TITUSVILLE, Fla. — NASA has decided on an ultraviolet observatory for construction however will prolong its release by way of two years on account of finances demanding situations.
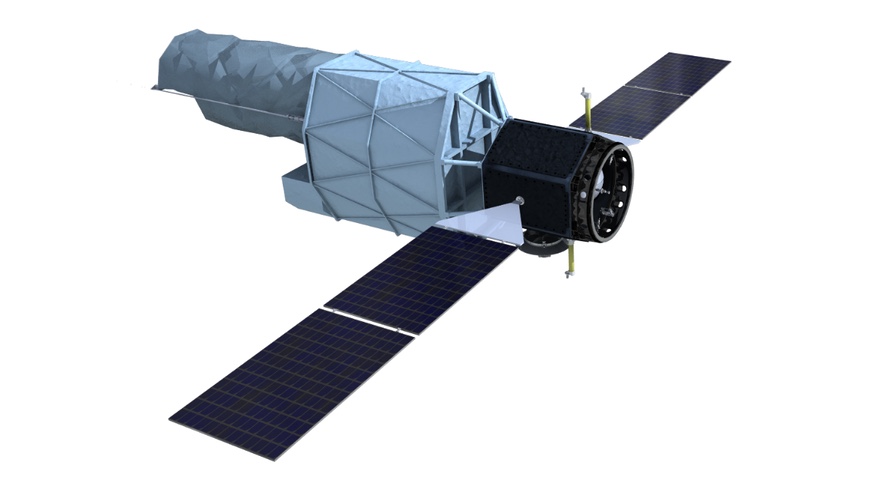
NASA introduced Feb. 13 that it selected the Ultraviolet Explorer, or UVEX, spacecraft as its subsequent astrophysics Medium-class Explorer challenge. The spacecraft will carry out an all-sky survey at ultraviolet wavelengths and be capable of determine ultraviolet resources of vigorous occasions like neutron superstar mergers that create bursts of gravitational waves.
“NASA’s UVEX will assist us higher perceive the character of each within sight and far away galaxies, in addition to apply up on dynamic occasions in our converting universe,” Nicola Fox, NASA affiliate administrator for science, stated in a commentary concerning the challenge’s variety.
The $300 million challenge might be led by way of Caltech astronomer Fiona Harrison, who used to be additionally the essential investigator at the Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR) Small Explorer challenge that introduced in 2012. Different companions on UVEX come with the College of California at Berkeley, Northrop Grumman and House Dynamics Laboratory.
NASA stated UVEX will release in 2030. Alternatively, when NASA decided on UVEX and every other proposal, the Survey and Time-domain Astrophysical Analysis Explorer (STAR-X) challenge, in August 2022 for additional find out about, the company stated the chosen challenge would fly in 2028.
NASA spokesperson Alise Fisher instructed SpaceNews Feb. 14 that the two-year prolong used to be related to finances problems inside NASA’s broader astrophysics program. “UVEX has a goal release date of 2030 to permit for a longer segment B to deal with finances demanding situations inside the Astrophysics Department portfolio,” she stated. Segment B covers preliminary design paintings on a challenge and features a initial design assessment.
“Extending UVEX’s segment B permits us to prioritize missions already in construction in order that NASA can nonetheless totally give a boost to them, whilst additionally supporting the leading edge UVEX idea,” she stated.
The previous director of NASA’s astrophysics department, Paul Hertz, warned of any such prolong in July 2022, mentioning decreased budgets then projected for fiscal 12 months 2023. That will imply, he stated then, having the challenge spend extra time in Segment B to gradual its spending ramp-up, delaying its release.
On the similar time NASA picked UVEX and STAR-X for added find out about, the company additionally decided on two different tasks as missions of alternative, more cost effective possible choices that frequently contain flying a payload on every other spacecraft or the World House Station. One, Moon Burst Energetics All-sky Track (MoonBEAM), would have flown a gamma-ray software in cislunar area on a smallsat very similar to NASA’s Lunar Trailblazer spacecraft. The opposite, A Massive House burst Polarimeter (LEAP), would have studied gamma-ray bursts the usage of an software at the ISS.
When NASA decided on LEAP and MoonBEAM for additional find out about, the company stated it might pick out one of the crucial missions, with an $80 million value cap, for flight by way of 2027. Alternatively, the company decided on neither challenge for construction, which NASA once more stated used to be in keeping with finances pressures.
“After detailed assessment by way of a panel of scientists and engineers, and after analysis in keeping with NASA’s present astrophysics portfolio coupled with to be had assets, NASA declined to choose a Undertaking of Alternative to proceed into construction,” Fisher stated. “NASA is in a constrained and unsure budgetary setting that necessitates considerate attention of plans and actions for all long run missions, whilst additionally making sure a balanced portfolio.”
NASA officers have warned of finances pressures at the company basically, together with its astrophysics systems. In October, Mark Clampin, present director of the company’s astrophysics department, stated cuts within the budgets for the Hubble House Telescope and Chandra X-Ray Observatory had been being regarded as in keeping with investment ranges for fiscal 12 months 2024 anticipated to be no upper than what the company won in 2023.
At a NASA the city corridor assembly throughout the American Astronomical Society assembly Jan. 8 in New Orleans, Clampin stated he used to be operating to prioritize missions of their high operations stages, just like the James Webb House Telescope, in addition to endured construction of the Roman House Telescope and early paintings on every other flagship telescope, the Liveable Worlds Observatory. Astrophysics analysis and research grants would even be safe, he stated.
That method, he stated, would make sure that a balanced portfolio throughout astrophysics. “We’re nonetheless extraordinarily well-funded. We’ve a large number of nice missions which can be running and we’ve a large number of nice systems which can be transferring ahead,” he stated. “I more or less have a look at this as a pitcher half-full. There’s a large number of alternative right here for each present astrophysics and long run astrophysics generations.”
Comparable











:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-2150879228-fad22bc836f0447c83ae797e2b768ce0.jpg)
