Contemporary observations via NASA’s X-ray telescopes have supplied extraordinary insights into rapid radio bursts (FRBs), robust and temporary cosmic occasions that experience at a loss for words astronomers. By means of finding out a quick radio burst from a magnetar inside our galaxy, scientists have complex our working out of those phenomena, revealing speedy adjustments in magnetar habits that might give an explanation for how FRBs are generated. Credit score: SciTechDaily.comUsing two of the company’s X-ray telescopes, researchers had been in a position to zoom in on a lifeless celebrity’s erratic habits because it launched a vivid, temporary burst of radio waves.What’s inflicting mysterious bursts of radio waves from deep house? Astronomers is also a step nearer to offering one solution to that query. Two NASA X-ray telescopes not too long ago seen one such match – referred to as a quick radio burst – mere mins prior to and after it passed off. This extraordinary view units scientists on a trail to higher perceive those excessive radio occasions.Whilst they just final for a fragment of a 2nd, rapid radio bursts can unlock about as a lot calories because the Solar does in a 12 months. Their gentle additionally paperwork a laser-like beam, atmosphere them except for extra chaotic cosmic explosions.The Supply of Rapid Radio BurstsBecause the bursts are so temporary, it’s regularly exhausting to pinpoint the place they arrive from. Previous to 2020, those who had been traced to their supply originated outdoor our personal galaxy – too a long way away for astronomers to peer what created them. Then a quick radio burst erupted in Earth’s house galaxy, originating from a particularly dense object referred to as a magnetar – the collapsed stays of an exploded celebrity.Working out Magnetar BehaviorIn October 2022, the similar magnetar – referred to as SGR 1935+2154 – produced any other rapid radio burst, this one studied intimately via NASA’s NICER (Neutron Megastar Inside Composition Explorer) at the World Area Station and NuSTAR (Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array) in low Earth orbit. The telescopes seen the magnetar for hours, catching a glimpse of what came about at the floor of the supply object and in its rapid environment, prior to and after the quick radio burst. The effects, described in a brand new find out about revealed on February 14 within the magazine Nature, are an instance of the way NASA telescopes can paintings in combination to look at and observe up on short-lived occasions within the cosmos.
Contemporary observations via NASA’s X-ray telescopes have supplied extraordinary insights into rapid radio bursts (FRBs), robust and temporary cosmic occasions that experience at a loss for words astronomers. By means of finding out a quick radio burst from a magnetar inside our galaxy, scientists have complex our working out of those phenomena, revealing speedy adjustments in magnetar habits that might give an explanation for how FRBs are generated. Credit score: SciTechDaily.comUsing two of the company’s X-ray telescopes, researchers had been in a position to zoom in on a lifeless celebrity’s erratic habits because it launched a vivid, temporary burst of radio waves.What’s inflicting mysterious bursts of radio waves from deep house? Astronomers is also a step nearer to offering one solution to that query. Two NASA X-ray telescopes not too long ago seen one such match – referred to as a quick radio burst – mere mins prior to and after it passed off. This extraordinary view units scientists on a trail to higher perceive those excessive radio occasions.Whilst they just final for a fragment of a 2nd, rapid radio bursts can unlock about as a lot calories because the Solar does in a 12 months. Their gentle additionally paperwork a laser-like beam, atmosphere them except for extra chaotic cosmic explosions.The Supply of Rapid Radio BurstsBecause the bursts are so temporary, it’s regularly exhausting to pinpoint the place they arrive from. Previous to 2020, those who had been traced to their supply originated outdoor our personal galaxy – too a long way away for astronomers to peer what created them. Then a quick radio burst erupted in Earth’s house galaxy, originating from a particularly dense object referred to as a magnetar – the collapsed stays of an exploded celebrity.Working out Magnetar BehaviorIn October 2022, the similar magnetar – referred to as SGR 1935+2154 – produced any other rapid radio burst, this one studied intimately via NASA’s NICER (Neutron Megastar Inside Composition Explorer) at the World Area Station and NuSTAR (Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array) in low Earth orbit. The telescopes seen the magnetar for hours, catching a glimpse of what came about at the floor of the supply object and in its rapid environment, prior to and after the quick radio burst. The effects, described in a brand new find out about revealed on February 14 within the magazine Nature, are an instance of the way NASA telescopes can paintings in combination to look at and observe up on short-lived occasions within the cosmos.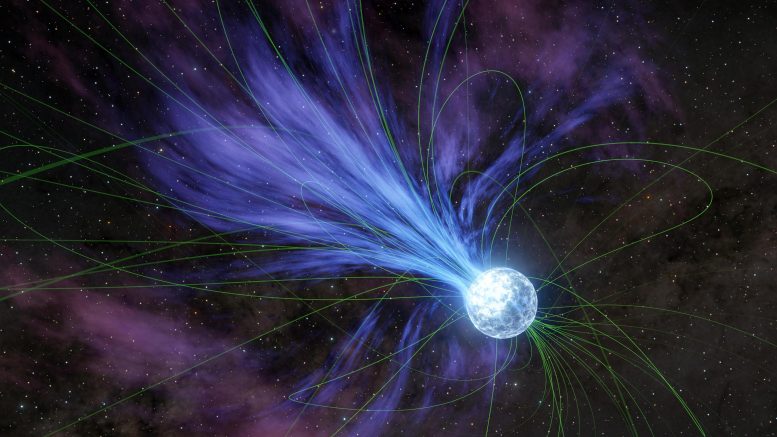 In an ejection that might have led to its rotation to sluggish, a magnetar is depicted dropping subject material into house on this artist’s idea. The magnetar’s sturdy, twisted magnetic box strains (proven in inexperienced) can affect the go with the flow of electrically charged subject material from the article, which is a kind of neutron celebrity. Credit score: NASA/JPL-CaltechThe burst passed off between two “system faults,” when the magnetar began spinning quicker. SGR 1935+2154 is estimated to be about 12 miles (20 kilometers) throughout and spinning about 3.2 occasions in step with 2nd, which means its floor was once shifting at about 7,000 mph (11,000 kph). Slowing it down or dashing it up will require a vital quantity of calories. That’s why find out about authors had been stunned to peer that during between system faults, the magnetar slowed right down to not up to its pre-glitch velocity in simply 9 hours, or about 100 occasions extra hastily than has ever been seen in a magnetar.“In most cases, when system faults occur, it takes the magnetar weeks or months to get again to its standard velocity,” stated Chin-Ping Hu, an astrophysicist at Nationwide Changhua College of Schooling in Taiwan and the lead writer of the brand new find out about. “So obviously issues are taking place with those items on a lot shorter time scales than we in the past concept, and that may well be associated with how briskly radio bursts are generated.”The Physics of MagnetarsWhen looking to piece in combination precisely how magnetars produce rapid radio bursts, scientists have numerous variables to believe.As an example, magnetars (which might be a kind of neutron celebrity) are so dense {that a} teaspoon in their subject material would weigh a few billion heaps on Earth. This type of excessive density additionally way a powerful gravitational pull: A marshmallow falling onto a regular neutron celebrity would affect with the drive of an early atomic bomb.The sturdy gravity way the outside of a magnetar is a risky position, continuously liberating bursts of X-rays and higher-energy gentle. Prior to the quick radio burst that passed off in 2022, the magnetar began liberating eruptions of X-rays and gamma rays (much more vigorous wavelengths of sunshine) that had been seen within the peripheral imaginative and prescient of high-energy house telescopes. This building up in process induced challenge operators to indicate NICER and NuSTAR without delay on the magnetar.“All the ones X-ray bursts that came about prior to this glitch would have had, in concept, sufficient calories to create a quick radio burst, however they didn’t,” stated find out about co-author Zorawar Wadiasingh, a analysis scientist on the College of Maryland, School Park, and NASA’s Goddard Area Flight Middle. “So it kind of feels like one thing modified throughout the slowdown length, developing the precise set of stipulations.”What else would possibly have came about with SGR 1935+2154 to provide a quick radio burst? One issue may well be that the outside of a magnetar is cast, and the excessive density crushes the inner right into a state referred to as a superfluid. Every so often, the 2 can get out of sync, like water sloshing round within a spinning fishbowl. When this occurs, the fluid can ship calories to the crust. The paper authors suppose that is most likely what led to each system faults that bookended the quick radio burst.If the preliminary glitch led to a crack within the magnetar’s floor, it will have launched subject material from the celebrity’s internal into house like a volcanic eruption. Shedding mass reasons spinning items to decelerate, so the researchers suppose this is able to give an explanation for the magnetar’s speedy deceleration.Implications for Long term ResearchBut having seen most effective any such occasions in actual time, the staff nonetheless can’t say needless to say which of those components (or others, such because the magnetar’s robust magnetic box) would possibly result in the manufacturing of a quick radio burst. Some will not be hooked up to the burst in any respect.“We’ve definitely seen one thing vital for our working out of rapid radio bursts,” stated George Younes, a researcher at Goddard and a member of the NICER science staff focusing on magnetars. “However I believe we nonetheless want much more knowledge to finish the thriller.”Reference: “Speedy spin adjustments round a magnetar rapid radio burst” via Chin-Ping Hu, Takuto Narita, Teruaki Enoto, George Younes, Zorawar Wadiasingh, Matthew G. Baring, Wynn C. G. Ho, Sebastien Guillot, Paul S. Ray, Tolga Güver, Kaustubh Rajwade, Zaven Arzoumanian, Chryssa Kouveliotou, Alice Ok. Harding and Keith C. Gendreau, 14 February 2024, Nature.
In an ejection that might have led to its rotation to sluggish, a magnetar is depicted dropping subject material into house on this artist’s idea. The magnetar’s sturdy, twisted magnetic box strains (proven in inexperienced) can affect the go with the flow of electrically charged subject material from the article, which is a kind of neutron celebrity. Credit score: NASA/JPL-CaltechThe burst passed off between two “system faults,” when the magnetar began spinning quicker. SGR 1935+2154 is estimated to be about 12 miles (20 kilometers) throughout and spinning about 3.2 occasions in step with 2nd, which means its floor was once shifting at about 7,000 mph (11,000 kph). Slowing it down or dashing it up will require a vital quantity of calories. That’s why find out about authors had been stunned to peer that during between system faults, the magnetar slowed right down to not up to its pre-glitch velocity in simply 9 hours, or about 100 occasions extra hastily than has ever been seen in a magnetar.“In most cases, when system faults occur, it takes the magnetar weeks or months to get again to its standard velocity,” stated Chin-Ping Hu, an astrophysicist at Nationwide Changhua College of Schooling in Taiwan and the lead writer of the brand new find out about. “So obviously issues are taking place with those items on a lot shorter time scales than we in the past concept, and that may well be associated with how briskly radio bursts are generated.”The Physics of MagnetarsWhen looking to piece in combination precisely how magnetars produce rapid radio bursts, scientists have numerous variables to believe.As an example, magnetars (which might be a kind of neutron celebrity) are so dense {that a} teaspoon in their subject material would weigh a few billion heaps on Earth. This type of excessive density additionally way a powerful gravitational pull: A marshmallow falling onto a regular neutron celebrity would affect with the drive of an early atomic bomb.The sturdy gravity way the outside of a magnetar is a risky position, continuously liberating bursts of X-rays and higher-energy gentle. Prior to the quick radio burst that passed off in 2022, the magnetar began liberating eruptions of X-rays and gamma rays (much more vigorous wavelengths of sunshine) that had been seen within the peripheral imaginative and prescient of high-energy house telescopes. This building up in process induced challenge operators to indicate NICER and NuSTAR without delay on the magnetar.“All the ones X-ray bursts that came about prior to this glitch would have had, in concept, sufficient calories to create a quick radio burst, however they didn’t,” stated find out about co-author Zorawar Wadiasingh, a analysis scientist on the College of Maryland, School Park, and NASA’s Goddard Area Flight Middle. “So it kind of feels like one thing modified throughout the slowdown length, developing the precise set of stipulations.”What else would possibly have came about with SGR 1935+2154 to provide a quick radio burst? One issue may well be that the outside of a magnetar is cast, and the excessive density crushes the inner right into a state referred to as a superfluid. Every so often, the 2 can get out of sync, like water sloshing round within a spinning fishbowl. When this occurs, the fluid can ship calories to the crust. The paper authors suppose that is most likely what led to each system faults that bookended the quick radio burst.If the preliminary glitch led to a crack within the magnetar’s floor, it will have launched subject material from the celebrity’s internal into house like a volcanic eruption. Shedding mass reasons spinning items to decelerate, so the researchers suppose this is able to give an explanation for the magnetar’s speedy deceleration.Implications for Long term ResearchBut having seen most effective any such occasions in actual time, the staff nonetheless can’t say needless to say which of those components (or others, such because the magnetar’s robust magnetic box) would possibly result in the manufacturing of a quick radio burst. Some will not be hooked up to the burst in any respect.“We’ve definitely seen one thing vital for our working out of rapid radio bursts,” stated George Younes, a researcher at Goddard and a member of the NICER science staff focusing on magnetars. “However I believe we nonetheless want much more knowledge to finish the thriller.”Reference: “Speedy spin adjustments round a magnetar rapid radio burst” via Chin-Ping Hu, Takuto Narita, Teruaki Enoto, George Younes, Zorawar Wadiasingh, Matthew G. Baring, Wynn C. G. Ho, Sebastien Guillot, Paul S. Ray, Tolga Güver, Kaustubh Rajwade, Zaven Arzoumanian, Chryssa Kouveliotou, Alice Ok. Harding and Keith C. Gendreau, 14 February 2024, Nature.
DOI: 10.1038/s41586-023-07012-5More In regards to the MissionA Small Explorer challenge led via Caltech and controlled via NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California for the company’s Science Project Directorate in Washington, NuSTAR was once evolved in partnership with the Danish Technical College and the Italian Area Company (ASI). The spacecraft was once constructed via Orbital Sciences Corp. in Dulles, Virginia. NuSTAR’s challenge operations heart is on the College of California, Berkeley, and the authentic knowledge archive is at NASA’s Top Power Astrophysics Science Archive Analysis Middle at NASA’s Goddard Area Flight Middle. ASI supplies the challenge’s floor station and a replicate knowledge archive. Caltech manages JPL for NASA.
NASA Telescopes Are Unlocking the Secrets and techniques In the back of Mysterious Deep Area Indicators