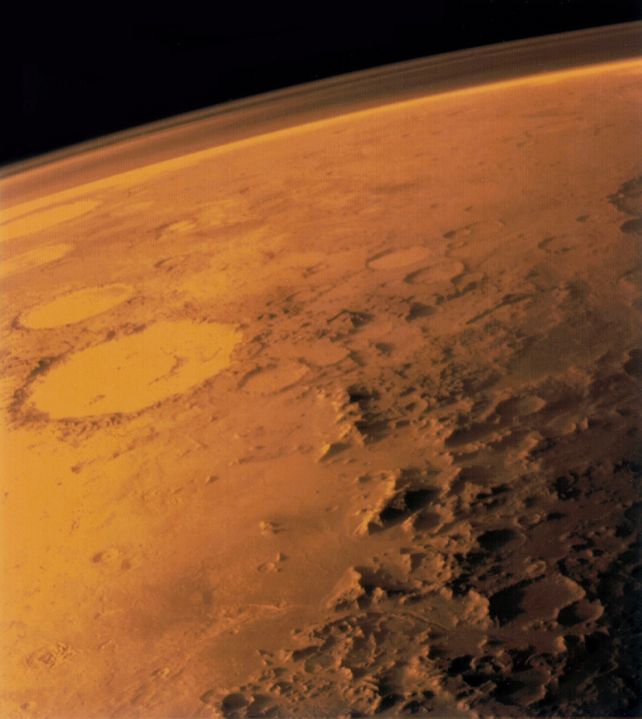
NASA has completed a big milestone through integrating its state of the art coronagraph device onto the Nancy Grace Roman House Telescope.
Set to release through 2027, the Roman Telescope objectives to advance the find out about of exoplanets through taking pictures pictures of planets orbiting far away stars—a feat made imaginable through this complicated coronagraph. The set up came about at NASA’s Goddard House Flight Heart in Maryland, marking the end result of years of construction and trying out on the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in California. This integration paves the best way for direct imaging of far away planets and provides a brand new size to NASA’s challenge of discovering liveable worlds.
The Energy and Promise of the Roman Coronagraph Software
The Roman Coronagraph Software is NASA’s maximum subtle coronagraph to this point, designed to dam the overpowering mild from stars so scientists can seize pictures of the faint planets orbiting them. It employs extremely exact mask and lively mirrors to take away superstar glare, revealing information about the ambience, composition, and attainable habitability of exoplanets. This generation is anticipated to be transformational for exoplanet research. Consistent with Rob Zellem, deputy undertaking scientist for communications at NASA, “we want the Roman Coronagraph to display this generation” as an crucial step towards long term missions designed to seek for Earth-like exoplanets.
As a generation demonstration, the Roman coronagraph will pave the best way for long term telescopes, together with NASA’s proposed Liveable Worlds Observatory, which might focal point on discovering indicators of existence on far away worlds. The Roman Telescope’s coronagraph is a proof-of-concept software that may display that such imaging is possible from area. The insights won from this challenge will probably be foundational for creating telescopes explicitly constructed to search out probably liveable planets.

The Intricate Means of Coronagraph Integration
The method of integrating the coronagraph into the Software Provider of the Roman Telescope required cautious alignment and intensive preparation. The software, related in dimension to a child grand piano, was once decreased the use of a specialised Horizontal Integration Device that allowed engineers to place it securely throughout the service. Insulation layers had been meticulously added across the device to take care of a strong temperature and protect it from stray mild that might intervene with its observations within the vacuum of area.
This milestone was once celebrated as a luck through NASA’s groups at Goddard and JPL. Liz Daly, integration and check lead at NASA Goddard, mirrored at the procedure, describing it as “the results of a large number of groups, lengthy hours, arduous paintings, sweat, and tears.” JPL’s integration and check lead, Gasia Bedrosian, echoed those sentiments, noting that “we celebrated our luck in combination.” This collaboration throughout groups highlights the precision and dedication required to combine the sort of complicated and significant device onto a state of the art telescope.
A Collaborative Project with World Contributions
The coronagraph integration is a vital fulfillment inside NASA’s Roman Telescope program, representing intensive collaboration throughout a couple of companies and global companions. The Eu House Company (ESA) and Japan Aerospace Exploration Company (JAXA) contributed to the coronagraph’s construction and are all for ongoing challenge arrangements. The Roman Science Improve Heart at Caltech/IPAC is managing knowledge for the coronagraph and aiding with operational fortify, whilst main aerospace corporations comparable to BAE Techniques and L3Harris Applied sciences have supplied an important instrumentation and methods.
With the coronagraph now in position, NASA’s subsequent steps come with integration of the Large Box Software, the Roman Telescope’s number one science software. In combination, those tools will permit the telescope to deal with a few of astronomy’s maximum compelling questions—from imaging far away exoplanets to finding out darkish power and the large-scale construction of the universe.

NASA, Roman House Telescope