This artist’s influence depicts NASA’s Cassini spacecraft flying thru a plume of presumed water erupting from the skin of Saturn’s moon Enceladus. Credit score: NASANASA researchers have discovered that amino acids, doable signs of lifestyles, may just continue to exist close to the skin of Europa and Enceladus, moons of Jupiter and Saturn respectively.Experiments point out that those natural molecules can resist radiation just below the ice, making them out there to long run robot landers with out deep drilling.Exploring Lifestyles Attainable on Icy MoonsEuropa, a moon of Jupiter, and Enceladus, a moon of Saturn, have proof of oceans underneath their ice crusts. A NASA experiment means that if those oceans beef up lifestyles, signatures of that lifestyles within the type of natural molecules (e.g. amino acids, nucleic acids, and so on.) may just continue to exist just below the skin ice regardless of the tough radiation on those worlds. If robot landers are despatched to those moons to search for lifestyles indicators, they do not have to dig very deep to seek out amino acids that experience survived being altered or destroyed by means of radiation.“In response to our experiments, the ‘secure’ sampling intensity for amino acids on Europa is nearly 8 inches (round 20 centimeters) at excessive latitudes of the trailing hemisphere (hemisphere reverse to the route of Europa’s movement round Jupiter) within the space the place the skin hasn’t been disturbed a lot by means of meteorite affects,” stated Alexander Pavlov of NASA’s Goddard Area Flight Middle in Greenbelt, Maryland, lead writer of a paper at the analysis revealed July 18 within the magazine Astrobiology. “Subsurface sampling isn’t required for the detection of amino acids on Enceladus – those molecules will continue to exist radiolysis (breakdown by means of radiation) at any location at the Enceladus floor lower than a 10th of an inch (underneath a couple of millimeters) from the skin.”
This artist’s influence depicts NASA’s Cassini spacecraft flying thru a plume of presumed water erupting from the skin of Saturn’s moon Enceladus. Credit score: NASANASA researchers have discovered that amino acids, doable signs of lifestyles, may just continue to exist close to the skin of Europa and Enceladus, moons of Jupiter and Saturn respectively.Experiments point out that those natural molecules can resist radiation just below the ice, making them out there to long run robot landers with out deep drilling.Exploring Lifestyles Attainable on Icy MoonsEuropa, a moon of Jupiter, and Enceladus, a moon of Saturn, have proof of oceans underneath their ice crusts. A NASA experiment means that if those oceans beef up lifestyles, signatures of that lifestyles within the type of natural molecules (e.g. amino acids, nucleic acids, and so on.) may just continue to exist just below the skin ice regardless of the tough radiation on those worlds. If robot landers are despatched to those moons to search for lifestyles indicators, they do not have to dig very deep to seek out amino acids that experience survived being altered or destroyed by means of radiation.“In response to our experiments, the ‘secure’ sampling intensity for amino acids on Europa is nearly 8 inches (round 20 centimeters) at excessive latitudes of the trailing hemisphere (hemisphere reverse to the route of Europa’s movement round Jupiter) within the space the place the skin hasn’t been disturbed a lot by means of meteorite affects,” stated Alexander Pavlov of NASA’s Goddard Area Flight Middle in Greenbelt, Maryland, lead writer of a paper at the analysis revealed July 18 within the magazine Astrobiology. “Subsurface sampling isn’t required for the detection of amino acids on Enceladus – those molecules will continue to exist radiolysis (breakdown by means of radiation) at any location at the Enceladus floor lower than a 10th of an inch (underneath a couple of millimeters) from the skin.”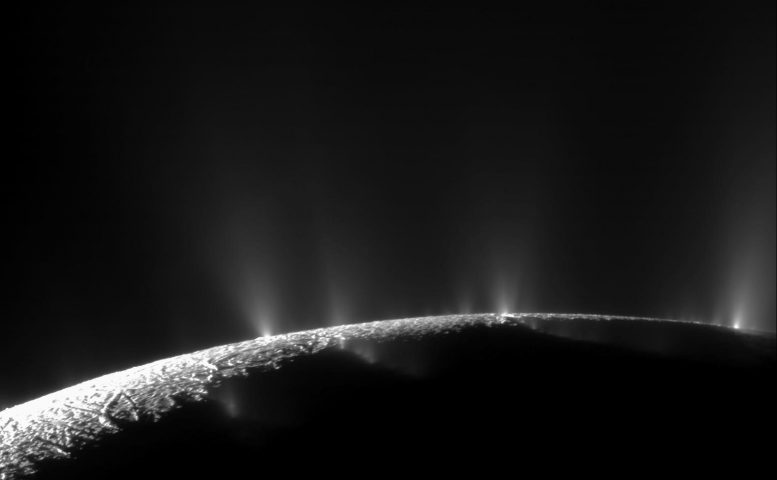 Dramatic plumes, each massive and small, spray water ice and vapor from many places alongside the famed “tiger stripes” close to the south pole of Saturn’s moon Enceladus. Credit score: NASA/JPL/Area Science InstituteThe frigid surfaces of those just about airless moons are most likely uninhabitable because of radiation from each high-speed debris trapped of their host planet’s magnetic fields and strong occasions in deep house, akin to exploding stars. Then again, each have oceans underneath their icy surfaces which can be heated by means of tides from the gravitational pull of the host planet and neighboring moons. Those subsurface oceans may just harbor lifestyles if they have got different prerequisites, akin to an calories provide in addition to components and compounds utilized in organic molecules.Experimental Approaches and FindingsThe analysis staff used amino acids in radiolysis experiments as imaginable representatives of biomolecules on icy moons. Amino acids may also be created by means of lifestyles or by means of non-biological chemistry. Then again, discovering positive varieties of amino acids on Europa or Enceladus can be a possible signal of lifestyles as a result of they’re utilized by terrestrial lifestyles as an element to construct proteins. Proteins are crucial to lifestyles as they’re used to make enzymes which accelerate or keep watch over chemical reactions and to make constructions. Amino acids and different compounds from subsurface oceans might be delivered to the skin by means of geyser task or the sluggish churning movement of the ice crust.
Dramatic plumes, each massive and small, spray water ice and vapor from many places alongside the famed “tiger stripes” close to the south pole of Saturn’s moon Enceladus. Credit score: NASA/JPL/Area Science InstituteThe frigid surfaces of those just about airless moons are most likely uninhabitable because of radiation from each high-speed debris trapped of their host planet’s magnetic fields and strong occasions in deep house, akin to exploding stars. Then again, each have oceans underneath their icy surfaces which can be heated by means of tides from the gravitational pull of the host planet and neighboring moons. Those subsurface oceans may just harbor lifestyles if they have got different prerequisites, akin to an calories provide in addition to components and compounds utilized in organic molecules.Experimental Approaches and FindingsThe analysis staff used amino acids in radiolysis experiments as imaginable representatives of biomolecules on icy moons. Amino acids may also be created by means of lifestyles or by means of non-biological chemistry. Then again, discovering positive varieties of amino acids on Europa or Enceladus can be a possible signal of lifestyles as a result of they’re utilized by terrestrial lifestyles as an element to construct proteins. Proteins are crucial to lifestyles as they’re used to make enzymes which accelerate or keep watch over chemical reactions and to make constructions. Amino acids and different compounds from subsurface oceans might be delivered to the skin by means of geyser task or the sluggish churning movement of the ice crust.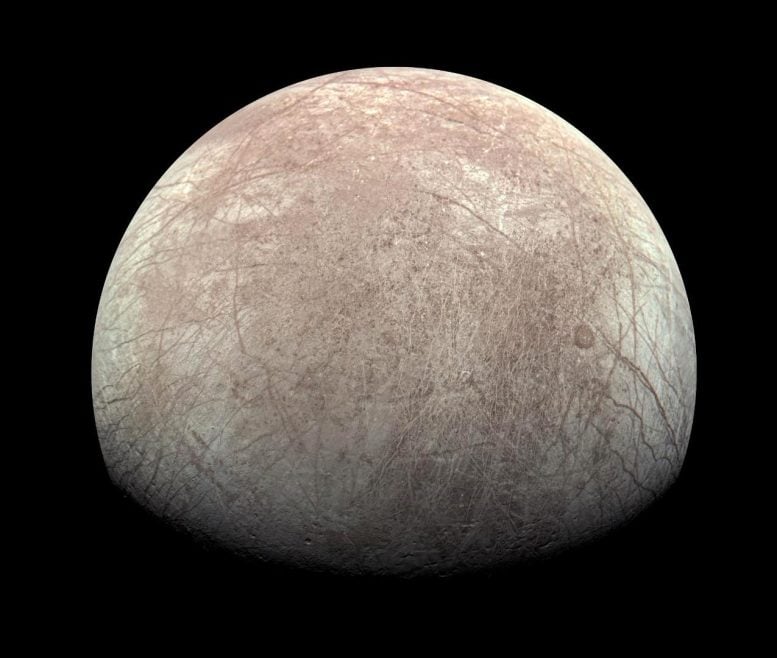 This view of Jupiter’s icy moon Europa used to be captured by means of JunoCam, the general public engagement digicam aboard NASA’s Juno spacecraft, right through the undertaking’s shut flyby on September 29, 2022. The image is a composite of JunoCam’s 2nd, 3rd, and fourth photographs taken right through the flyby, as observed from the standpoint of the fourth symbol. North is to the left. The pictures have a answer of simply over 0.5 to two.5 miles in line with pixel (1 to 4 kilometers in line with pixel). As with our Moon and Earth, one facet of Europa at all times faces Jupiter, and that’s the facet of Europa visual right here. Europa’s floor is crisscrossed by means of fractures, ridges, and bands, that have erased terrain older than about 90 million years. Citizen scientist Kevin M. Gill processed the pictures to toughen the colour and distinction. Credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech/SwRI/MSSS, Kevin M. Gill CC BY 3.0To assessment the survival of amino acids on those worlds, the staff blended samples of amino acids with ice chilled to about minus 321 Fahrenheit (-196 Celsius) in sealed, airless vials and bombarded them with gamma-rays, a kind of high-energy gentle, at quite a lot of doses. Because the oceans may host microscopic lifestyles, additionally they examined the survival of amino acids in useless micro organism in ice. After all, they examined samples of amino acids in ice blended with silicate mud to imagine the possible blending of subject material from meteorites or the inner with floor ice.Implications for Long run Area MissionsThe experiments supplied pivotal knowledge to resolve the charges at which amino acids smash down, referred to as radiolysis constants. With those, the staff used the age of the ice floor and the radiation surroundings at Europa and Enceladus to calculate the drilling intensity and places the place 10 p.c of the amino acids would continue to exist radiolytic destruction.Despite the fact that experiments to check the survival of amino acids in ice had been carried out prior to, that is the primary to make use of decrease radiation doses that don’t totally smash aside the amino acids, since simply changing or degrading them is sufficient to make it not possible to resolve if they’re doable indicators of lifestyles. This could also be the primary experiment the usage of Europa/Enceladus stipulations to judge the survival of those compounds in microorganisms and the primary to check the survival of amino acids blended with mud.The staff discovered that amino acids degraded quicker when blended with mud however slower when coming from microorganisms.
This view of Jupiter’s icy moon Europa used to be captured by means of JunoCam, the general public engagement digicam aboard NASA’s Juno spacecraft, right through the undertaking’s shut flyby on September 29, 2022. The image is a composite of JunoCam’s 2nd, 3rd, and fourth photographs taken right through the flyby, as observed from the standpoint of the fourth symbol. North is to the left. The pictures have a answer of simply over 0.5 to two.5 miles in line with pixel (1 to 4 kilometers in line with pixel). As with our Moon and Earth, one facet of Europa at all times faces Jupiter, and that’s the facet of Europa visual right here. Europa’s floor is crisscrossed by means of fractures, ridges, and bands, that have erased terrain older than about 90 million years. Citizen scientist Kevin M. Gill processed the pictures to toughen the colour and distinction. Credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech/SwRI/MSSS, Kevin M. Gill CC BY 3.0To assessment the survival of amino acids on those worlds, the staff blended samples of amino acids with ice chilled to about minus 321 Fahrenheit (-196 Celsius) in sealed, airless vials and bombarded them with gamma-rays, a kind of high-energy gentle, at quite a lot of doses. Because the oceans may host microscopic lifestyles, additionally they examined the survival of amino acids in useless micro organism in ice. After all, they examined samples of amino acids in ice blended with silicate mud to imagine the possible blending of subject material from meteorites or the inner with floor ice.Implications for Long run Area MissionsThe experiments supplied pivotal knowledge to resolve the charges at which amino acids smash down, referred to as radiolysis constants. With those, the staff used the age of the ice floor and the radiation surroundings at Europa and Enceladus to calculate the drilling intensity and places the place 10 p.c of the amino acids would continue to exist radiolytic destruction.Despite the fact that experiments to check the survival of amino acids in ice had been carried out prior to, that is the primary to make use of decrease radiation doses that don’t totally smash aside the amino acids, since simply changing or degrading them is sufficient to make it not possible to resolve if they’re doable indicators of lifestyles. This could also be the primary experiment the usage of Europa/Enceladus stipulations to judge the survival of those compounds in microorganisms and the primary to check the survival of amino acids blended with mud.The staff discovered that amino acids degraded quicker when blended with mud however slower when coming from microorganisms.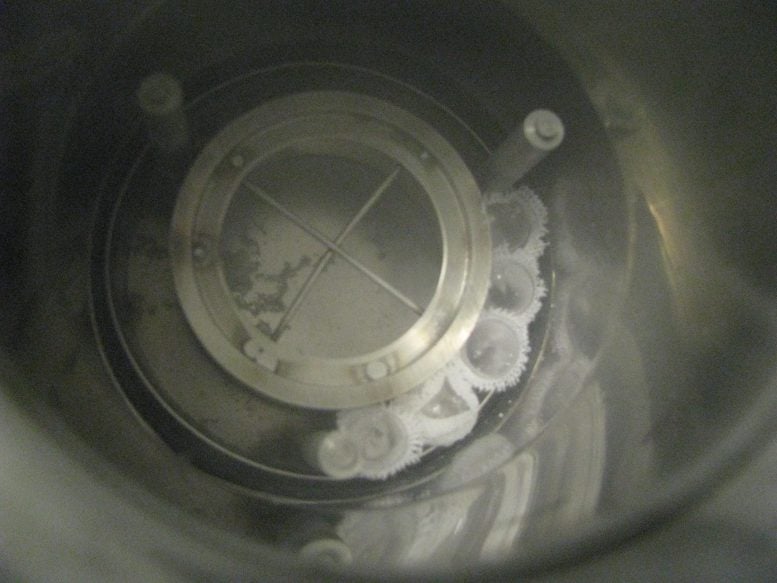 This symbol displays experiment samples loaded within the specifically designed dewar which might be full of liquid nitrogen in a while after and positioned underneath gamma radiation. Understand that the flame-sealed check tubes are wrapped in cotton cloth to stay them in combination as a result of check tubes transform buoyant in liquid nitrogen and get started floating round within the dewar, interfering with the correct radiation publicity. Credit score: Candace Davison“Gradual charges of amino acid destruction in organic samples underneath Europa and Enceladus-like floor stipulations bolster the case for long run life-detection measurements by means of Europa and Enceladus lander missions,” stated Pavlov. “Our effects point out that the charges of doable natural biomolecules’ degradation in silica-rich areas on each Europa and Enceladus are upper than in natural ice and, thus, imaginable long run missions to Europa and Enceladus will have to be wary in sampling silica-rich places on each icy moons.”A possible cause of why amino acids survived longer in micro organism comes to the techniques ionizing radiation adjustments molecules — without delay by means of breaking their chemical bonds or not directly by means of growing reactive compounds within reach which then adjust or smash down the molecule of pastime. It’s imaginable that bacterial mobile subject material safe amino acids from the reactive compounds produced by means of the radiation.Reference: “Variable and Huge Losses of Diagnostic Biomarkers After Simulated Cosmic Radiation Publicity in Clay- and Carbonate-Wealthy Mars Analog Samples” by means of Anaïs Roussel, Amy C. McAdam, Alex A. Pavlov, Christine A. Knudson, Cherie N. Achilles, Dionysis I. Foustoukos, Jason P. Dworkin, S. Andrejkovičová, Dina M. Bower and Sarah Stewart Johnson, 18 July 2024, Astrobiology.
This symbol displays experiment samples loaded within the specifically designed dewar which might be full of liquid nitrogen in a while after and positioned underneath gamma radiation. Understand that the flame-sealed check tubes are wrapped in cotton cloth to stay them in combination as a result of check tubes transform buoyant in liquid nitrogen and get started floating round within the dewar, interfering with the correct radiation publicity. Credit score: Candace Davison“Gradual charges of amino acid destruction in organic samples underneath Europa and Enceladus-like floor stipulations bolster the case for long run life-detection measurements by means of Europa and Enceladus lander missions,” stated Pavlov. “Our effects point out that the charges of doable natural biomolecules’ degradation in silica-rich areas on each Europa and Enceladus are upper than in natural ice and, thus, imaginable long run missions to Europa and Enceladus will have to be wary in sampling silica-rich places on each icy moons.”A possible cause of why amino acids survived longer in micro organism comes to the techniques ionizing radiation adjustments molecules — without delay by means of breaking their chemical bonds or not directly by means of growing reactive compounds within reach which then adjust or smash down the molecule of pastime. It’s imaginable that bacterial mobile subject material safe amino acids from the reactive compounds produced by means of the radiation.Reference: “Variable and Huge Losses of Diagnostic Biomarkers After Simulated Cosmic Radiation Publicity in Clay- and Carbonate-Wealthy Mars Analog Samples” by means of Anaïs Roussel, Amy C. McAdam, Alex A. Pavlov, Christine A. Knudson, Cherie N. Achilles, Dionysis I. Foustoukos, Jason P. Dworkin, S. Andrejkovičová, Dina M. Bower and Sarah Stewart Johnson, 18 July 2024, Astrobiology.
DOI: 10.1089/ast.2023.0123The analysis used to be supported by means of NASA underneath award quantity 80GSFC21M0002, NASA’s Planetary Science Department Interior Scientist Investment Program during the Basic Laboratory Analysis paintings bundle at Goddard, and NASA Astrobiology NfoLD award 80NSSC18K1140.
NASA Experiment Unearths: Lifestyles Indicators May just Continue to exist Close to Surfaces of Enceladus and Europa