Scientists have found out that the objective asteroid of NASA’s Double Asteroid Redirection Take a look at (DART) can have been reshaped by way of the affect. A brand new investigation into the collision’s aftermath printed that the asteroid, which is the smaller element of a binary asteroid gadget, shows a free “rubble-pile” composition.DART slammed into the moonlet Dimorphos, which orbits the bigger area rock Didymos, on Sept. 26, 2023. The purpose of this cosmic attack was once to peer if a kinetic affect may shift an asteroid’s trajectory round a bigger object and examine that this system may well be used to shunt an area rock in the future if its trail fell on a collision path with Earth.Six months after the affect, NASA showed the undertaking were a success, with the time it takes Dimorphos to orbit its greater asteroid significant other lowered by way of 33 mins. Submit-impact, considered one of Dimorphos’ orbits round Didymos takes about 11 hours and 23 mins. And now, new analysis presentations the affect may additionally have had main results at the form of Dimorphos.Similar: Scientists hail DART good fortune 6 months after ancient asteroid crashA group led by way of College of Bern scientist Sabina Raducan used state of the art laptop modeling to first decide that Dimorphos is a free, rubble-pile asteroid. This additionally way the moonlet can have shaped from subject matter that was once ejected from its greater asteroid spouse, Didymos.The simulations that had been the nearest fit to observations of the affect recommend Dimorphos is handiest weakly cohesive and has a loss of huge boulders on its floor.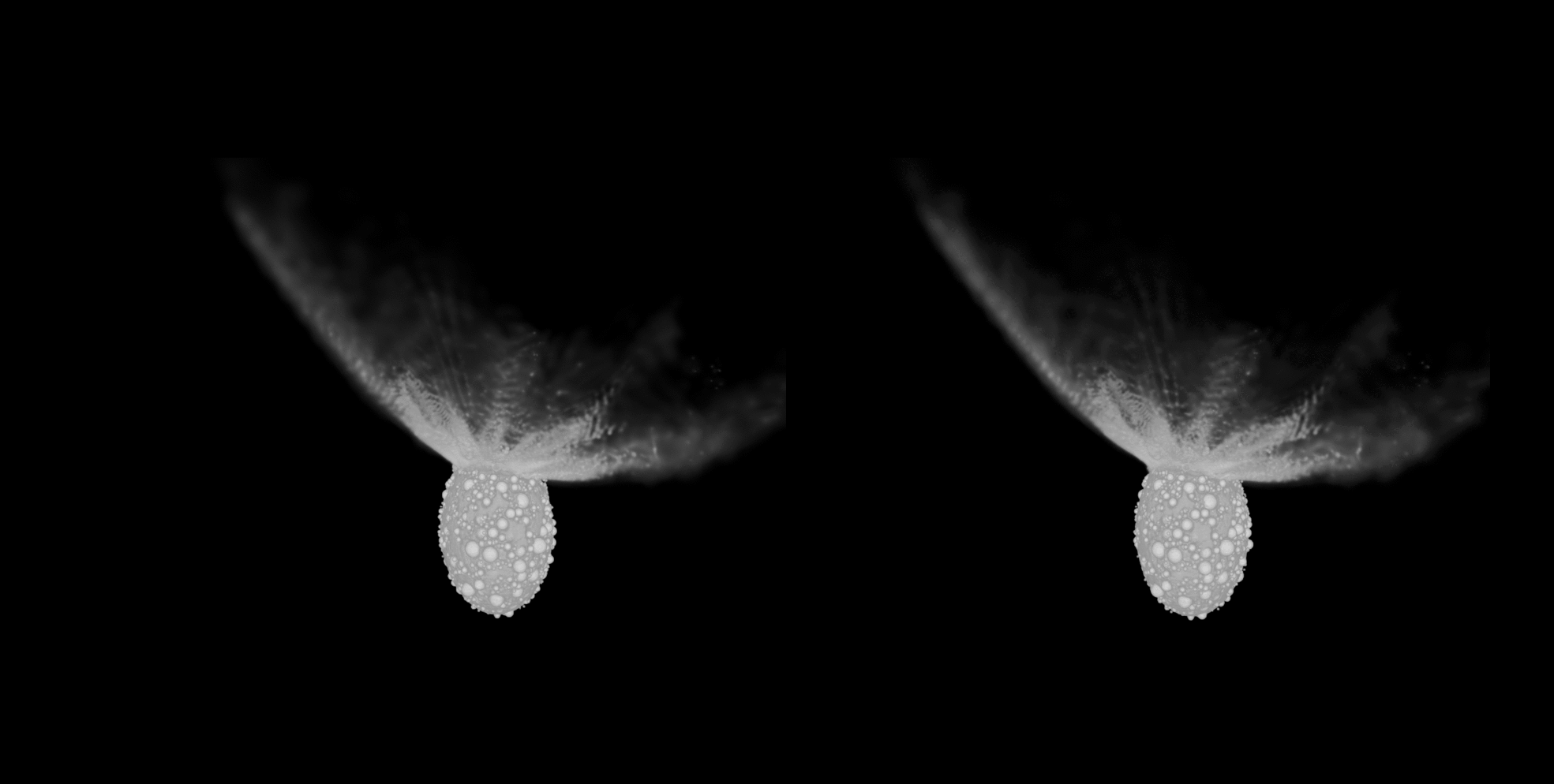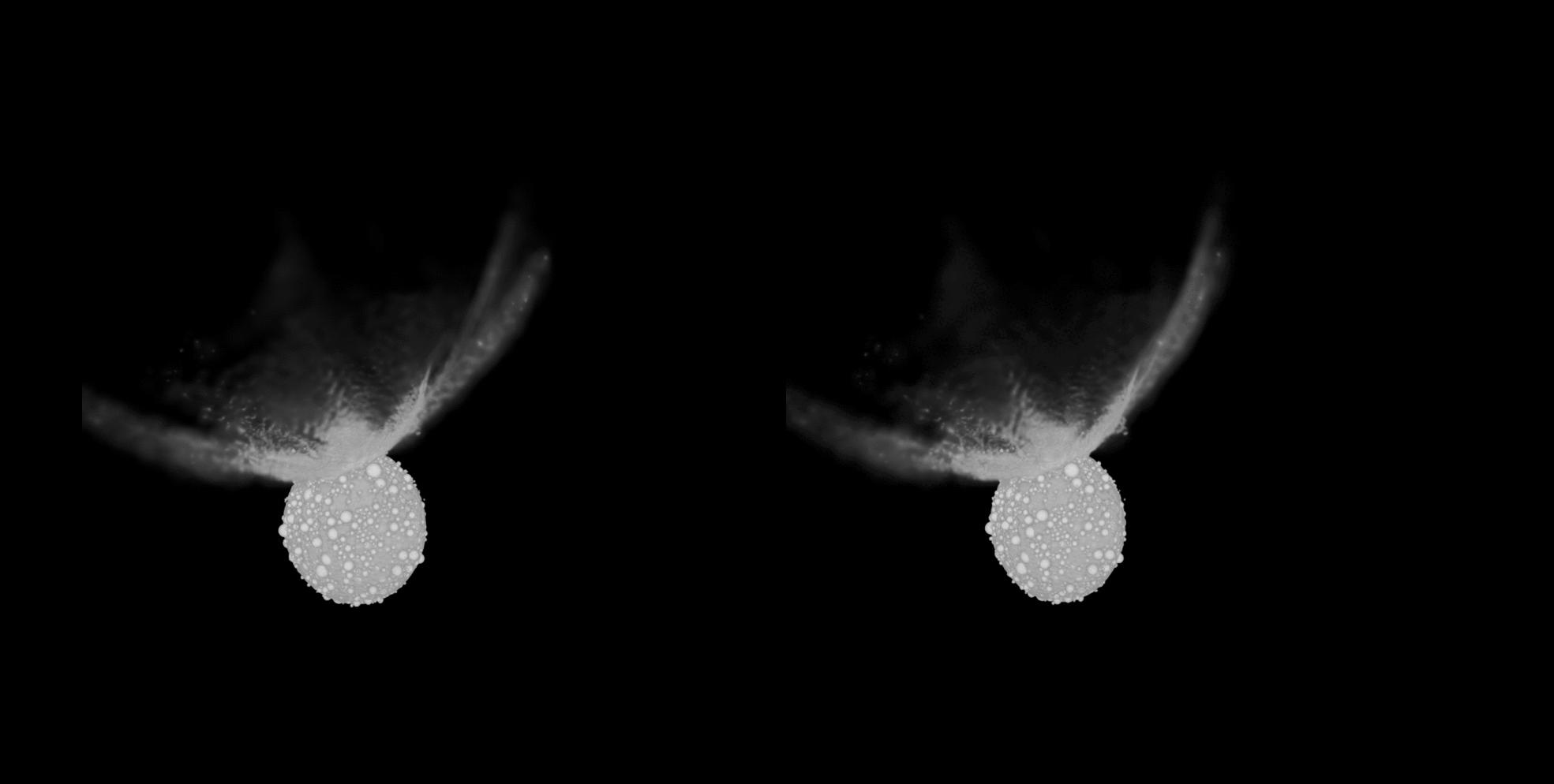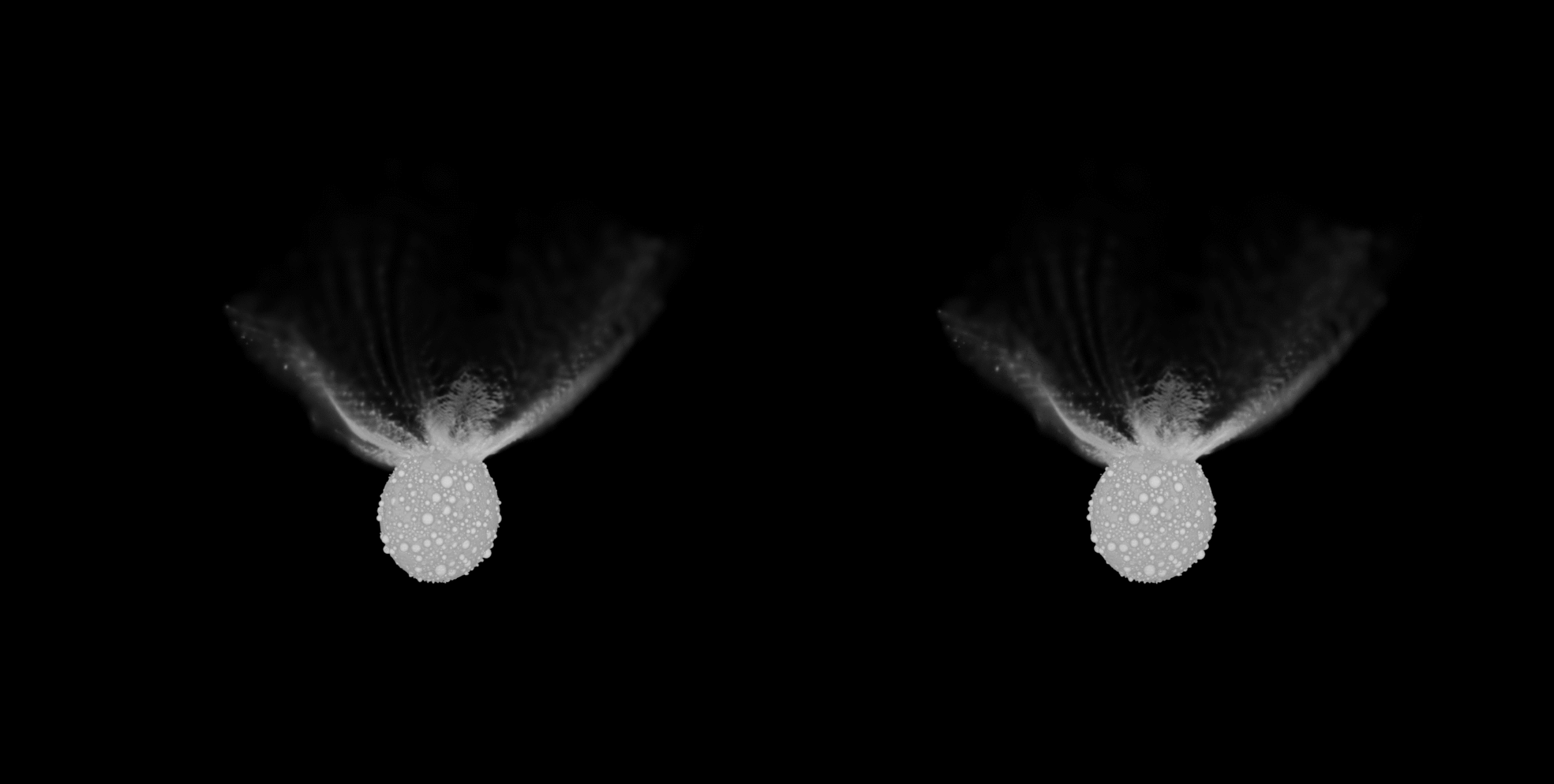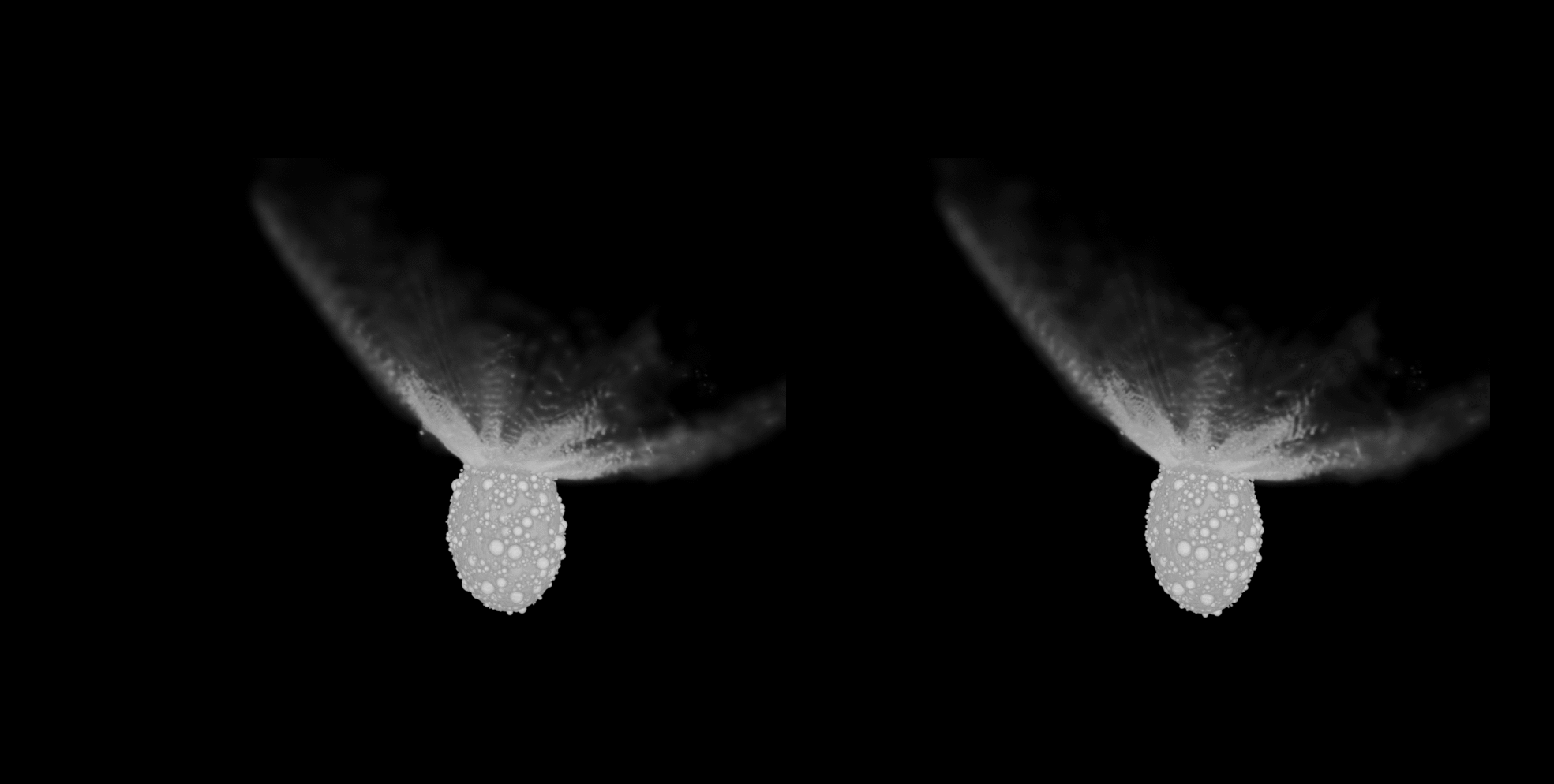 The DART affect on Didymos simulated in 3-d (Symbol credit score: S.D. Raducan)”Sooner than DART’s arrival at Dimorphos, we didn’t know what to anticipate. Since the gadget is to this point clear of Earth, Dimorphos was once now not correctly resolved. Due to this fact, we can have encountered anything else from a monolithic frame — necessarily a big boulder the dimensions of Dimorphos — to a cohesionless rubble pile or anything else in between,” Raducan instructed Area.com. “So, whilst the affect end result got here as a marvel to maximum, it was once one of the crucial predicted situations.”Raducan added that, whilst preparedness supposed the rubble-pile nature of Dimorphos wasn’t too unexpected, DART has printed different issues that did take the group off guard.”Dimorphos have an excessively other composition from asteroids Ryugu and Bennu, however their response to affects, seeming to be very equivalent, was once unexpected,” Raducan mentioned. “For all of those asteroids, cratering happens in a low-gravity, low-cohesion regime, the place the crater grows time and again greater than the projectile.
The DART affect on Didymos simulated in 3-d (Symbol credit score: S.D. Raducan)”Sooner than DART’s arrival at Dimorphos, we didn’t know what to anticipate. Since the gadget is to this point clear of Earth, Dimorphos was once now not correctly resolved. Due to this fact, we can have encountered anything else from a monolithic frame — necessarily a big boulder the dimensions of Dimorphos — to a cohesionless rubble pile or anything else in between,” Raducan instructed Area.com. “So, whilst the affect end result got here as a marvel to maximum, it was once one of the crucial predicted situations.”Raducan added that, whilst preparedness supposed the rubble-pile nature of Dimorphos wasn’t too unexpected, DART has printed different issues that did take the group off guard.”Dimorphos have an excessively other composition from asteroids Ryugu and Bennu, however their response to affects, seeming to be very equivalent, was once unexpected,” Raducan mentioned. “For all of those asteroids, cratering happens in a low-gravity, low-cohesion regime, the place the crater grows time and again greater than the projectile.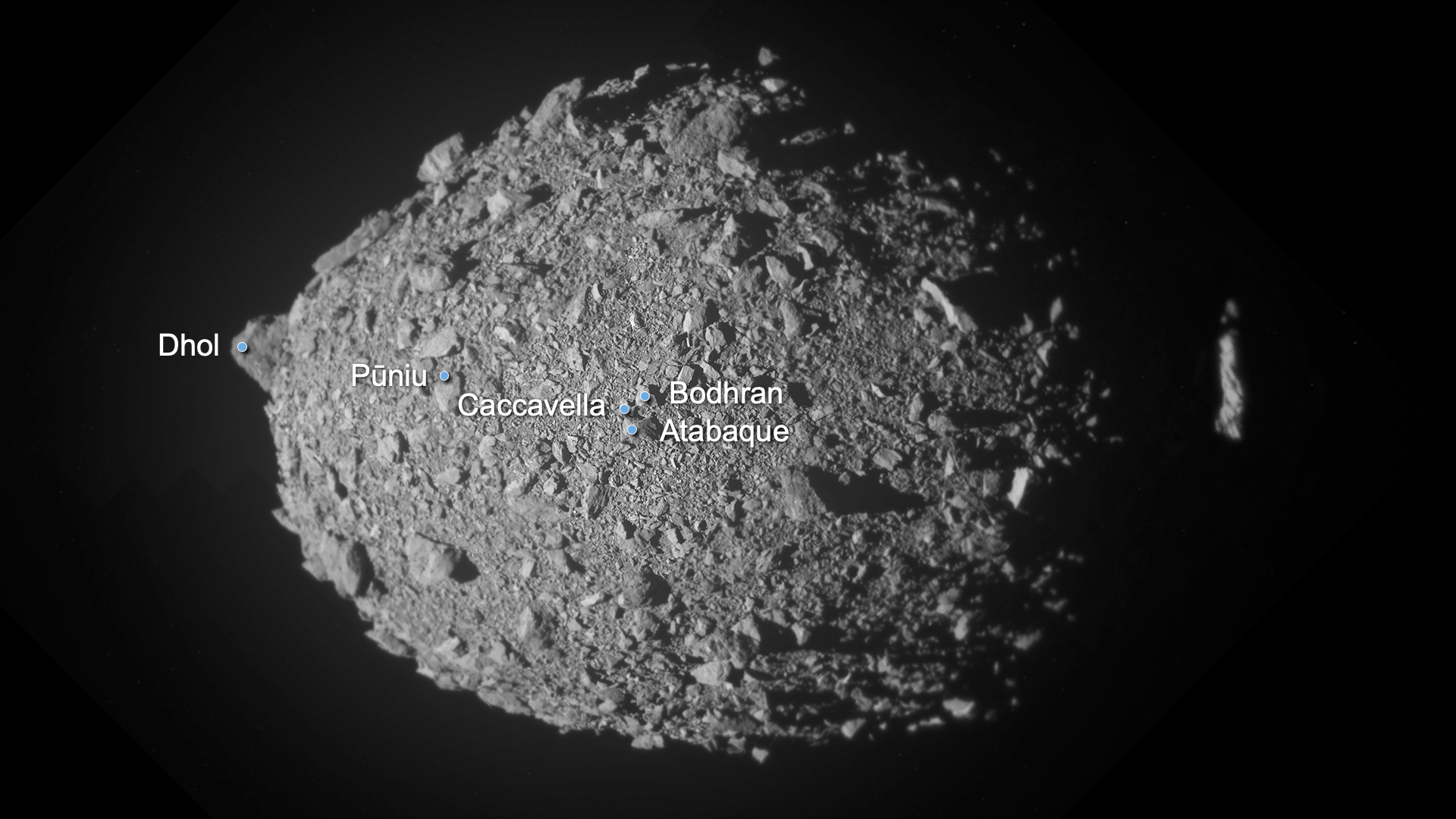 DART view of Dimorphos, with newly named options annotated. 3 of the 5 options are on the middle of Dimorphos, whilst Dhol marks the large boulder at the moon’s limb. Pūniu is a tiny rock that will likely be used to notice latitudes and longitudes, scientists mentioned. (Symbol credit score: NASA/Johns Hopkins APL)Plus, in keeping with the group’s calculations, slightly than simply developing an affect crater, the DART collision turns out to have utterly reshaped Dimorphos. This may’ve came about thru a procedure known as international deformation. In flip, the reshaping seems to have led to the outside of the moonlet to be resurfaced with subject matter from its internal.The group’s simulations confirmed that between 0.5% and 1% of Dimorphos’ mass was once ejected on account of the DART affect, whilst 8% of its mass was once redistributed, resulting in vital reshaping and resurfacing of the asteroid. Raducan added that those findings recommend the structural integrities and responses to affects of small asteroids are most probably profoundly influenced by way of their inside compositions and the distributions in their constituent fabrics.
DART view of Dimorphos, with newly named options annotated. 3 of the 5 options are on the middle of Dimorphos, whilst Dhol marks the large boulder at the moon’s limb. Pūniu is a tiny rock that will likely be used to notice latitudes and longitudes, scientists mentioned. (Symbol credit score: NASA/Johns Hopkins APL)Plus, in keeping with the group’s calculations, slightly than simply developing an affect crater, the DART collision turns out to have utterly reshaped Dimorphos. This may’ve came about thru a procedure known as international deformation. In flip, the reshaping seems to have led to the outside of the moonlet to be resurfaced with subject matter from its internal.The group’s simulations confirmed that between 0.5% and 1% of Dimorphos’ mass was once ejected on account of the DART affect, whilst 8% of its mass was once redistributed, resulting in vital reshaping and resurfacing of the asteroid. Raducan added that those findings recommend the structural integrities and responses to affects of small asteroids are most probably profoundly influenced by way of their inside compositions and the distributions in their constituent fabrics.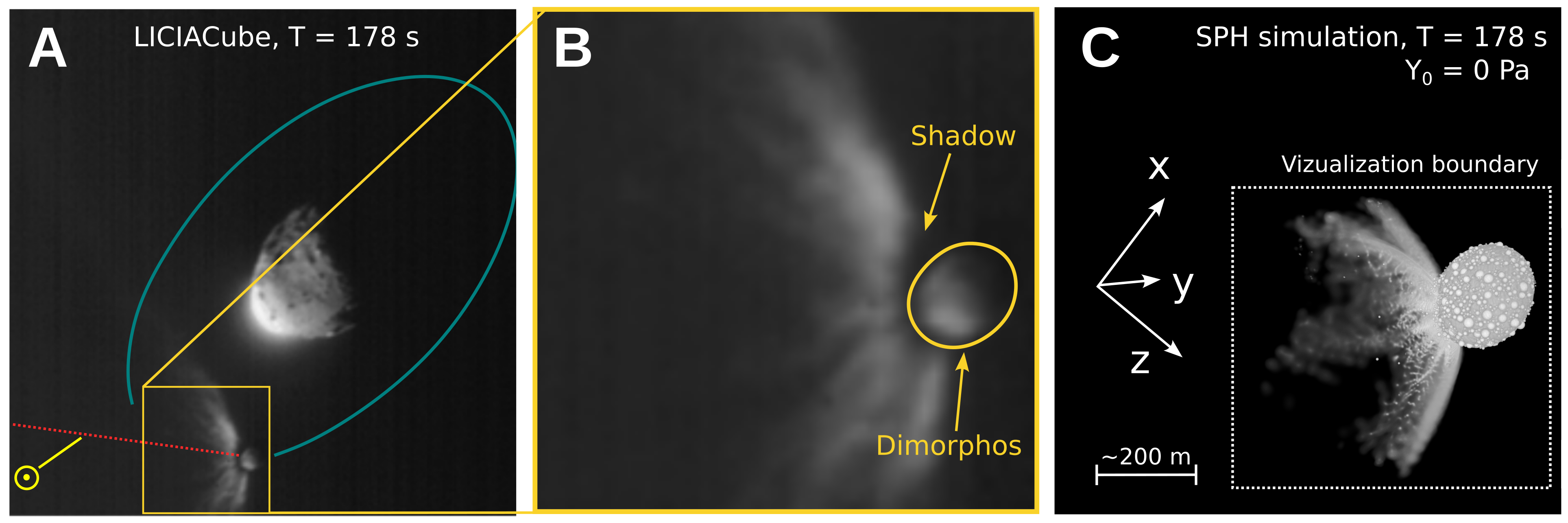 The impact of the DART affect on Didymos. (Symbol credit score: S.D. Raducan)The group’s effects may lend a hand scientists higher perceive the Dimorphos and Didymos asteroid gadget in addition to dissect the dynamics of alternative binary asteroids within the sun gadget. “The fabric houses and construction of Dimorphos as derived on this find out about suggests the small moon most probably shaped thru rotational mass losing and re-accumulation from Didymos,” Raducan mentioned. “Those findings be offering clues in regards to the occurrence and traits of equivalent binary programs in our sun gadget, contributing to our broader working out in their formation histories and evolution.”
The impact of the DART affect on Didymos. (Symbol credit score: S.D. Raducan)The group’s effects may lend a hand scientists higher perceive the Dimorphos and Didymos asteroid gadget in addition to dissect the dynamics of alternative binary asteroids within the sun gadget. “The fabric houses and construction of Dimorphos as derived on this find out about suggests the small moon most probably shaped thru rotational mass losing and re-accumulation from Didymos,” Raducan mentioned. “Those findings be offering clues in regards to the occurrence and traits of equivalent binary programs in our sun gadget, contributing to our broader working out in their formation histories and evolution.”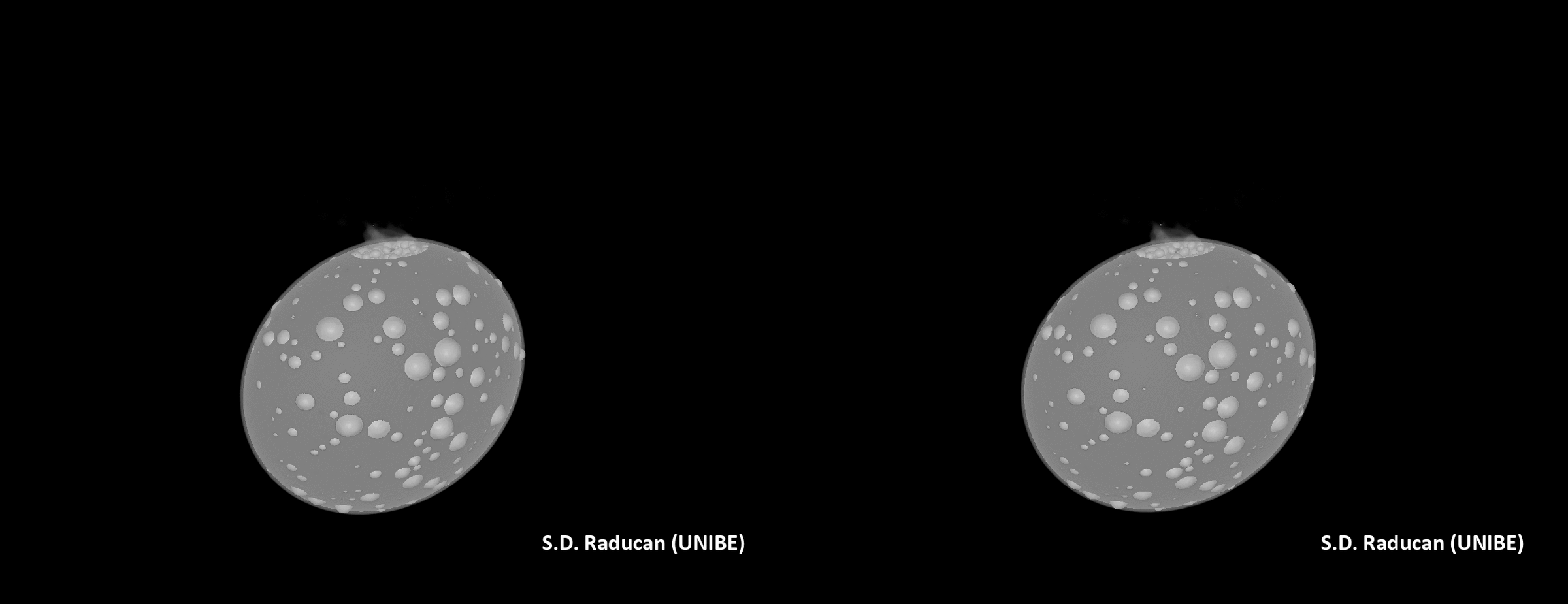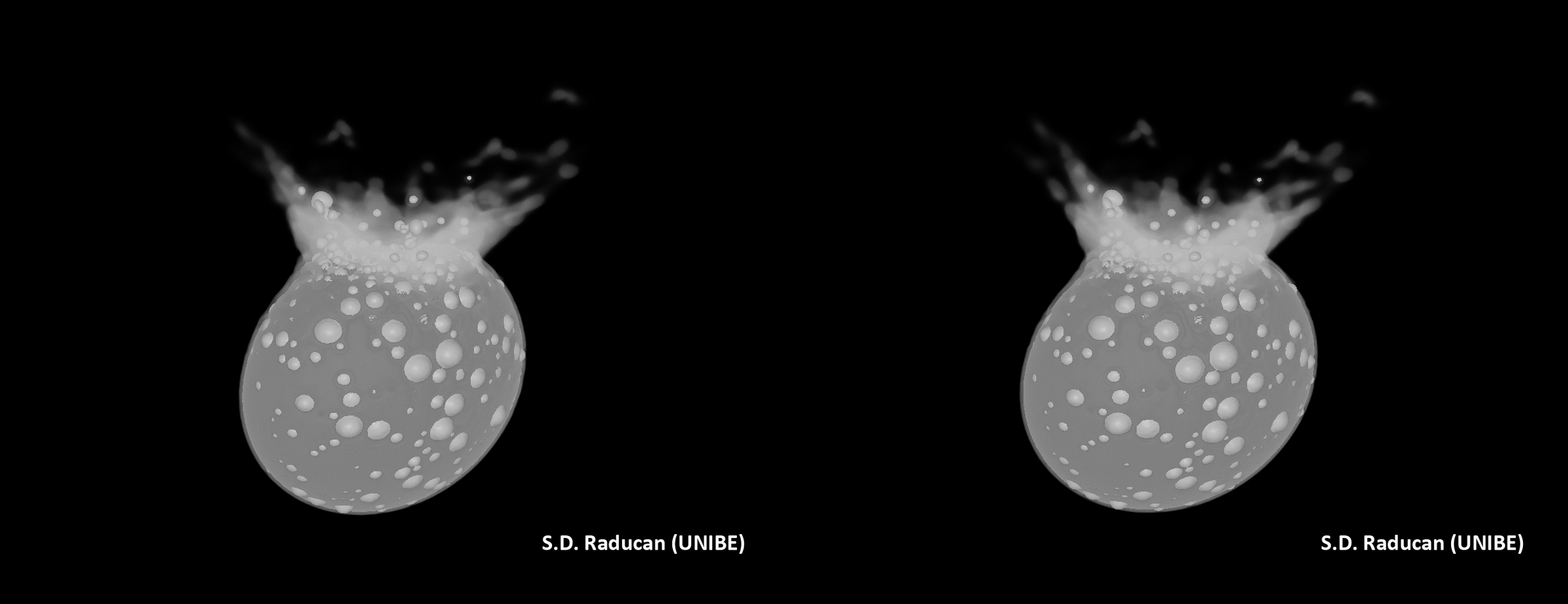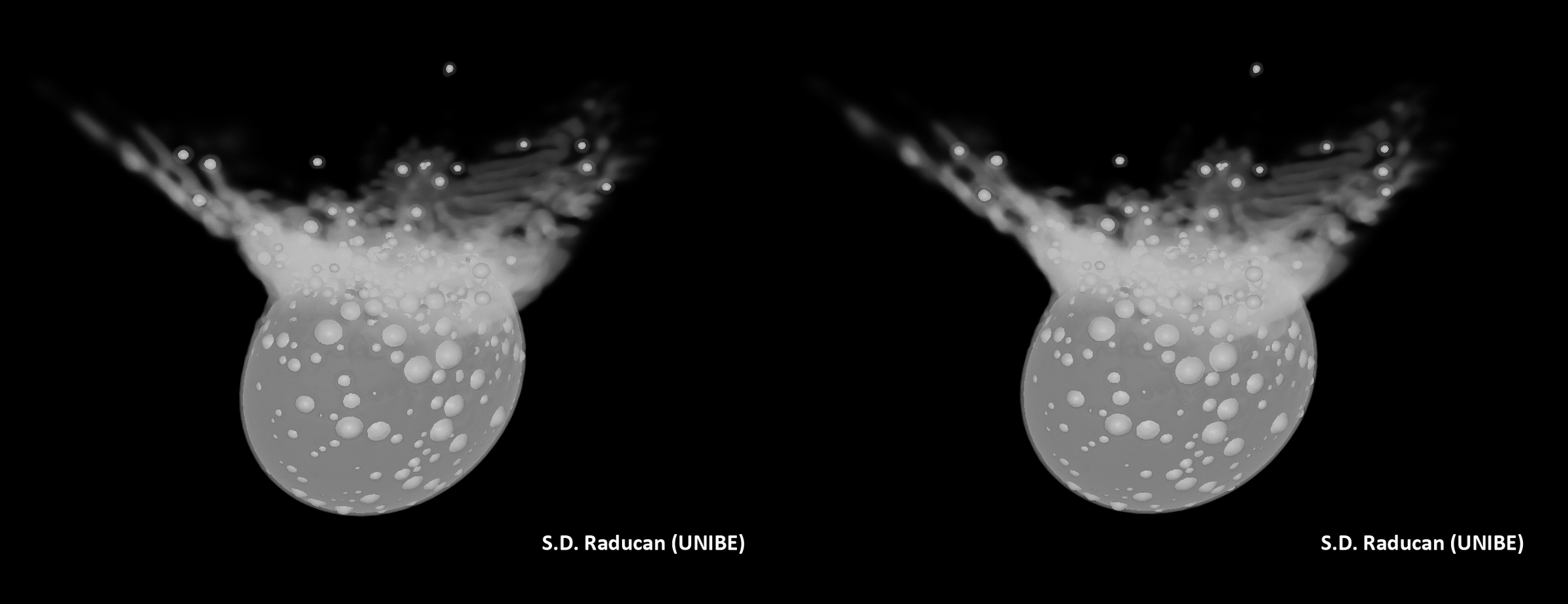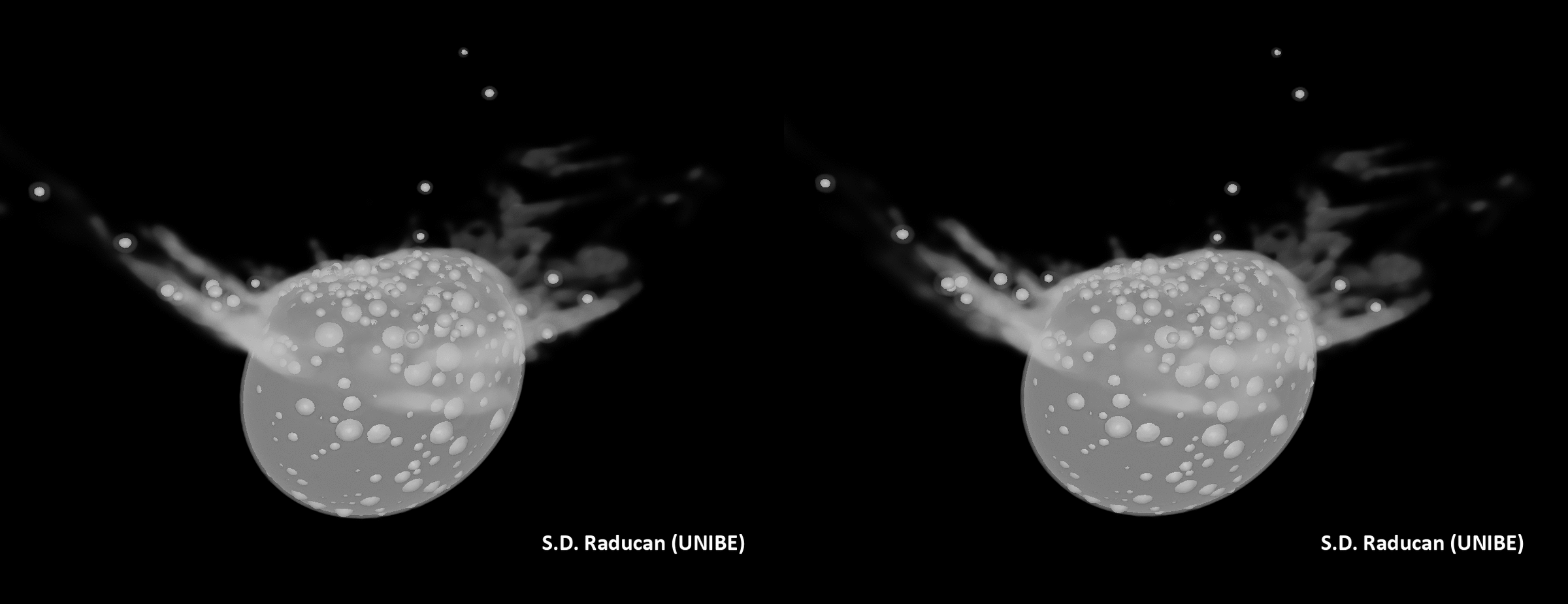 A simulation of the affect of DART on Didymos. (Symbol credit score: S.D. Raducan)The principle intention of DART was once to check planetary protection strategies, and Raducan mentioned the undertaking has no doubt delivered on this recognize. She defined that those effects will tell the improvement of long term asteroid exploration missions and could have an affect on asteroid collision mitigation methods, guiding the design of long term planetary protection projects. “The implication for planetary protection is that small, rubble-pile asteroids, like Dimorphos, are very environment friendly to deflect, and the kinetic impactor methodology could be an acceptable deflection mechanism,” Raducan mentioned. “Alternatively, ahead of making an attempt deflection, a reconnaissance undertaking would most probably be essential to correctly assess the asteroid’s houses.”The researchers now plan to match simulation effects to information accrued by way of the impending Ecu Area Company (ESA) Dimorphos-visiting undertaking, Hera, to validate and refine their fashions.”The Hera undertaking’s findings will likely be instrumental in validating our fashions and remodeling a kinetic impactor into a competent asteroid deflection mechanism,” Raducan concluded. “We additionally plan to increase our research to a broader vary of asteroid varieties and/or shapes, like Dinkinesh, as just lately imaged by way of the Lucy undertaking. “Those research will beef up the robustness of our predictions for planetary protection and give a contribution to a extra complete working out of asteroid mechanics and composition.”The group’s analysis was once printed on Monday (Feb. 26) within the magazine Nature Astronomy.
A simulation of the affect of DART on Didymos. (Symbol credit score: S.D. Raducan)The principle intention of DART was once to check planetary protection strategies, and Raducan mentioned the undertaking has no doubt delivered on this recognize. She defined that those effects will tell the improvement of long term asteroid exploration missions and could have an affect on asteroid collision mitigation methods, guiding the design of long term planetary protection projects. “The implication for planetary protection is that small, rubble-pile asteroids, like Dimorphos, are very environment friendly to deflect, and the kinetic impactor methodology could be an acceptable deflection mechanism,” Raducan mentioned. “Alternatively, ahead of making an attempt deflection, a reconnaissance undertaking would most probably be essential to correctly assess the asteroid’s houses.”The researchers now plan to match simulation effects to information accrued by way of the impending Ecu Area Company (ESA) Dimorphos-visiting undertaking, Hera, to validate and refine their fashions.”The Hera undertaking’s findings will likely be instrumental in validating our fashions and remodeling a kinetic impactor into a competent asteroid deflection mechanism,” Raducan concluded. “We additionally plan to increase our research to a broader vary of asteroid varieties and/or shapes, like Dinkinesh, as just lately imaged by way of the Lucy undertaking. “Those research will beef up the robustness of our predictions for planetary protection and give a contribution to a extra complete working out of asteroid mechanics and composition.”The group’s analysis was once printed on Monday (Feb. 26) within the magazine Nature Astronomy.
NASA’s asteroid-impacting DART undertaking utterly modified the form of its goal