A key function of healing IVT mRNAs is they include changed ribonucleotides, which were proven to lower innate immunogenicity and will moreover build up mRNA balance, either one of which might be beneficial traits for mRNA therapies1,2,3,4,5. As an example, clinically licensed SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccines incorporate N1-methylpseudouridine (1-methylΨ), which has been proven to lower IVT mRNA innate immunogenicity3,4,5. Some changed ribonucleotides, comparable to 5-methylcytidine (5-methylC), are naturally going on post-transcriptional mRNA adjustments in eukaryotes, while others don’t seem to be, comparable to 1-methylΨ (refs. 6,7,8,9,10).We investigated how 5-methoxyuridine (5-methoxyU), 5-methylC and 1-methylΨ impact translation of IVT mRNA. 5-methoxyU, 5-methylC and 1-methylΨ had been used in IVT mRNAs to try to build up recombinant protein synthesis in vitro, and for preclinical evidence of idea for IVT mRNA-based therapies11,12. As discussed, 1-methylΨ is a ribonucleotide integrated in approved IVT mRNA-based SARS-CoV-2 vaccines, but in addition mRNA-based human vaccines and remedies in development2,13,14.Regardless of their common use, unusually little is understood about how ribonucleotide amendment impacts protein synthesis, in particular for translation of healing IVT mRNAs. We had been concerned with how changed ribonucleotides impact the constancy of mRNA translation for a number of causes. Sure ribonucleotide adjustments can recode mRNA sequences (for instance, inosine15). 5-methylC has prior to now been proven to extend misreading all the way through mRNA translation in prokaryotes, however its impact on eukaryotic mRNA translation constancy has now not been explored16. The impact of 5-methoxyU on translation constancy has now not been investigated. Pseudouridine (Ψ) is understood to extend misreading of mRNA quit codons in eukaryotes, and will impact misreading all the way through prokaryotic mRNA translation16,17,18. 1-methylΨ does now not appear to impact codon misreading, however has been proven to impact protein synthesis charges and ribosome density on mRNAs, suggesting a right away impact on mRNA translation19,20.At the moment, it’s unclear which changed ribonucleotides impact mRNA translation constancy and present research are most commonly restricted to working out misreading frequencies most effective at a given codon. Misreading of mRNA codons may be just one form of post-transcriptional mechanism that may modify a polypeptide collection. To this point, no find out about has investigated the elemental query of whether or not changed ribonucleotides can impact the upkeep of the right kind studying body all the way through translation of a man-made transcript. Figuring out those processes is important to extend our wisdom of protein synthesis from changed mRNAs typically, however may be crucial for the tough design and analysis of recent mRNA-based therapeutics that employ changed ribonucleotides inside extensively differing RNA sequences or healing contexts.To analyze how ribonucleotide amendment impacts studying body upkeep all the way through translation of mRNA, we designed and synthesized IVT mRNAs (Fluc+1FS) that file on out-of-frame protein synthesis (Fig. 1a). Fluc+1FS mRNAs encode an amino-terminal section of firefly luciferase (NFluc) and a complementary carboxy-terminal section of Fluc (CFluc), without delay downstream. CFluc is encoded within the +1 studying body. Fluc+1FS mRNAs are designed to supply catalytically inactive (truncated) NFluc when translated typically. Alternatively, if ribosomes transfer out of body all the way through translation, elongated polypeptides containing residues from each in-frame NFluc and out-of-frame CFluc will also be produced, which will build up catalytic task.Fig. 1: Translation of 1-methylΨ-modified mRNA produces +1 frameshifted polypeptides.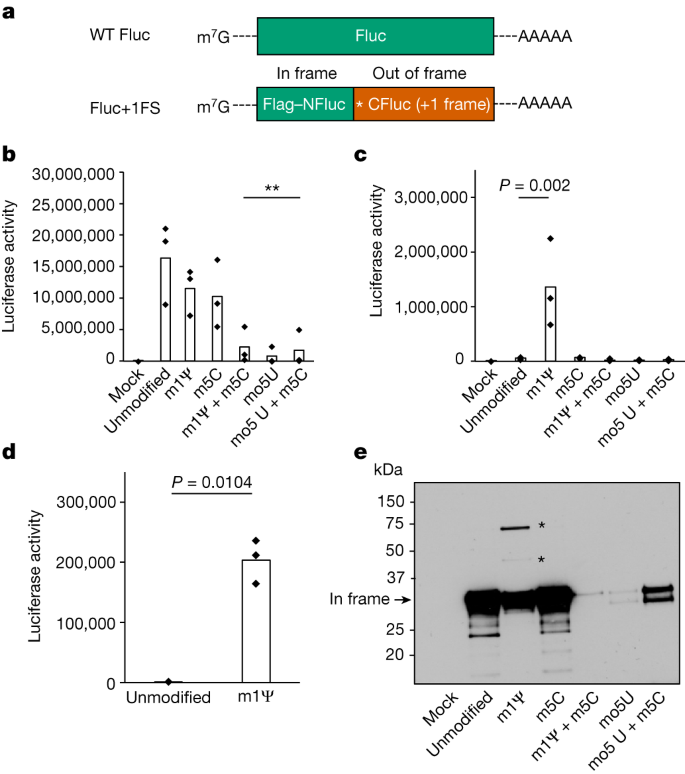 a, Constructions of IVT mRNA transcripts used to probe protein synthesis constancy. WT Fluc accommodates most effective (in-frame) Fluc coding collection. For Fluc+1FS, the golf green section represents in-frame N-terminal Fluc coding collection (NFluc), and the orange section represents +1 frameshifted C-terminal Fluc coding collection (CFluc). Asterisk represents a untimely quit codon. b, Luciferase task produced by means of translation of WT Fluc mRNAs, both unmodified keep an eye on (canonical nucleotides), or containing 1-methylΨ (m1Ψ), 5-methylC (m5C), 5-methoxyU (mo5U) or the combos indicated. **P < 0.01 (1-methylΨ + 5-methylC, P = 0.0051; 5-methoxyU, P = 0.0023; 5-methoxyU + 5-methylC, P = 0.0042; one-way research of variance (ANOVA) with Dunnett’s check). c, Luciferase task produced by means of translation of changed Fluc+1FS mRNAs and unmodified keep an eye on. 1-methylΨ, P = 0.002 (one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s check). d, Luciferase task in lysates produced by means of transfection of HeLa cells with unmodified or 1-methylΨ Fluc+1FS mRNA for 8 h. P = 0.0104 (Welch’s one-tailed t-test). e, Western blot research (anti-Flag epitope) of polypeptides produced by means of translation of mRNAs in c. All information are acquired from n = 3 replicated experiments. e displays a unmarried blot from n = 3 replicated experiments. Asterisks constitute bands at upper molecular weight. For gel supply information, see Supplementary Fig. 2.We synthesized unmodified Fluc+1FS mRNAs, which include canonical ribonucleotides, and translated them in vitro. We showed that Fluc+1FS mRNAs produce catalytically inactive NFluc (Prolonged Information Fig. 1). By means of comparability, unmodified wild-type (WT) Fluc mRNA, containing your complete in-frame Fluc coding collection, produced the predicted energetic protein (Prolonged Information Fig. 1). Then we synthesized and translated every mRNA containing 5-methoxyU, 5-methylC, 1-methylΨ, 5-methoxyU + 5-methylC or 1-methylΨ + 5-methylC. Translation of WT Fluc mRNA used to be now not considerably suffering from both 1-methylΨ or 5-methylC adjustments by myself, however used to be lowered by means of incorporating each ribonucleotides right into a unmarried transcript (Fig. 1b). 5-methoxyU incorporation by myself, or mixed with 5-methylC, considerably lowered translation of WT Fluc mRNA (Fig. 1b). Incorporation of 1-methylΨ in Fluc+1FS mRNA considerably larger ribosomal +1 frameshifting to about 8% of the corresponding in-frame protein, which used to be now not noticed for different ribonucleotides (Fig. 1c). HeLa cells transfected with 1-methylΨ Fluc+1FS mRNA recapitulated the effects from in vitro translation (Fig. 1d). At the foundation of those observations, we concluded that IVT mRNA containing 1-methylΨ or 5-methylC reveals an identical translation potency to unmodified mRNA, however 1-methylΨ considerably will increase ribosomal +1 frameshifting all the way through mRNA translation.We noticed a big build up in ribosomal +1 frameshifting all the way through translation of 1-methylΨ mRNA and reasoned that gaining higher working out of the interpretation merchandise would supplement the reporter assay information and assist to give an explanation for how +1 frameshifted merchandise originate. To deal with those facets, we probed the polypeptides produced all the way through IVT mRNA translation by means of western blotting. Translation of unmodified Fluc+1FS mRNA produced the predicted in-frame truncated product, which used to be additionally true for 5-methylC mRNA (Fig. 1e). Translation of 1-methylΨ mRNA produced the predicted in-frame product, but in addition produced two further bands at upper molecular weight (Fig. 1e). We reasoned that those merchandise had been +1 frameshifted polypeptides. We additionally showed that 1-methylΨ + 5-methylC-, 5-methoxyU- and 5-methoxyU + 5-methylC mRNAs had been relatively deficient mRNA templates for protein synthesis (Fig. 1e).1-methylΨ may be utilized in clinically licensed SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccines3,4. As 1-methylΨ larger +1 ribosome frameshifting all the way through translation in vitro, we investigated whether or not this happens in vivo for BNT162b2, a SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine containing 1-methylΨ. We reasoned that +1 ribosomal frameshifting all the way through recombinant antigen mRNA translation may just result in presentation of +1 frameshifted merchandise to T cells, and elicit off-target cell immune responses (Fig. 2a). Antigen presentation from mistranslation of endogenous tumour mRNA has been proven to happen in vivo (for instance, ref. 21). To deal with this risk, we vaccinated mice with BNT162b2 and quantified their T mobile reaction to in-frame SARS-CoV-2 spike protein and +1 frameshifted merchandise predicted to happen by means of translation of the mRNA +1 body, in addition to an unrelated keep an eye on antigen (SARS-CoV-2 M protein), by means of interferon-γ (IFNγ) ELISpot assay. Junction peptides consisting of in-frame N-terminal residues and C-terminal +1 frameshifted residues weren’t incorporated. We discovered that responses to +1 frameshifted spike peptides had been considerably larger in vaccinated mice in comparison to untreated mice or the ones vaccinated with ChAdOx nCoV-19, which doesn’t produce antigen from translation of N1-methylpseudouridylated mRNA22 (Fig. 2b). Each BNT162b2 and ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccination produced ELISpot responses to in-frame SARS-CoV-2 spike (Fig. 2c). Those information recommend that +1 frameshifted merchandise encoded in BNT162b2 spike mRNA are T mobile antigens for inbred mice, to which off-target immunity will also be detected following vaccination.Fig. 2: +1 frameshifted merchandise elicit off-target cell immune responses following changed mRNA vaccination.
a, Constructions of IVT mRNA transcripts used to probe protein synthesis constancy. WT Fluc accommodates most effective (in-frame) Fluc coding collection. For Fluc+1FS, the golf green section represents in-frame N-terminal Fluc coding collection (NFluc), and the orange section represents +1 frameshifted C-terminal Fluc coding collection (CFluc). Asterisk represents a untimely quit codon. b, Luciferase task produced by means of translation of WT Fluc mRNAs, both unmodified keep an eye on (canonical nucleotides), or containing 1-methylΨ (m1Ψ), 5-methylC (m5C), 5-methoxyU (mo5U) or the combos indicated. **P < 0.01 (1-methylΨ + 5-methylC, P = 0.0051; 5-methoxyU, P = 0.0023; 5-methoxyU + 5-methylC, P = 0.0042; one-way research of variance (ANOVA) with Dunnett’s check). c, Luciferase task produced by means of translation of changed Fluc+1FS mRNAs and unmodified keep an eye on. 1-methylΨ, P = 0.002 (one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s check). d, Luciferase task in lysates produced by means of transfection of HeLa cells with unmodified or 1-methylΨ Fluc+1FS mRNA for 8 h. P = 0.0104 (Welch’s one-tailed t-test). e, Western blot research (anti-Flag epitope) of polypeptides produced by means of translation of mRNAs in c. All information are acquired from n = 3 replicated experiments. e displays a unmarried blot from n = 3 replicated experiments. Asterisks constitute bands at upper molecular weight. For gel supply information, see Supplementary Fig. 2.We synthesized unmodified Fluc+1FS mRNAs, which include canonical ribonucleotides, and translated them in vitro. We showed that Fluc+1FS mRNAs produce catalytically inactive NFluc (Prolonged Information Fig. 1). By means of comparability, unmodified wild-type (WT) Fluc mRNA, containing your complete in-frame Fluc coding collection, produced the predicted energetic protein (Prolonged Information Fig. 1). Then we synthesized and translated every mRNA containing 5-methoxyU, 5-methylC, 1-methylΨ, 5-methoxyU + 5-methylC or 1-methylΨ + 5-methylC. Translation of WT Fluc mRNA used to be now not considerably suffering from both 1-methylΨ or 5-methylC adjustments by myself, however used to be lowered by means of incorporating each ribonucleotides right into a unmarried transcript (Fig. 1b). 5-methoxyU incorporation by myself, or mixed with 5-methylC, considerably lowered translation of WT Fluc mRNA (Fig. 1b). Incorporation of 1-methylΨ in Fluc+1FS mRNA considerably larger ribosomal +1 frameshifting to about 8% of the corresponding in-frame protein, which used to be now not noticed for different ribonucleotides (Fig. 1c). HeLa cells transfected with 1-methylΨ Fluc+1FS mRNA recapitulated the effects from in vitro translation (Fig. 1d). At the foundation of those observations, we concluded that IVT mRNA containing 1-methylΨ or 5-methylC reveals an identical translation potency to unmodified mRNA, however 1-methylΨ considerably will increase ribosomal +1 frameshifting all the way through mRNA translation.We noticed a big build up in ribosomal +1 frameshifting all the way through translation of 1-methylΨ mRNA and reasoned that gaining higher working out of the interpretation merchandise would supplement the reporter assay information and assist to give an explanation for how +1 frameshifted merchandise originate. To deal with those facets, we probed the polypeptides produced all the way through IVT mRNA translation by means of western blotting. Translation of unmodified Fluc+1FS mRNA produced the predicted in-frame truncated product, which used to be additionally true for 5-methylC mRNA (Fig. 1e). Translation of 1-methylΨ mRNA produced the predicted in-frame product, but in addition produced two further bands at upper molecular weight (Fig. 1e). We reasoned that those merchandise had been +1 frameshifted polypeptides. We additionally showed that 1-methylΨ + 5-methylC-, 5-methoxyU- and 5-methoxyU + 5-methylC mRNAs had been relatively deficient mRNA templates for protein synthesis (Fig. 1e).1-methylΨ may be utilized in clinically licensed SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccines3,4. As 1-methylΨ larger +1 ribosome frameshifting all the way through translation in vitro, we investigated whether or not this happens in vivo for BNT162b2, a SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine containing 1-methylΨ. We reasoned that +1 ribosomal frameshifting all the way through recombinant antigen mRNA translation may just result in presentation of +1 frameshifted merchandise to T cells, and elicit off-target cell immune responses (Fig. 2a). Antigen presentation from mistranslation of endogenous tumour mRNA has been proven to happen in vivo (for instance, ref. 21). To deal with this risk, we vaccinated mice with BNT162b2 and quantified their T mobile reaction to in-frame SARS-CoV-2 spike protein and +1 frameshifted merchandise predicted to happen by means of translation of the mRNA +1 body, in addition to an unrelated keep an eye on antigen (SARS-CoV-2 M protein), by means of interferon-γ (IFNγ) ELISpot assay. Junction peptides consisting of in-frame N-terminal residues and C-terminal +1 frameshifted residues weren’t incorporated. We discovered that responses to +1 frameshifted spike peptides had been considerably larger in vaccinated mice in comparison to untreated mice or the ones vaccinated with ChAdOx nCoV-19, which doesn’t produce antigen from translation of N1-methylpseudouridylated mRNA22 (Fig. 2b). Each BNT162b2 and ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccination produced ELISpot responses to in-frame SARS-CoV-2 spike (Fig. 2c). Those information recommend that +1 frameshifted merchandise encoded in BNT162b2 spike mRNA are T mobile antigens for inbred mice, to which off-target immunity will also be detected following vaccination.Fig. 2: +1 frameshifted merchandise elicit off-target cell immune responses following changed mRNA vaccination.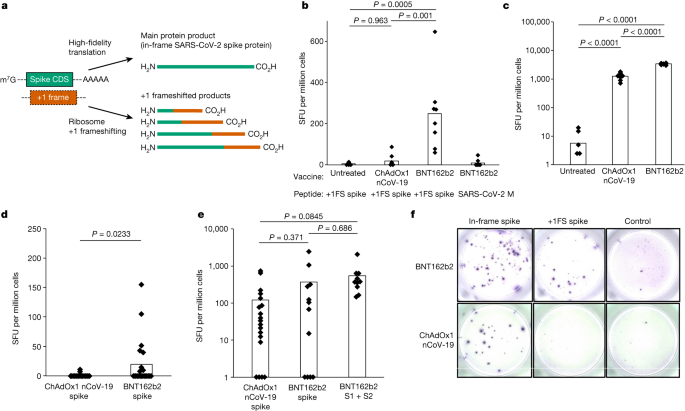 a, Depiction of spike and +1 frameshifted (+1FS) merchandise produced by means of 1-methylΨ-modified spike mRNA translation. CDS, coding collection. b, Splenocyte IFNγ ELISpot responses from untreated, ChAdOx1 nCoV-19-vaccinated or BNT162b2-vaccinated mice stimulated with +1FS spike peptides. IFNγ ELISpot reaction from BNT162b2-vaccinated mice stimulated with SARS-CoV-2 M peptides (unrelated keep an eye on antigen) is incorporated for extra comparability. SFU, spot-forming devices. Every workforce n = 8. Untreated as opposed to ChAdOx1 nCoV-19, P = 0.963; untreated as opposed to BNT162b2, P = 0.0005; ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 as opposed to BNT162b2, P = 0.001. c, Splenocyte IFNγ ELISpot responses from mice in b stimulated with spike peptides. Untreated as opposed to ChAdOx1 nCoV-19, P = 2.05 × 10−9; untreated as opposed to BNT162b2, P = 4.5 × 10−14; ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 as opposed to BNT162b2, P = 1.88 × 10−13. d, Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) IFNγ ELISpot responses from donors vaccinated with ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 (n = 20) or BNT162b2 (n = 21) stimulated with +1FS spike peptides. P = 0.0233 (Welch’s one-tailed t-test). e, PBMC IFNγ ELISpot responses from donors in c stimulated with in-frame spike peptides: overall spike pool or spike S1 + S2 subpools. ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 spike as opposed to BNT162b2 spike, P = 0.371; ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 spike as opposed to BNT162b2 S1 + S2, P = 0.0845; BNT162b2 spike as opposed to BNT162b2 S1 + S2, P = 0.686. f, Consultant photographs of PBMC IFNγ ELISpot reaction wells for 2 folks vaccinated with both BNT162b2 responder (most sensible) or ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 (backside). Left to proper: in-frame spike reaction (spike peptides); +1FS spike reaction (+1FS spike peptides); no peptide keep an eye on. P values in b,c,e had been made up our minds by means of one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s check.Supply DataWe then when put next IFNγ ELISpot responses to predicted +1 frameshifted SARS-CoV-2 spike protein merchandise in 21 folks vaccinated with BNT162b2 and when put next those responses to these of 20 folks vaccinated with ChAdOx1 nCoV-19, none of whom reported undue results because of vaccination. We detected a considerably upper IFNγ reaction to +1 frameshifted antigen within the BNT162b2 vaccine workforce, in comparison to ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 (Fig. 2nd). There used to be no affiliation between T mobile responses to +1 frameshifted antigen and age, intercourse or HLA subtype (Supplementary Desk 1 and Prolonged Information Figs. 2 and three). Each ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 and BNT162b2 vaccination produced ELISpot responses to in-frame SARS-CoV-2 spike, however responses to +1 frameshifted merchandise had been noticed most effective in folks vaccinated with BNT162b2 (Fig. 2e,f). Right through SARS-CoV-2 viral replication, a programmed −1 ribosomal frameshift happens naturally all the way through translation of open studying body (ORF) 1a and ORF1b (ref. 23). It’s not possible that those information are a end result of herbal SARS-CoV-2 an infection for the next, non-exhaustive, causes. First, no frameshifting task is understood to happen all the way through SARS-CoV-2 spike subgenomic mRNA translation (which might be a big discovery in its personal proper). 2d, −1 frameshifting (and now not +1 frameshifting) is specific to a unmarried programmed website in ORF1a and ORF1b (ref. 23). 3rd, +1 frameshifted peptides are predicted from the BNT162b2 mRNA collection, and now not the S gene collection from wild virus (Prolonged Information Fig. 4). As a substitute, those information recommend that vaccination with 1-methylΨ mRNA can elicit cell immunity to peptide antigens produced by means of +1 ribosomal frameshifting in each main histocompatibility advanced (MHC)-diverse other people and MHC-uniform mice.To supply additional mechanistic perception into +1 ribosome frameshifting all the way through translation of 1-methylΨ mRNA, and determine possible frameshift websites or sequences, we translated 1-methylΨ Fluc+1FS mRNA, purified the foremost putative +1 frameshifted polypeptide and performed liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (LC–MS/MS) of tryptic digests. From this unmarried polypeptide, we known six in-frame peptides and 9 peptides derived from the mRNA +1 body (Fig. 3a and Prolonged Information Desk 1). All in-frame peptides had been mapped to the N-terminal area, while +1 frameshifted peptides had been mapped downstream (Fig. 3a). We then repeated this research the usage of a distinct protease and known a junction peptide spanning the principle body and the +1 body (Fig. 3b). Those information demonstrated that the elongated polypeptide used to be certainly a chimeric polypeptide consisting of in-frame N-terminal residues and +1 frameshifted C-terminal residues. As anticipated, shorter frameshifted merchandise had been additionally constituted of translation of 1-methylΨ mRNA encoding full-length Fluc (Prolonged Information Fig. 5).Fig. 3: Mistranslation of 1-methylΨ mRNA is because of +1 ribosomal frameshifting and now not transcriptional mistakes.
a, Depiction of spike and +1 frameshifted (+1FS) merchandise produced by means of 1-methylΨ-modified spike mRNA translation. CDS, coding collection. b, Splenocyte IFNγ ELISpot responses from untreated, ChAdOx1 nCoV-19-vaccinated or BNT162b2-vaccinated mice stimulated with +1FS spike peptides. IFNγ ELISpot reaction from BNT162b2-vaccinated mice stimulated with SARS-CoV-2 M peptides (unrelated keep an eye on antigen) is incorporated for extra comparability. SFU, spot-forming devices. Every workforce n = 8. Untreated as opposed to ChAdOx1 nCoV-19, P = 0.963; untreated as opposed to BNT162b2, P = 0.0005; ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 as opposed to BNT162b2, P = 0.001. c, Splenocyte IFNγ ELISpot responses from mice in b stimulated with spike peptides. Untreated as opposed to ChAdOx1 nCoV-19, P = 2.05 × 10−9; untreated as opposed to BNT162b2, P = 4.5 × 10−14; ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 as opposed to BNT162b2, P = 1.88 × 10−13. d, Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) IFNγ ELISpot responses from donors vaccinated with ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 (n = 20) or BNT162b2 (n = 21) stimulated with +1FS spike peptides. P = 0.0233 (Welch’s one-tailed t-test). e, PBMC IFNγ ELISpot responses from donors in c stimulated with in-frame spike peptides: overall spike pool or spike S1 + S2 subpools. ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 spike as opposed to BNT162b2 spike, P = 0.371; ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 spike as opposed to BNT162b2 S1 + S2, P = 0.0845; BNT162b2 spike as opposed to BNT162b2 S1 + S2, P = 0.686. f, Consultant photographs of PBMC IFNγ ELISpot reaction wells for 2 folks vaccinated with both BNT162b2 responder (most sensible) or ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 (backside). Left to proper: in-frame spike reaction (spike peptides); +1FS spike reaction (+1FS spike peptides); no peptide keep an eye on. P values in b,c,e had been made up our minds by means of one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s check.Supply DataWe then when put next IFNγ ELISpot responses to predicted +1 frameshifted SARS-CoV-2 spike protein merchandise in 21 folks vaccinated with BNT162b2 and when put next those responses to these of 20 folks vaccinated with ChAdOx1 nCoV-19, none of whom reported undue results because of vaccination. We detected a considerably upper IFNγ reaction to +1 frameshifted antigen within the BNT162b2 vaccine workforce, in comparison to ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 (Fig. 2nd). There used to be no affiliation between T mobile responses to +1 frameshifted antigen and age, intercourse or HLA subtype (Supplementary Desk 1 and Prolonged Information Figs. 2 and three). Each ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 and BNT162b2 vaccination produced ELISpot responses to in-frame SARS-CoV-2 spike, however responses to +1 frameshifted merchandise had been noticed most effective in folks vaccinated with BNT162b2 (Fig. 2e,f). Right through SARS-CoV-2 viral replication, a programmed −1 ribosomal frameshift happens naturally all the way through translation of open studying body (ORF) 1a and ORF1b (ref. 23). It’s not possible that those information are a end result of herbal SARS-CoV-2 an infection for the next, non-exhaustive, causes. First, no frameshifting task is understood to happen all the way through SARS-CoV-2 spike subgenomic mRNA translation (which might be a big discovery in its personal proper). 2d, −1 frameshifting (and now not +1 frameshifting) is specific to a unmarried programmed website in ORF1a and ORF1b (ref. 23). 3rd, +1 frameshifted peptides are predicted from the BNT162b2 mRNA collection, and now not the S gene collection from wild virus (Prolonged Information Fig. 4). As a substitute, those information recommend that vaccination with 1-methylΨ mRNA can elicit cell immunity to peptide antigens produced by means of +1 ribosomal frameshifting in each main histocompatibility advanced (MHC)-diverse other people and MHC-uniform mice.To supply additional mechanistic perception into +1 ribosome frameshifting all the way through translation of 1-methylΨ mRNA, and determine possible frameshift websites or sequences, we translated 1-methylΨ Fluc+1FS mRNA, purified the foremost putative +1 frameshifted polypeptide and performed liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (LC–MS/MS) of tryptic digests. From this unmarried polypeptide, we known six in-frame peptides and 9 peptides derived from the mRNA +1 body (Fig. 3a and Prolonged Information Desk 1). All in-frame peptides had been mapped to the N-terminal area, while +1 frameshifted peptides had been mapped downstream (Fig. 3a). We then repeated this research the usage of a distinct protease and known a junction peptide spanning the principle body and the +1 body (Fig. 3b). Those information demonstrated that the elongated polypeptide used to be certainly a chimeric polypeptide consisting of in-frame N-terminal residues and +1 frameshifted C-terminal residues. As anticipated, shorter frameshifted merchandise had been additionally constituted of translation of 1-methylΨ mRNA encoding full-length Fluc (Prolonged Information Fig. 5).Fig. 3: Mistranslation of 1-methylΨ mRNA is because of +1 ribosomal frameshifting and now not transcriptional mistakes.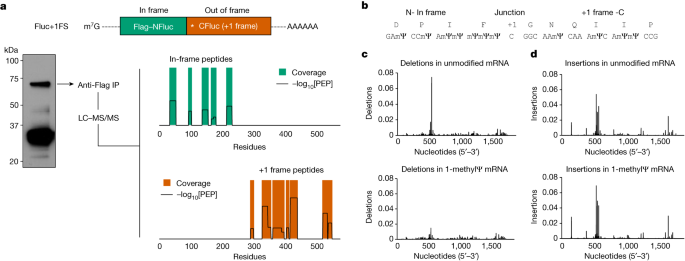 a, Tryptic peptide protection plot of the purified excessive molecular weight polypeptide produced by means of translation of 1-methylΨ Fluc+1FS mRNA, appearing in-frame residues (most sensible) and +1 frameshifted residues (backside). −log10[PEP] is the mass spectrum percolator ranking (most effective top quality peptides are proven). IP, immunoprecipitate. The construction of Fluc+1FS mRNA from Fig. 1 is re-displayed and a western blot of the interpretation response earlier than immunoprecipitation is displayed. For gel supply information, see Supplementary Fig. 3. b, Junction peptide derived from +1 ribosomal frameshifting and the originating mRNA collection. c, Nucleotide deletions in unmodified (most sensible) and 1-methylΨ (backside) Fluc+1FS mRNA, quantified by means of n = 3 RNA-sequencing analyses. d, Nucleotide insertions in unmodified (most sensible) and 1-methylΨ (backside) Fluc+1FS mRNA.Obvious mistakes in protein synthesis, together with frameshifting, will also be penalties of DNA mutation or transcriptional errors24. Therefore, trustworthy translation of an mistaken mRNA collection can produce mistaken proteins. In vitro transcripts are presumed to be precise RNA copies of template DNA, the accuracy of that could be estimated by means of the constancy of the used RNA polymerase. Alternatively, the substitution of canonical substrate ribonucleoside triphosphates for changed nucleotides would possibly build up transcriptional mistakes. To deal with this risk, we performed high-throughput RNA sequencing of unmodified and 1-methylΨ Fluc+1FS mRNA and quantified nucleotide insertions and deletions in every inhabitants of IVT mRNA. Nucleotide deletion profiles for every mRNA had been very an identical (Fig. 3c), as had been nucleotide insertions (Fig. 3d), suggesting few site-specific variations. The full frequency of insertions and deletions used to be low, and didn’t range considerably between unmodified and 1-methylΨ mRNA (Prolonged Information Desk 2), which is supported by means of contemporary observations25. From those findings, we concluded that frameshifted merchandise of 1-methylΨ mRNA translation weren’t because of transcriptional mistakes, however had been because of bona fide ribosomal +1 frameshifting—a post-transcriptional mechanism.Ribosome frameshifting is a well-documented phenomenon that happens all the way through translation of many naturally going on mRNAs24. As ribosome stalling is implicated in different cases of +1 frameshifting, we queried how the presence of 1-methylΨ in IVT mRNA impacts translation elongation26,27,28. To try this, we assayed protein synthesis all the way through translation of unmodified or 1-methylΨ WT Fluc mRNA the usage of co-translational [35S]methionine labelling29. Translation elongation of 1-methylΨ mRNA used to be slower than for unmodified mRNA (Fig. 4a), which is supported by means of earlier observations20. All reactions had been run for 30 min and there used to be much less full-length protein constituted of the interpretation of 1-methylΨ-containing mRNAs, suggesting a slower elongation charge in comparison to that of unmodified mRNA, with a better share of untimely polypeptide merchandise. Those information advised that elongating ribosomes stall all the way through translation of mRNA containing 1-methylΨ.Fig. 4: +1 ribosomal frameshifting depends on mRNA slippery sequences and related to ribosome stalling all the way through 1-methylΨ mRNA translation.
a, Tryptic peptide protection plot of the purified excessive molecular weight polypeptide produced by means of translation of 1-methylΨ Fluc+1FS mRNA, appearing in-frame residues (most sensible) and +1 frameshifted residues (backside). −log10[PEP] is the mass spectrum percolator ranking (most effective top quality peptides are proven). IP, immunoprecipitate. The construction of Fluc+1FS mRNA from Fig. 1 is re-displayed and a western blot of the interpretation response earlier than immunoprecipitation is displayed. For gel supply information, see Supplementary Fig. 3. b, Junction peptide derived from +1 ribosomal frameshifting and the originating mRNA collection. c, Nucleotide deletions in unmodified (most sensible) and 1-methylΨ (backside) Fluc+1FS mRNA, quantified by means of n = 3 RNA-sequencing analyses. d, Nucleotide insertions in unmodified (most sensible) and 1-methylΨ (backside) Fluc+1FS mRNA.Obvious mistakes in protein synthesis, together with frameshifting, will also be penalties of DNA mutation or transcriptional errors24. Therefore, trustworthy translation of an mistaken mRNA collection can produce mistaken proteins. In vitro transcripts are presumed to be precise RNA copies of template DNA, the accuracy of that could be estimated by means of the constancy of the used RNA polymerase. Alternatively, the substitution of canonical substrate ribonucleoside triphosphates for changed nucleotides would possibly build up transcriptional mistakes. To deal with this risk, we performed high-throughput RNA sequencing of unmodified and 1-methylΨ Fluc+1FS mRNA and quantified nucleotide insertions and deletions in every inhabitants of IVT mRNA. Nucleotide deletion profiles for every mRNA had been very an identical (Fig. 3c), as had been nucleotide insertions (Fig. 3d), suggesting few site-specific variations. The full frequency of insertions and deletions used to be low, and didn’t range considerably between unmodified and 1-methylΨ mRNA (Prolonged Information Desk 2), which is supported by means of contemporary observations25. From those findings, we concluded that frameshifted merchandise of 1-methylΨ mRNA translation weren’t because of transcriptional mistakes, however had been because of bona fide ribosomal +1 frameshifting—a post-transcriptional mechanism.Ribosome frameshifting is a well-documented phenomenon that happens all the way through translation of many naturally going on mRNAs24. As ribosome stalling is implicated in different cases of +1 frameshifting, we queried how the presence of 1-methylΨ in IVT mRNA impacts translation elongation26,27,28. To try this, we assayed protein synthesis all the way through translation of unmodified or 1-methylΨ WT Fluc mRNA the usage of co-translational [35S]methionine labelling29. Translation elongation of 1-methylΨ mRNA used to be slower than for unmodified mRNA (Fig. 4a), which is supported by means of earlier observations20. All reactions had been run for 30 min and there used to be much less full-length protein constituted of the interpretation of 1-methylΨ-containing mRNAs, suggesting a slower elongation charge in comparison to that of unmodified mRNA, with a better share of untimely polypeptide merchandise. Those information advised that elongating ribosomes stall all the way through translation of mRNA containing 1-methylΨ.Fig. 4: +1 ribosomal frameshifting depends on mRNA slippery sequences and related to ribosome stalling all the way through 1-methylΨ mRNA translation.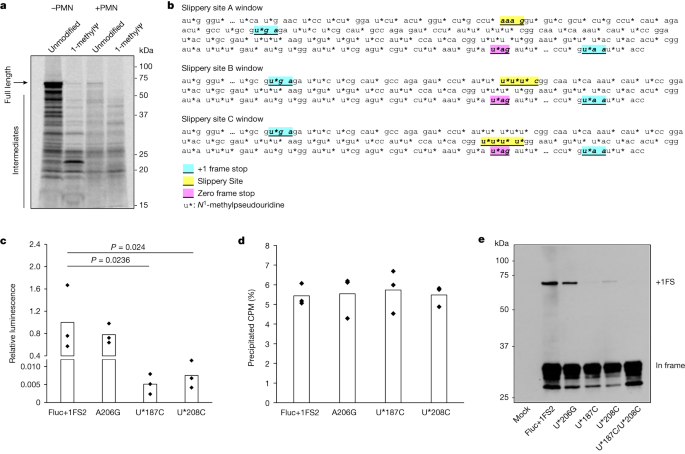 a, SDS–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis autoradiograph of [35S]methionine-labelled polypeptides produced by means of translation of unmodified or 1-methylΨ Fluc mRNA for 30 min, together with or omitting 100 μM paromomycin (+PMN and −PMN, respectively). b, Diagram appearing putative mRNA slippery sequences and stop-codon-flanked home windows. c, Process of +1 frameshifted merchandise after translation of 1-methylΨ mutant mRNAs, or 1-methylΨ Fluc+1FS2 keep an eye on mRNA, for two h. Fluc+1FS2 as opposed to U*187C, P = 0.024; Fluc+1FS2 as opposed to U*208C, P = 0.0236 (one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s check). d, General mRNA translation over 2 h for every of Fluc+1FS2 mRNA or mutant mRNAs, quantified by means of [35S]methionine incorporation. CPM, counts in line with minute. e, Western blot research (anti-Flag epitope) of polypeptides produced by means of translation of mRNAs in c, and U*187C/U*208C double-mutant 1-methylΨ mRNA. Information are from n = 3 replicated experiments. a and e display consultant photographs from n = 3 replicated experiments. For gel supply information, see Supplementary Figs. 4 and 5.It used to be unclear whether or not 1-methylΨ affected mRNA deciphering charges, or every other procedure, all the way through elongation. We reasoned that slower deciphering of 1-methylΨ codons all the way through translation elongation may just result in ribosome stalling, very similar to earlier observations for ‘hungry’ codons at websites of +1 frameshifting all the way through translation of naturally going on mRNA21,28. We probed the molecular mechanism of ribosome stalling all the way through 1-methylΨ mRNA translation the usage of the aminoglycoside paromomycin. In short, all the way through mRNA deciphering, cognate aminoacyl-tRNA anticodon–codon interplay reasons native conformational adjustments in 18S rRNA (in eukaryotes), and then a brand new peptide bond is shaped, ribosome subunit rotation happens, and next ribosome conformational adjustments, elongation issue 2 binding and translocation to the following codon completes the elongation cycle30. Paromomycin binds to helix 44 of 18S rRNA in elongating ribosomes and alters its conformation within the deciphering centre, which inhibits translation but in addition allows the productive binding of near- and non-cognate aminoacyl-tRNAs to the 80S ribosome A-site31. In doing so, paromomycin will increase the misincorporation of amino acids into elongating polypeptides32. We reasoned that if sluggish deciphering all the way through 1-methylΨ mRNA translation used to be because of altered aminoacyl-tRNA binding kinetics, this procedure might be lowered by means of paromomycin. It’s because paromomycin-bound ribosomes may just incorporate further near- or non-cognate aminoacyl-tRNAs and successfully build up the substrate aminoacyl-tRNA pool at ribosome stall websites. Translation of 1-methylΨ mRNA used to be slower than that of unmodified mRNA and the share of untimely polypeptide merchandise used to be better (Fig. 4a). Alternatively, all the way through 1-methylΨ mRNA translation, polypeptide elongation used to be advanced by means of the addition of paromomycin, while paromomycin used to be inhibitory most effective to unmodified mRNA translation (Fig. 4a). In combination, those information display that sluggish translation of 1-methylΨ mRNA is most probably because of ribosome stalling, which is led to by means of altered aminoacyl-tRNA binding, and which will also be rescued by means of expanding the incorporation of near- or non-cognate amino acids into elongating polypeptides.Despite the fact that there’s no proof that frameshifted merchandise in people generated from BNT162b2 vaccination are related to adversarial results, for long term use of mRNA era it is crucial that mRNA collection design is changed to cut back ribosome frameshifting occasions, as this may increasingly restrict its long term use for packages that require upper doses or extra common dosing, such because the in vivo manufacturing of hormones. You will need to proceed investigating healing mRNA mistranslation and immunogenicity, because the evolution of antibody and cytolytic T mobile responses towards +1 frameshifted spike variants and peptides has now not been systematically evaluated in people and ELISpot responses acquired from pooled peptides might also underestimate T mobile responses. The principle in-frame mRNA-encoded product is not likely to elicit an adaptive immune reaction, however presentation of +1 frameshifted merchandise may just turn on T cells that concentrate on host cells. We reasoned that if we had been in a position to spot +1 ribosome frameshift websites or sequences it could be conceivable to change the mRNA collection to cut back such results. As evidence of concept, we used our reporter IVT mRNA device. LC–MS/MS research confirmed that translation of 1-methylΨ mRNA results in synthesis of +1 frameshifted merchandise throughout the space of coding collection between detected in-frame residues and downstream +1 frameshifted residues (Fig. 3a). We searched the RNA collection comparable to this area in the junction peptide coding collection (Fig. 3b) and determinants of ribosome frameshifting from printed mechanisms, from which we known 3 possible ribosome slippery sequences (Fig. 4c), with all 3 sequences having the possible to be decoded by means of the similar aminoacyl-tRNA at an in-frame codon or within the quick +1 body codon. Significantly, six slippery websites just like Fluc+1FS slippery websites B and C had been additionally disbursed within the BNT162b2 spike mRNA coding collection. Those websites had been annotated within the Fluc+1FS coding collection (Fig. 4b) and the BNT163b2 spike mRNA coding collection (Prolonged Information Fig. 6). We reasoned that those sequences may just due to this fact serve as as websites for +1 ribosomal frameshifting. We synonymously mutated every website in 1-methylΨ Fluc+1FS mRNA such that the in-frame amino acid used to be unchanged, however the quick +1 body codon used to be mutated to a non-cognate amino acid, therefore destroying the ribosome slippery collection, and translated the mRNAs to judge the contribution of every website to +1 ribosomal frameshifting (Fig. 4c). A +1 body quit codon used to be provide downstream of slippery website A, and it used to be not likely that frameshifting at this website contributed to larger luciferase task. As anticipated, luciferase task produced by means of translation of website A mutant A206G mRNA used to be the similar as keep an eye on ranges (Fig. 4c). Alternatively, each slippery website B mutant U*187C mRNA and slippery website C mutant U*208C mRNA strongly lowered +1 ribosome frameshifting (Fig. 4c). Significantly, translation potency of every mRNA used to be equivalent, which implies that no mutation adversely affected mRNA translation general, however only +1 ribosomal frameshifting task (Fig. 4d). Translation of a U*187C/U*208C double-mutant 1-methylΨ Fluc+1FS mRNA produced no detectable +1 ribosome frameshifting (Fig. 4e). The transframe protein product predicted by means of +1 frameshifting at slippery website C accommodates an alteration of nineteen amino acid residues (in comparison to WT Fluc), while +1 frameshifting at slippery website B produces a transframe product this is successfully 100% homologous to WT Fluc. As well as, for the reason that mutation of both slippery website B or C (U*187C or U*208C) considerably lowered luciferase task, however that slightly extra frameshifted product used to be produced by means of translation of U*208C mRNA (Fig. 4e), we reasoned that the transframe product produced by means of frameshifting at slippery website C had decrease particular luciferase task, and that frameshifting at slippery website B contributed to many of the detected luciferase task attributable to +1 ribosome frameshifting. Taken in combination, those information recommend that N1-methylpseudouridylation at outlined mRNA sequences triggers ribosome +1 frameshifting; then again, with suitable mRNA collection design, it’s conceivable to ameliorate this factor.
a, SDS–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis autoradiograph of [35S]methionine-labelled polypeptides produced by means of translation of unmodified or 1-methylΨ Fluc mRNA for 30 min, together with or omitting 100 μM paromomycin (+PMN and −PMN, respectively). b, Diagram appearing putative mRNA slippery sequences and stop-codon-flanked home windows. c, Process of +1 frameshifted merchandise after translation of 1-methylΨ mutant mRNAs, or 1-methylΨ Fluc+1FS2 keep an eye on mRNA, for two h. Fluc+1FS2 as opposed to U*187C, P = 0.024; Fluc+1FS2 as opposed to U*208C, P = 0.0236 (one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s check). d, General mRNA translation over 2 h for every of Fluc+1FS2 mRNA or mutant mRNAs, quantified by means of [35S]methionine incorporation. CPM, counts in line with minute. e, Western blot research (anti-Flag epitope) of polypeptides produced by means of translation of mRNAs in c, and U*187C/U*208C double-mutant 1-methylΨ mRNA. Information are from n = 3 replicated experiments. a and e display consultant photographs from n = 3 replicated experiments. For gel supply information, see Supplementary Figs. 4 and 5.It used to be unclear whether or not 1-methylΨ affected mRNA deciphering charges, or every other procedure, all the way through elongation. We reasoned that slower deciphering of 1-methylΨ codons all the way through translation elongation may just result in ribosome stalling, very similar to earlier observations for ‘hungry’ codons at websites of +1 frameshifting all the way through translation of naturally going on mRNA21,28. We probed the molecular mechanism of ribosome stalling all the way through 1-methylΨ mRNA translation the usage of the aminoglycoside paromomycin. In short, all the way through mRNA deciphering, cognate aminoacyl-tRNA anticodon–codon interplay reasons native conformational adjustments in 18S rRNA (in eukaryotes), and then a brand new peptide bond is shaped, ribosome subunit rotation happens, and next ribosome conformational adjustments, elongation issue 2 binding and translocation to the following codon completes the elongation cycle30. Paromomycin binds to helix 44 of 18S rRNA in elongating ribosomes and alters its conformation within the deciphering centre, which inhibits translation but in addition allows the productive binding of near- and non-cognate aminoacyl-tRNAs to the 80S ribosome A-site31. In doing so, paromomycin will increase the misincorporation of amino acids into elongating polypeptides32. We reasoned that if sluggish deciphering all the way through 1-methylΨ mRNA translation used to be because of altered aminoacyl-tRNA binding kinetics, this procedure might be lowered by means of paromomycin. It’s because paromomycin-bound ribosomes may just incorporate further near- or non-cognate aminoacyl-tRNAs and successfully build up the substrate aminoacyl-tRNA pool at ribosome stall websites. Translation of 1-methylΨ mRNA used to be slower than that of unmodified mRNA and the share of untimely polypeptide merchandise used to be better (Fig. 4a). Alternatively, all the way through 1-methylΨ mRNA translation, polypeptide elongation used to be advanced by means of the addition of paromomycin, while paromomycin used to be inhibitory most effective to unmodified mRNA translation (Fig. 4a). In combination, those information display that sluggish translation of 1-methylΨ mRNA is most probably because of ribosome stalling, which is led to by means of altered aminoacyl-tRNA binding, and which will also be rescued by means of expanding the incorporation of near- or non-cognate amino acids into elongating polypeptides.Despite the fact that there’s no proof that frameshifted merchandise in people generated from BNT162b2 vaccination are related to adversarial results, for long term use of mRNA era it is crucial that mRNA collection design is changed to cut back ribosome frameshifting occasions, as this may increasingly restrict its long term use for packages that require upper doses or extra common dosing, such because the in vivo manufacturing of hormones. You will need to proceed investigating healing mRNA mistranslation and immunogenicity, because the evolution of antibody and cytolytic T mobile responses towards +1 frameshifted spike variants and peptides has now not been systematically evaluated in people and ELISpot responses acquired from pooled peptides might also underestimate T mobile responses. The principle in-frame mRNA-encoded product is not likely to elicit an adaptive immune reaction, however presentation of +1 frameshifted merchandise may just turn on T cells that concentrate on host cells. We reasoned that if we had been in a position to spot +1 ribosome frameshift websites or sequences it could be conceivable to change the mRNA collection to cut back such results. As evidence of concept, we used our reporter IVT mRNA device. LC–MS/MS research confirmed that translation of 1-methylΨ mRNA results in synthesis of +1 frameshifted merchandise throughout the space of coding collection between detected in-frame residues and downstream +1 frameshifted residues (Fig. 3a). We searched the RNA collection comparable to this area in the junction peptide coding collection (Fig. 3b) and determinants of ribosome frameshifting from printed mechanisms, from which we known 3 possible ribosome slippery sequences (Fig. 4c), with all 3 sequences having the possible to be decoded by means of the similar aminoacyl-tRNA at an in-frame codon or within the quick +1 body codon. Significantly, six slippery websites just like Fluc+1FS slippery websites B and C had been additionally disbursed within the BNT162b2 spike mRNA coding collection. Those websites had been annotated within the Fluc+1FS coding collection (Fig. 4b) and the BNT163b2 spike mRNA coding collection (Prolonged Information Fig. 6). We reasoned that those sequences may just due to this fact serve as as websites for +1 ribosomal frameshifting. We synonymously mutated every website in 1-methylΨ Fluc+1FS mRNA such that the in-frame amino acid used to be unchanged, however the quick +1 body codon used to be mutated to a non-cognate amino acid, therefore destroying the ribosome slippery collection, and translated the mRNAs to judge the contribution of every website to +1 ribosomal frameshifting (Fig. 4c). A +1 body quit codon used to be provide downstream of slippery website A, and it used to be not likely that frameshifting at this website contributed to larger luciferase task. As anticipated, luciferase task produced by means of translation of website A mutant A206G mRNA used to be the similar as keep an eye on ranges (Fig. 4c). Alternatively, each slippery website B mutant U*187C mRNA and slippery website C mutant U*208C mRNA strongly lowered +1 ribosome frameshifting (Fig. 4c). Significantly, translation potency of every mRNA used to be equivalent, which implies that no mutation adversely affected mRNA translation general, however only +1 ribosomal frameshifting task (Fig. 4d). Translation of a U*187C/U*208C double-mutant 1-methylΨ Fluc+1FS mRNA produced no detectable +1 ribosome frameshifting (Fig. 4e). The transframe protein product predicted by means of +1 frameshifting at slippery website C accommodates an alteration of nineteen amino acid residues (in comparison to WT Fluc), while +1 frameshifting at slippery website B produces a transframe product this is successfully 100% homologous to WT Fluc. As well as, for the reason that mutation of both slippery website B or C (U*187C or U*208C) considerably lowered luciferase task, however that slightly extra frameshifted product used to be produced by means of translation of U*208C mRNA (Fig. 4e), we reasoned that the transframe product produced by means of frameshifting at slippery website C had decrease particular luciferase task, and that frameshifting at slippery website B contributed to many of the detected luciferase task attributable to +1 ribosome frameshifting. Taken in combination, those information recommend that N1-methylpseudouridylation at outlined mRNA sequences triggers ribosome +1 frameshifting; then again, with suitable mRNA collection design, it’s conceivable to ameliorate this factor.
N1-methylpseudouridylation of mRNA reasons +1 ribosomal frameshifting – Nature















