed decreases in SO2 ranges recorded at two air high quality tracking websites in New York state over 20 years would have made water droplets much less acidic through no less than an element of ten.Much less acidic water vapor may permit Legionella micro organism to continue to exist their airborne adventure and infect whoever inhales them.If truth be told, in a secondary research, the researchers discovered a one-week lag between diminished SO2 concentrations and rises in instances of Legionnaires’ illness, which is concerning the incubation time from publicity to symptom onset.Through mapping their places, additionally they recognized a placing hyperlink between instances of Legionnaires’ illness and their proximity to cooling towers in New York state.
Legionnaires’ instances in New York state (black diamonds) higher whilst SO2 ranges at two websites in New York state (blue dots) and throughout america (red triangles) diminished over the similar length. Modeling displays the pH of rainwater (crimson stars) and water droplets (yellow line) has additionally higher, making the ones droplets much less acidic. (Yu et al., PNAS Nexus, 2024)The usage of a type of water-based chemistry, they confirmed how atmospheric SO2 may also be absorbed into water droplets, and transformed into sulfuric acid, making the droplets extra acidic and no more hospitable to Legionella micro organism.Conversely, the type confirmed decreases in SO2 ranges recorded at two air high quality tracking websites in New York state over 20 years would have made water droplets much less acidic through no less than an element of ten.Much less acidic water vapor may permit Legionella micro organism to continue to exist their airborne adventure and infect whoever inhales them.If truth be told, in a secondary research, the researchers discovered a one-week lag between diminished SO2 concentrations and rises in instances of Legionnaires’ illness, which is concerning the incubation time from publicity to symptom onset.Through mapping their places, additionally they recognized a placing hyperlink between instances of Legionnaires’ illness and their proximity to cooling towers in New York state. Declining atmospheric SO2 may build up Legionella micro organism survival charges. (Yu et al., PNAS Nexus, 2024)This affiliation does not turn out reason and impact, and a couple of elements might be contributing to the upward thrust in Legionnaires’ illness, which the researchers plan to research in long term research.Communities situated as much as 7.3 kilometers (4.5 miles) from a cooling tower had a considerably upper chance of hospitalizations for Legionnaires’ illness. This vary has been expanding over the past twenty years as SO2 ranges diminished, perhaps extending the survival of Legionella within the air.It highlights the significance of shielding prone populations residing close to commercial or densely populated spaces – in the beginning from air air pollution, and secondly from this newfound chance of Legionnaires’ illness that includes clearer skies.The researchers rigidity that lowering air pollution is no doubt excellent for other folks and the surroundings; it is now a question of the use of those findings to lend a hand tell methods to restrict Legionella publicity whilst keeping up excellent air high quality and its many advantages.The learn about has been printed in PNAS Nexus.
Declining atmospheric SO2 may build up Legionella micro organism survival charges. (Yu et al., PNAS Nexus, 2024)This affiliation does not turn out reason and impact, and a couple of elements might be contributing to the upward thrust in Legionnaires’ illness, which the researchers plan to research in long term research.Communities situated as much as 7.3 kilometers (4.5 miles) from a cooling tower had a considerably upper chance of hospitalizations for Legionnaires’ illness. This vary has been expanding over the past twenty years as SO2 ranges diminished, perhaps extending the survival of Legionella within the air.It highlights the significance of shielding prone populations residing close to commercial or densely populated spaces – in the beginning from air air pollution, and secondly from this newfound chance of Legionnaires’ illness that includes clearer skies.The researchers rigidity that lowering air pollution is no doubt excellent for other folks and the surroundings; it is now a question of the use of those findings to lend a hand tell methods to restrict Legionella publicity whilst keeping up excellent air high quality and its many advantages.The learn about has been printed in PNAS Nexus.
Mysterious, Fast Surge in Legionnaires' Illness Connected to Cleaner Air














