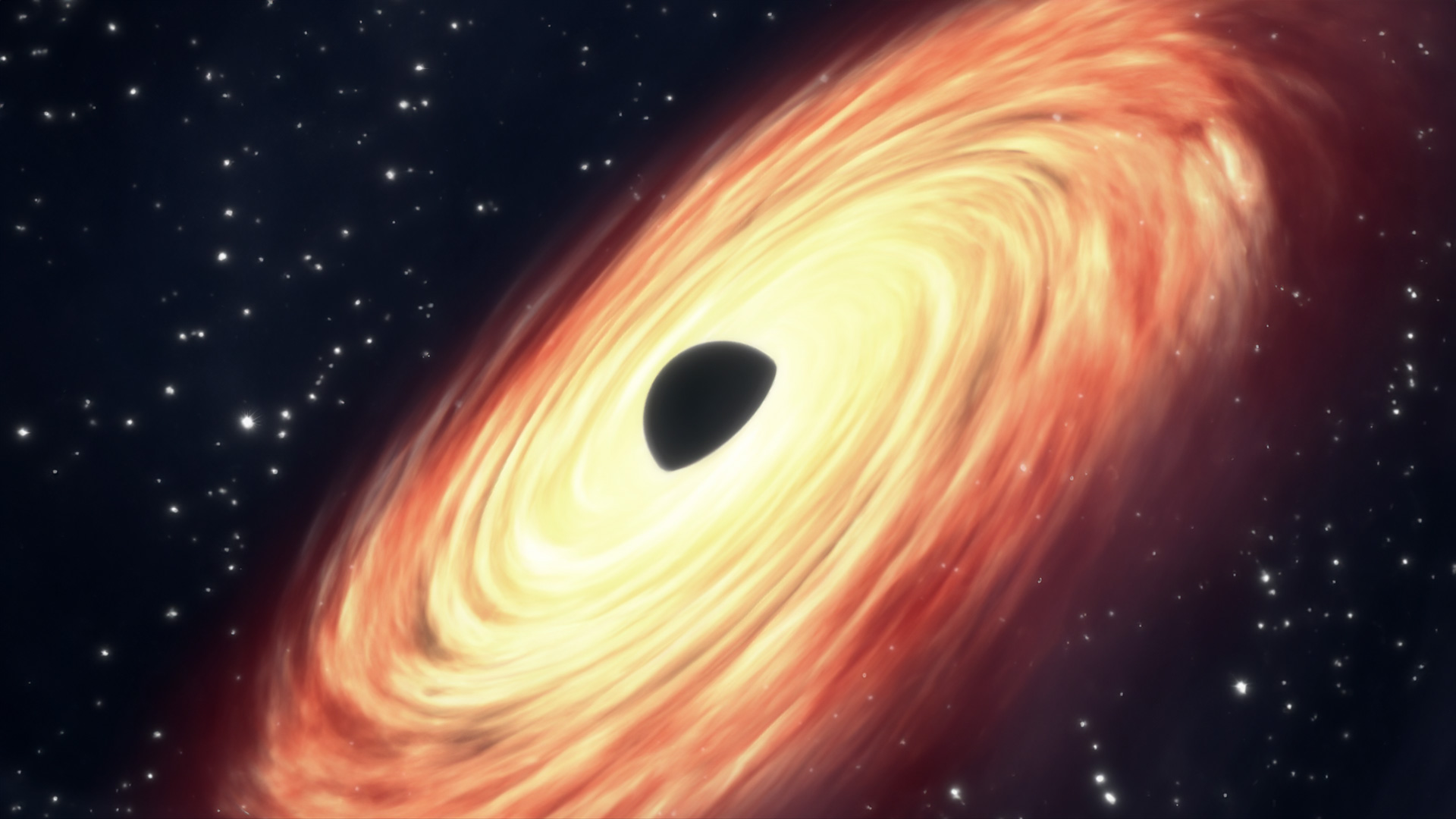
Astronomers have found out essentially the most far-off black hollow ever noticed in X-rays, positioned in galaxy UHZ1, over 13 billion light-years away. The usage of knowledge from the Chandra X-ray Observatory and the James Webb House Telescope, the findings counsel the black hollow used to be huge at beginning, difficult present theories concerning the early universe’s supermassive black holes. Credit score: NASAA key indicator of a rising supermassive black hollow – X-ray emission – has been present in a particularly far-off galaxy.This galaxy, UHZ1, is 13.2 billion light-years away, noticed when the universe used to be handiest 3% of its present age.NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory and James Webb House Telescope joined forces to make this discovery.This is regarded as the most efficient proof so far that some early black holes shaped from huge clouds of gasoline.
Astronomers have found out essentially the most far-off black hollow ever noticed in X-rays, positioned in galaxy UHZ1, over 13 billion light-years away. The usage of knowledge from the Chandra X-ray Observatory and the James Webb House Telescope, the findings counsel the black hollow used to be huge at beginning, difficult present theories concerning the early universe’s supermassive black holes. Credit score: NASAA key indicator of a rising supermassive black hollow – X-ray emission – has been present in a particularly far-off galaxy.This galaxy, UHZ1, is 13.2 billion light-years away, noticed when the universe used to be handiest 3% of its present age.NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory and James Webb House Telescope joined forces to make this discovery.This is regarded as the most efficient proof so far that some early black holes shaped from huge clouds of gasoline. Astronomers discovered essentially the most far-off black hollow ever detected in X-rays (in a galaxy dubbed UHZ1) the use of the Chandra and Webb house telescopes. X-ray emission is a telltale signature of a rising supermassive black hollow. This end result would possibly provide an explanation for how probably the most first supermassive black holes within the universe shaped. Those pictures display the galaxy cluster Abell 2744 that UHZ1 is positioned at the back of, in X-rays from Chandra and infrared knowledge from Webb, in addition to close-ups of the black hollow host galaxy UHZ1. Credit score: X-ray: NASA/CXC/SAO/Ákos Bogdán; Infrared: NASA/ESA/CSA/STScI; Symbol Processing: NASA/CXC/SAO/L. Frattare & Ok. ArcandNASA Telescopes Uncover Report-Breaking Black HoleThis symbol finds essentially the most far flung black hollow ever recognized thru X-rays, probably dropping gentle at the formation of the earliest supermassive black holes within the cosmos. This discovery used to be made the use of X-rays from NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory (depicted in red) and infrared knowledge from the James Webb House Telescope (proven in pink, inexperienced, blue).Galactic Distances and ObservationsThe extraordinarily far-off black hollow is positioned within the galaxy UHZ1 within the route of the galaxy cluster Abell 2744. The galaxy cluster is set 3.5 billion light-years from Earth. Webb knowledge, on the other hand, disclose that UHZ1 is far farther away than Abell 2744. At some 13.2 billion light-years away, UHZ1 is noticed when the universe used to be handiest 3% of its present age.Gravitational Lensing and X-ray DetectionBy the use of over two weeks of observations from Chandra, researchers had been in a position to stumble on X-ray emission from UHZ1 — a telltale signature of a rising supermassive black hollow within the middle of the galaxy. The X-ray sign is very faint and Chandra used to be handiest in a position to stumble on it — even with this lengthy statement — on account of the phenomenon referred to as gravitational lensing that enhanced the sign via an element of 4.Imaging Tactics and OrientationThe red portions of the picture display X-rays from massive quantities of scorching gasoline in Abell 2744. The infrared symbol displays loads of galaxies within the cluster, together with a couple of foreground stars. The insets zoom right into a small space focused on UHZ1. The small object within the Webb symbol is the far-off galaxy UHZ1 and the middle of the Chandra symbol displays X-rays from subject matter just about the supermassive black hollow in the course of UHZ1. The massive dimension of the X-ray supply in comparison to the infrared view of the galaxy is as it represents the smallest dimension that Chandra can get to the bottom of. The X-rays in reality come from a area this is a lot smaller than the galaxy.Other smoothing used to be carried out to the full-field Chandra symbol and to the Chandra symbol within the close-up. Smoothing throughout many pixels used to be carried out for the massive symbol, to spotlight the faint cluster emission, on the expense of now not appearing faint X-ray level resources like UHZ1. A lot much less smoothing used to be carried out to the close-up so faint X-ray resources are visual. The picture is orientated in order that north issues 42.5 levels to the appropriate of vertical.
Astronomers discovered essentially the most far-off black hollow ever detected in X-rays (in a galaxy dubbed UHZ1) the use of the Chandra and Webb house telescopes. X-ray emission is a telltale signature of a rising supermassive black hollow. This end result would possibly provide an explanation for how probably the most first supermassive black holes within the universe shaped. Those pictures display the galaxy cluster Abell 2744 that UHZ1 is positioned at the back of, in X-rays from Chandra and infrared knowledge from Webb, in addition to close-ups of the black hollow host galaxy UHZ1. Credit score: X-ray: NASA/CXC/SAO/Ákos Bogdán; Infrared: NASA/ESA/CSA/STScI; Symbol Processing: NASA/CXC/SAO/L. Frattare & Ok. ArcandNASA Telescopes Uncover Report-Breaking Black HoleThis symbol finds essentially the most far flung black hollow ever recognized thru X-rays, probably dropping gentle at the formation of the earliest supermassive black holes within the cosmos. This discovery used to be made the use of X-rays from NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory (depicted in red) and infrared knowledge from the James Webb House Telescope (proven in pink, inexperienced, blue).Galactic Distances and ObservationsThe extraordinarily far-off black hollow is positioned within the galaxy UHZ1 within the route of the galaxy cluster Abell 2744. The galaxy cluster is set 3.5 billion light-years from Earth. Webb knowledge, on the other hand, disclose that UHZ1 is far farther away than Abell 2744. At some 13.2 billion light-years away, UHZ1 is noticed when the universe used to be handiest 3% of its present age.Gravitational Lensing and X-ray DetectionBy the use of over two weeks of observations from Chandra, researchers had been in a position to stumble on X-ray emission from UHZ1 — a telltale signature of a rising supermassive black hollow within the middle of the galaxy. The X-ray sign is very faint and Chandra used to be handiest in a position to stumble on it — even with this lengthy statement — on account of the phenomenon referred to as gravitational lensing that enhanced the sign via an element of 4.Imaging Tactics and OrientationThe red portions of the picture display X-rays from massive quantities of scorching gasoline in Abell 2744. The infrared symbol displays loads of galaxies within the cluster, together with a couple of foreground stars. The insets zoom right into a small space focused on UHZ1. The small object within the Webb symbol is the far-off galaxy UHZ1 and the middle of the Chandra symbol displays X-rays from subject matter just about the supermassive black hollow in the course of UHZ1. The massive dimension of the X-ray supply in comparison to the infrared view of the galaxy is as it represents the smallest dimension that Chandra can get to the bottom of. The X-rays in reality come from a area this is a lot smaller than the galaxy.Other smoothing used to be carried out to the full-field Chandra symbol and to the Chandra symbol within the close-up. Smoothing throughout many pixels used to be carried out for the massive symbol, to spotlight the faint cluster emission, on the expense of now not appearing faint X-ray level resources like UHZ1. A lot much less smoothing used to be carried out to the close-up so faint X-ray resources are visual. The picture is orientated in order that north issues 42.5 levels to the appropriate of vertical. Representation: Formation of a Heavy Seed Black Hollow from Direct Cave in of a Large Cloud of Fuel. Credit score: NASA/STScI/Leah HustakSignificance of the DiscoveryThis discovery is vital for working out how some supermassive black holes — those who include as much as billions of sun plenty and are living within the facilities of galaxies — can achieve colossal plenty quickly after the Large Bang. Do they shape immediately from the cave in of big clouds of gasoline, growing black holes weighing between about 10000 and 100 thousand suns? Or do they arrive from explosions of the primary stars that create black holes weighing handiest between about ten and 100 suns?Analysis Findings and Theoretical ImplicationsThe group of astronomers discovered robust proof that the newly found out black hollow in UHZ1 used to be born huge. They estimate its mass falls between 10 and 100 million suns, in keeping with the brightness and effort of the X-rays. This mass vary is very similar to that of the entire stars within the galaxy the place it lives, which is in stark distinction to black holes within the facilities of galaxies within the within reach universe that typically include handiest a couple of 10th of a % of the mass in their host galaxy’s stars.The massive mass of the black hollow at a tender age, plus the quantity of X-rays it produces and the brightness of the galaxy detected via Webb, all consider theoretical predictions in 2017 for an “Outsize Black Hollow” that immediately shaped from the cave in of an enormous cloud of gasoline.Ongoing Analysis and CollaborationThe researchers plan to make use of this and different effects pouring in from Webb and the ones combining knowledge from different telescopes to fill out a bigger image of the early universe.The paper describing the consequences seems in Nature Astronomy. The authors come with Akos Bogdan (Heart for Astrophysics | Harvard & Smithsonian), Andy Goulding (Princeton College), Priyamvada Natarajan (Yale College), Orsolya Kovacs (Masaryk College, Czech Republic), Grant Tremblay (CfA), Urmila Chadayammuri (CfA), Marta Volonteri (Institut d’Astrophysique de Paris, France), Ralph Kraft (CfA), William Forman (CfA), Christine Jones (CfA), Eugene Churazov (Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics, Germany), and Irina Zhuravleva (College of Chicago).The Webb knowledge utilized in each papers is a part of a survey known as the Ultradeep Nirspec and nirCam ObserVations sooner than the Epoch of Reionization (UNCOVER). The paper led via UNCOVER group member Andy Goulding seems within the Astrophysical Magazine Letters. The co-authors come with different UNCOVER group contributors, plus Bogdan and Natarajan. An in depth interpretation paper that compares noticed homes of UHZ1 with theoretical fashions for Outsize Black Hollow Galaxies is lately underneath evaluate and a preprint is to be had right here.References:“Proof for heavy-seed beginning of early supermassive black holes from a z ≈ 10 X-ray quasar” via Ákos Bogdán, Andy D. Goulding, Priyamvada Natarajan, Orsolya E. Kovács, Grant R. Tremblay, Urmila Chadayammuri, Marta Volonteri, Ralph P. Kraft, William R. Forman, Christine Jones, Eugene Churazov and Irina Zhuravleva, 6 November 2023, Nature Astronomy.
Representation: Formation of a Heavy Seed Black Hollow from Direct Cave in of a Large Cloud of Fuel. Credit score: NASA/STScI/Leah HustakSignificance of the DiscoveryThis discovery is vital for working out how some supermassive black holes — those who include as much as billions of sun plenty and are living within the facilities of galaxies — can achieve colossal plenty quickly after the Large Bang. Do they shape immediately from the cave in of big clouds of gasoline, growing black holes weighing between about 10000 and 100 thousand suns? Or do they arrive from explosions of the primary stars that create black holes weighing handiest between about ten and 100 suns?Analysis Findings and Theoretical ImplicationsThe group of astronomers discovered robust proof that the newly found out black hollow in UHZ1 used to be born huge. They estimate its mass falls between 10 and 100 million suns, in keeping with the brightness and effort of the X-rays. This mass vary is very similar to that of the entire stars within the galaxy the place it lives, which is in stark distinction to black holes within the facilities of galaxies within the within reach universe that typically include handiest a couple of 10th of a % of the mass in their host galaxy’s stars.The massive mass of the black hollow at a tender age, plus the quantity of X-rays it produces and the brightness of the galaxy detected via Webb, all consider theoretical predictions in 2017 for an “Outsize Black Hollow” that immediately shaped from the cave in of an enormous cloud of gasoline.Ongoing Analysis and CollaborationThe researchers plan to make use of this and different effects pouring in from Webb and the ones combining knowledge from different telescopes to fill out a bigger image of the early universe.The paper describing the consequences seems in Nature Astronomy. The authors come with Akos Bogdan (Heart for Astrophysics | Harvard & Smithsonian), Andy Goulding (Princeton College), Priyamvada Natarajan (Yale College), Orsolya Kovacs (Masaryk College, Czech Republic), Grant Tremblay (CfA), Urmila Chadayammuri (CfA), Marta Volonteri (Institut d’Astrophysique de Paris, France), Ralph Kraft (CfA), William Forman (CfA), Christine Jones (CfA), Eugene Churazov (Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics, Germany), and Irina Zhuravleva (College of Chicago).The Webb knowledge utilized in each papers is a part of a survey known as the Ultradeep Nirspec and nirCam ObserVations sooner than the Epoch of Reionization (UNCOVER). The paper led via UNCOVER group member Andy Goulding seems within the Astrophysical Magazine Letters. The co-authors come with different UNCOVER group contributors, plus Bogdan and Natarajan. An in depth interpretation paper that compares noticed homes of UHZ1 with theoretical fashions for Outsize Black Hollow Galaxies is lately underneath evaluate and a preprint is to be had right here.References:“Proof for heavy-seed beginning of early supermassive black holes from a z ≈ 10 X-ray quasar” via Ákos Bogdán, Andy D. Goulding, Priyamvada Natarajan, Orsolya E. Kovács, Grant R. Tremblay, Urmila Chadayammuri, Marta Volonteri, Ralph P. Kraft, William R. Forman, Christine Jones, Eugene Churazov and Irina Zhuravleva, 6 November 2023, Nature Astronomy.
DOI: 10.1038/s41550-023-02111-9“UNCOVER: The Expansion of the First Large Black Holes from JWST/NIRSpec—Spectroscopic Redshift Affirmation of an X-Ray Luminous AGN at z = 10.1” via Andy D. Goulding, Jenny E. Greene, David J. Setton, Ivo Labbe, Rachel Bezanson, Tim B. Miller, Hakim Atek, Ákos Bogdán, Gabriel Brammer, Iryna Chemerynska, Sam E. Cutler, Pratika Dayal, Yoshinobu Fudamoto, Seiji Fujimoto, Lukas J. Furtak, Vasily Kokorev, Gourav Khullar, Joel Leja, Danilo Marchesini, Priyamvada Natarajan, Erica Nelson, Pascal A. Oesch, Richard Pan, Casey Papovich, Sedona H. Worth, Pieter van Dokkum, Bingjie Wang, 冰洁 王, John R. Weaver, Katherine E. Whitaker and Adi Zitrin, 22 September 2023, The Astrophysical Magazine Letters.
DOI: 10.3847/2041-8213/acf7c5NASA’s Marshall House Flight Heart manages the Chandra program. The Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory’s Chandra X-ray Heart controls science operations from Cambridge, Massachusetts, and flight operations from Burlington, Massachusetts.The James Webb House Telescope is the arena’s premier house science observatory. Webb will resolve mysteries in our sun device, glance past to far-off worlds round different stars, and probe the mysterious constructions and origins of our universe and our position in it. Webb is a global program led via NASA with its companions, ESA (Eu House Company) and the Canadian House Company.
NASA Discovers Report-Breaking Supermassive Black Hollow Over 13 Billion Gentle-Years Away