NASA’s most effective house telescope devoted to planetary protection has became off its transmitter for the final time, finishing its 15-year occupation detecting near-Earth asteroids and comets.The spacecraft — named NEOWISE (Close to-Earth Object Large-field Infrared Survey Explorer) — hugely outlived its unique seven-month undertaking to scan the sky for infrared alerts. It in the long run detected greater than 200 in the past unknown near-Earth items, together with 25 new comets, and equipped a wealth of knowledge on 44,000 different items that zoom thru our sun gadget, in line with NASA.NEOWISE’s undertaking, which formally ended on July 31, is in the end coming to an finish because the solar’s generation of top job, referred to as sun most, threatens to tug the satellite tv for pc into Earth’s environment for a last, fiery reentry. The spacecraft, which lacks propellant to thrust itself into the next orbit, has been often falling towards Earth for years and is predicted to securely deplete within the environment in overdue 2024.”This telescope has actually outlived its unique [lifespan],” Amy Mainzer, a professor on the College of California, Los Angeles and important investigator for each NEOWISE and its deliberate successor, NEO Surveyor, instructed Reside Science in an interview final 12 months. “We were given so a lot more out of it than we have been anticipating to get.”Comparable: ‘Planet killer’ asteroids are hiding within the solar’s glare. Are we able to prevent them in time?Retirement and rebirthNEOWISE introduced in 2009 as merely WISE, the Large-field Infrared Survey Explorer. Like a prototypical model of the James Webb House Telescope, WISE entered orbit with a undertaking to map all of the sky in infrared gentle, on the lookout for lines of faint and historic emissions from the early universe.Its unique seven-month undertaking confirmed that WISE was once way more delicate than scientists had anticipated. NASA then prolonged the undertaking underneath the identify NEOWISE to final till 2011, so the telescope may just survey the principle asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter. The telescope was once then put into hibernation after working out of coolant, which stored the spacecraft’s warmth from leaching into NEOWISE’s infrared sensors and lowering their sensitivity.Get the sector’s most attractive discoveries delivered instantly on your inbox.Nonetheless, later research of the telescope’s information confirmed it was once nonetheless able to detecting within reach sun gadget items that mirror daylight. Thus, NEOWISE was once introduced out of hibernation in 2013 to proceed its survey of near-Earth items for every other decade.A number of the loads of items the telescope came upon, its most renowned detection is the brilliant comet that bears its identify: comet C/2020 F3 NEOWISE, which zoomed previous Earth in July 2020.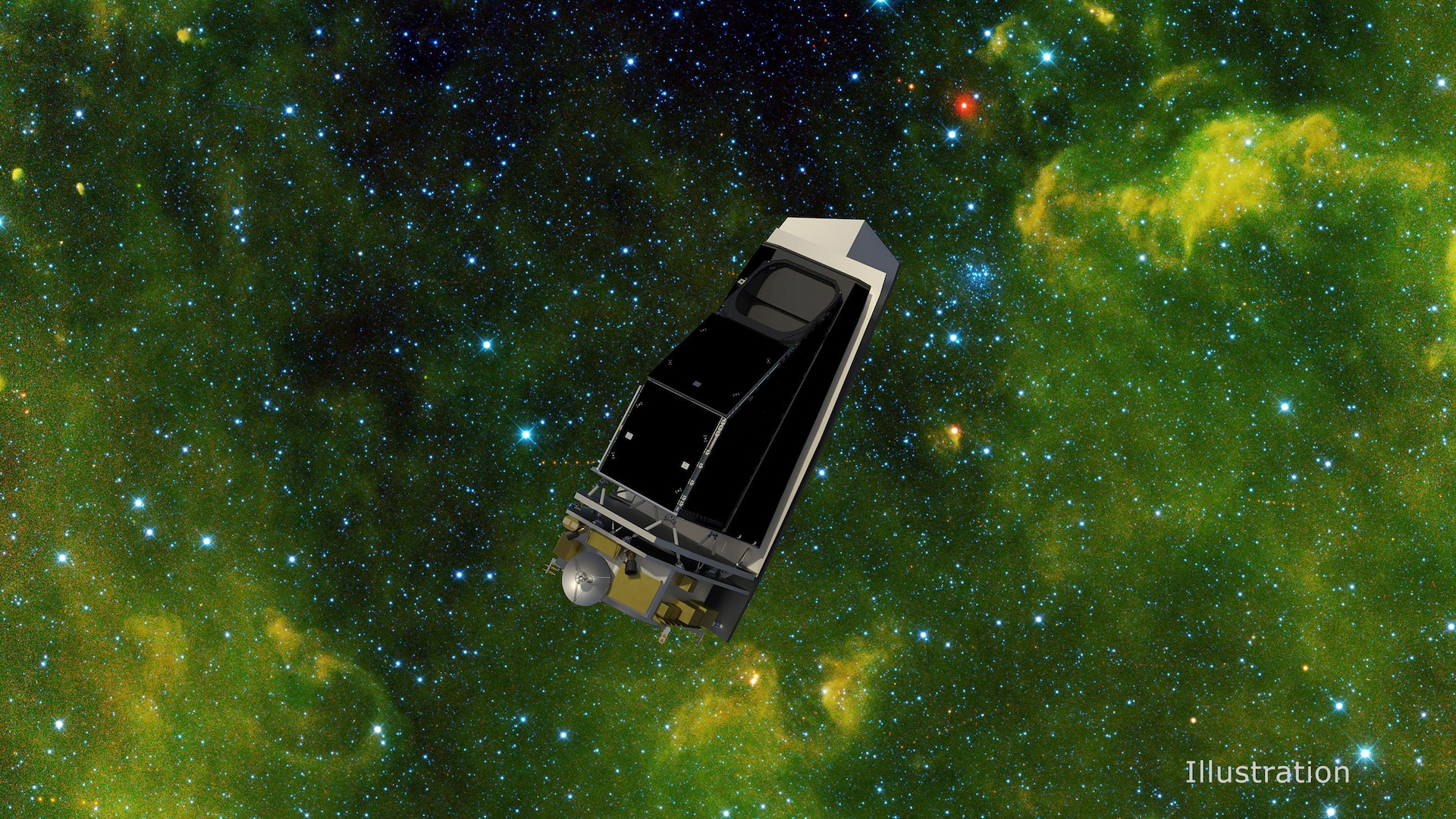 NEO Surveyor, deliberate for release no faster than 2027, will proceed the asteroid-hunting paintings of NEOWISE. (Symbol credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech/College of Arizona)An opening within the skiesThe death of NEOWISE leaves a brief planetary protection hole in Earth’s orbit. No different NASA house telescope devotes 100% of its time to attempting to find near-Earth items, a few of which might pose a threat to our planet.Alternatively, an much more robust infrared telescope referred to as NEO Surveyor is already within the works to proceed NEOWISE’s undertaking, with a deliberate release date of no faster than 2027. As soon as deployed, NEO Surveyor will whole a complete scan of the sky each and every two weeks, Mainzer mentioned. A purpose-built sun color will even permit the telescope to seek for asteroids positioned close to the glare of the solar — a area of house that is regarded as our greatest planetary protection blind spot.Within the intervening time, scientists will depend on robust ground-based observatories to ensure no pesky near-Earth asteroids sneak up on us.”We’re going to have the bottom founded telescopes, and this present day they to find the vast majority of the items anyway,” Mainzer mentioned. “Catalina Sky Survey [in Arizona] and Pan-STARRS [in Hawaii] are the 2 surveys which are finding the most important collection of items presently, and that’s the reason been that approach for a very long time.”With the assistance of surveys like those, astronomers have mapped the orbits of greater than 34,000 near-Earth asteroids, in line with NASA — and none pose a danger to Earth for no less than the following 100 years.
NEO Surveyor, deliberate for release no faster than 2027, will proceed the asteroid-hunting paintings of NEOWISE. (Symbol credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech/College of Arizona)An opening within the skiesThe death of NEOWISE leaves a brief planetary protection hole in Earth’s orbit. No different NASA house telescope devotes 100% of its time to attempting to find near-Earth items, a few of which might pose a threat to our planet.Alternatively, an much more robust infrared telescope referred to as NEO Surveyor is already within the works to proceed NEOWISE’s undertaking, with a deliberate release date of no faster than 2027. As soon as deployed, NEO Surveyor will whole a complete scan of the sky each and every two weeks, Mainzer mentioned. A purpose-built sun color will even permit the telescope to seek for asteroids positioned close to the glare of the solar — a area of house that is regarded as our greatest planetary protection blind spot.Within the intervening time, scientists will depend on robust ground-based observatories to ensure no pesky near-Earth asteroids sneak up on us.”We’re going to have the bottom founded telescopes, and this present day they to find the vast majority of the items anyway,” Mainzer mentioned. “Catalina Sky Survey [in Arizona] and Pan-STARRS [in Hawaii] are the 2 surveys which are finding the most important collection of items presently, and that’s the reason been that approach for a very long time.”With the assistance of surveys like those, astronomers have mapped the orbits of greater than 34,000 near-Earth asteroids, in line with NASA — and none pose a danger to Earth for no less than the following 100 years.