NASA’s oldest energetic astronaut simply gave Earth a jaw-dropping have a look at one of the crucial planet’s rarest and most lovely phenomena—from over 250 miles above. As reported through House.com, astronaut Don Pettit captured vibrant movies of inexperienced auroras dancing throughout Earth’s surroundings from the Global House Station (ISS)—and the view is natural cosmic magic.
Celestial Lighting Stuck in Movement
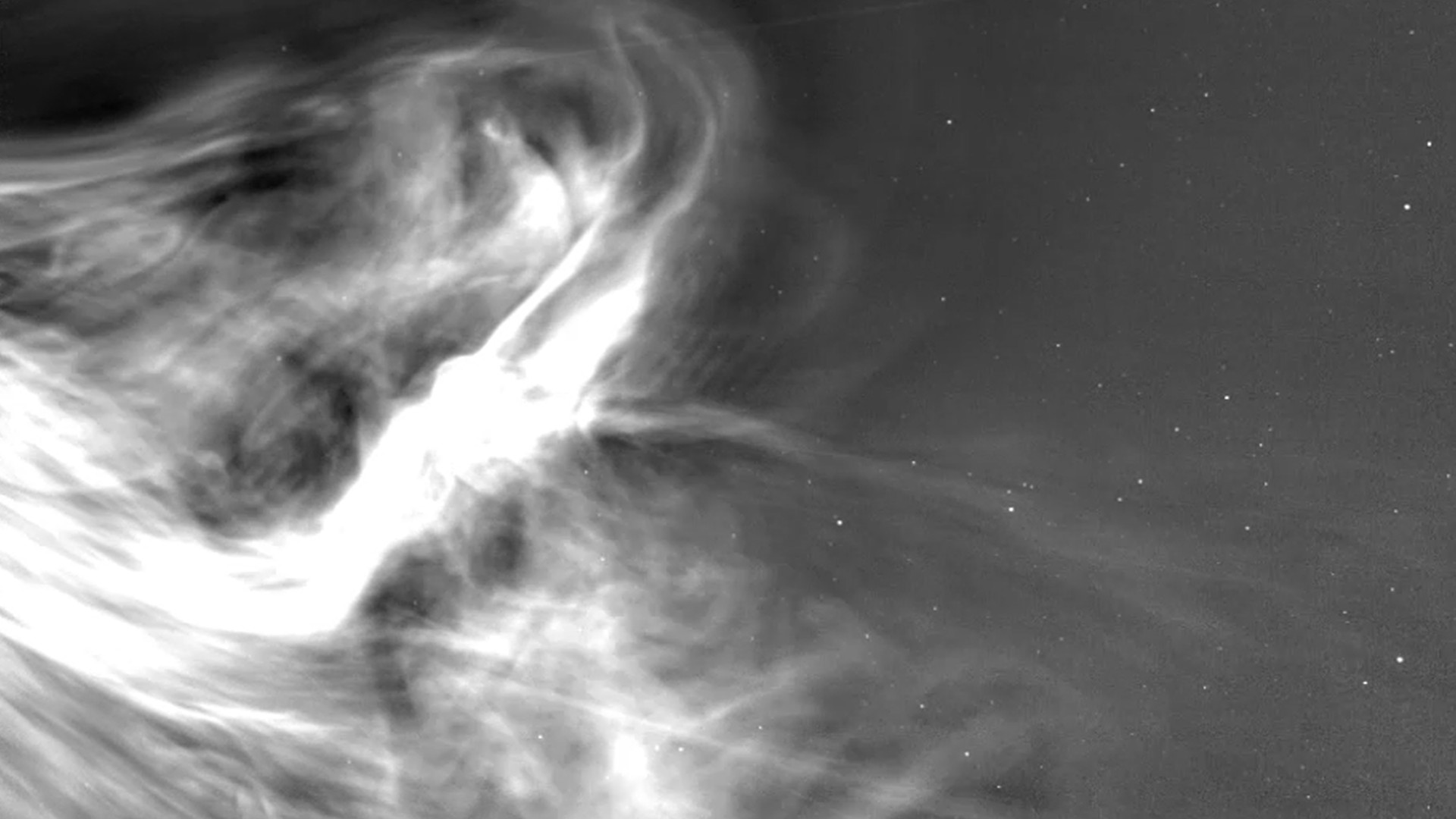
On April 4 and 5, Don Pettit, who’s lately aboard the ISS, posted two quick however impressive movies to X (previously Twitter), revealing sheets of luminous inexperienced auroras rippling around the sky underneath the gap station. One video captures the lighting because the ISS passes above the icy waters between Australia and Antarctica, whilst the opposite displays an airy scene Pettit described as “inexperienced vaporous turbulence” over an undisclosed area.
Considered from orbit, the auroras appear to be sparkling waves of smoke rolling over Earth’s higher surroundings—an impact led to through sun debris colliding with atoms in our planet’s magnetosphere.
What Are Auroras and How Do They Shape?
Auroras—repeatedly known as the northern lighting (aurora borealis) and southern lighting (aurora australis)—are created when sun wind debris, essentially electrons and protons, have interaction with Earth’s magnetosphere and higher surroundings. Those charged debris observe Earth’s magnetic box traces and input the ambience close to the poles, the place they collide with atoms of oxygen and nitrogen, thrilling the ones atoms and inflicting them to emit mild.
The fairway colour noticed within the movies is feature of oxygen atoms at altitudes between 100 and 300 kilometers. When those atoms go back to their flooring state after being energized, they emit inexperienced photons—a visual glow that may unfold throughout 1000’s of kilometers below the precise prerequisites.
Auroras are extra widespread and intense across the time of sun most, when the Solar’s magnetic job peaks each and every 11 years. As sun job will increase, so does the frequency of coronal mass ejections (CMEs) and sun flares, which free up bursts of charged debris in a position to triggering auroras. The auroral presentations captured on this pictures most likely resulted from one such sun match achieving Earth.