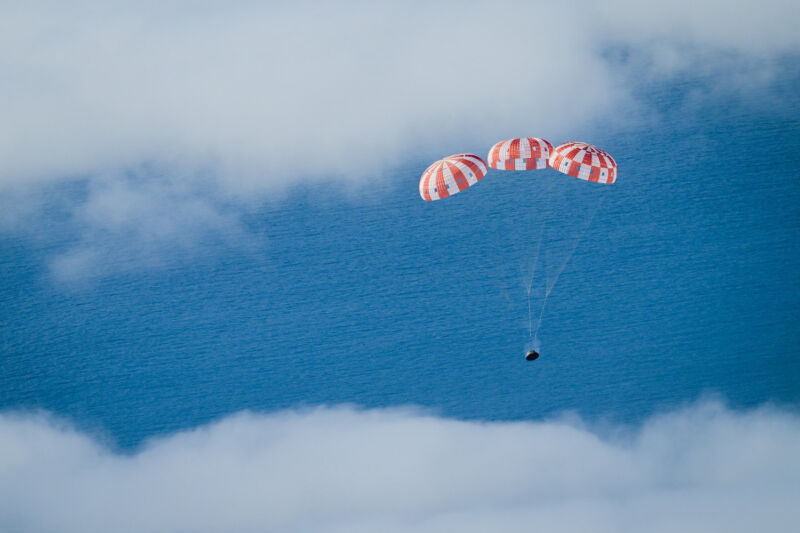
Magnify / NASA’s Orion spacecraft descends towards the Pacific Ocean on December 11, 2021, on the finish of the Artemis I venture.NASA
NASA officers declared the Artemis I venture a hit in past due 2021, and it is exhausting to argue with that overview. The House Release Device rocket and Orion spacecraft carried out just about flawlessly on an unpiloted flight that took it across the Moon and again to Earth, surroundings the level for the Artemis II, this system’s first workforce venture.
However one of the crucial issues engineers noticed on Artemis I that did not rather fit expectancies was once a subject with the Orion spacecraft’s warmth protect. Because the pill streaked again into Earth’s surroundings on the finish of the venture, the warmth protect ablated, or burned off, in a unique method than predicted by means of laptop fashions.
Extra of the charred subject matter than anticipated got here off the warmth protect right through the Artemis I reentry, and how it got here off was once slightly asymmetric, NASA officers stated. Orion’s warmth protect is made from a subject matter referred to as Avcoat, which is designed to burn off because the spacecraft plunges into the ambience at 25,000 mph (40,000 km in step with hour). Getting back from the Moon, Orion encountered temperatures as much as 5,000° Fahrenheit (2,760° Celsius), warmer than a spacecraft sees when it reenters the ambience from low-Earth orbit.
Regardless of warmth protect factor, the Orion spacecraft safely splashed down within the Pacific Ocean. Engineers came upon the asymmetric charring right through post-flight inspections.
No solutions but
Amit Kshatriya, who oversees building for the Artemis missions in NASA’s exploration department, stated Friday that the company continues to be on the lookout for the basis explanation for the warmth protect factor. Managers need to be sure that they perceive the purpose sooner than continuing with Artemis II, which can ship astronauts Reid Wiseman, Victor Glover, Christina Koch, and Jeremy Hansen on a 10-day flight across the some distance facet of the Moon.
Commercial
This would be the first time people fly close to the Moon because the remaining Apollo venture in 1972. In January, NASA introduced a lengthen within the release of Artemis II from past due 2024 till September 2025, in large part because of the unresolved investigation into the warmth protect factor.
“We’re nonetheless in the midst of our investigation at the efficiency of the warmth protect from Artemis I,” Kshatriya stated Friday in a gathering with a committee of the NASA Advisory Council.
Engineers have carried out sub-scale warmth protect checks in wind tunnels and arc jet amenities to higher perceive what ended in the asymmetric charring on Artemis I. “We’re getting as regards to the general solution on the subject of that purpose,” Kshatriya stated.
NASA officers prior to now stated it’s not going they are going to wish to make adjustments to the warmth protect already put in at the Orion spacecraft for Artemis II, however have not dominated it out. A redesign or adjustments to the Orion warmth protect on Artemis II would almost definitely lengthen the venture by means of a minimum of a yr.
As an alternative, engineers are inspecting the entire imaginable trajectories the Orion spacecraft may fly when it reenters the ambience on the finish of the Artemis II venture. On Artemis I, Orion flew a skip reentry profile, the place it dipped into the ambience, skipped again into house, after which made a last descent into the ambience, kind of like a rock skipping throughout a pond. This profile permits Orion to make extra exact splashdowns close to restoration groups within the Pacific Ocean and decreases g-forces at the spacecraft and the workforce using within. It additionally splits up the warmth load at the spacecraft into two levels.
Commercial
The Apollo missions flew a right away reentry profile. There may be a reentry mode to be had referred to as a ballistic access, during which the spacecraft would fly during the surroundings unguided.
 Magnify / Flooring groups at NASA’s Kennedy House Middle in Florida moved the Orion spacecraft for the Artemis II venture into an altitude chamber previous this month.
Magnify / Flooring groups at NASA’s Kennedy House Middle in Florida moved the Orion spacecraft for the Artemis II venture into an altitude chamber previous this month.
The charred subject matter started flying off the warmth protect within the first segment of the skip reentry. Engineers are taking a look at how the skip reentry profile affected the efficiency of the Orion warmth protect. NASA desires to know the way the Orion warmth protect would carry out right through each and every of the imaginable reentry trajectories for Artemis II.
“What we’ve got the research groups off doing is pronouncing, ‘OK, unbiased of what the limitations are going to be, what are we able to tolerate?” Kshatriya stated.
As soon as officers perceive the reason for the warmth protect charring, engineers will decide what sort of trajectory Artemis II must fly on reentry to reduce possibility to the workforce. Then, managers will have a look at construction what NASA calls flight rationale. Necessarily, this can be a means of convincing themselves the spacecraft is protected to fly.
“Once we sew all of it in combination, we’ll both have flight rationale or we received’t,” Kshatriya stated.
Assuming NASA approves the flight rationale for Artemis II, there shall be further discussions about how to make sure Orion warmth shields are protected to fly on downstream Artemis missions, which could have higher-speed reentry profiles as astronauts go back from landings at the Moon.
Within the period in-between, arrangements at the Orion spacecraft for Artemis II proceed at NASA’s Kennedy House Middle. The workforce and repair modules for Artemis II had been mated in combination previous this yr, and all of the Orion spacecraft is now within a vacuum chamber for environmental checking out.