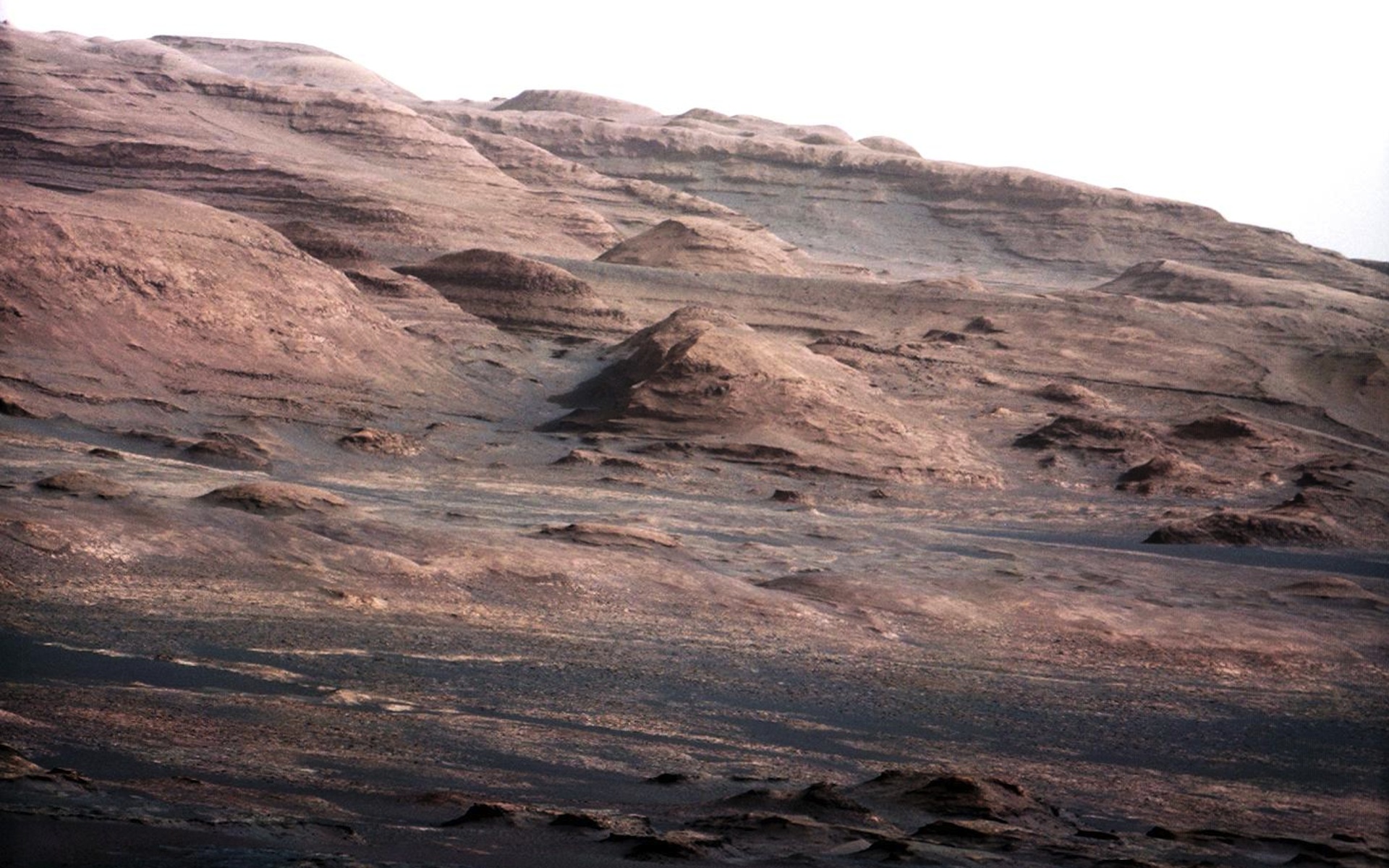
Whilst slowly hiking the slopes of Mount Sharp — a towering height inside of Mars’ Gale Crater — NASA’s Interest rover made a outstanding discovery: massive deposits of carbon locked away in carbonate minerals. That can sound a little bit dry in the beginning, however if truth be told this in finding can be a primary piece of the puzzle in our seek for historical existence at the Purple Planet.Carbonate minerals shape when carbon dioxide interacts with water and rock, making them crucial marker of previous environmental prerequisites. Scientists have noticed those minerals ahead of on Mars — by way of rovers at the flooring, orbiters above, or even in Martian meteorites that fell to Earth — however Interest’s newest information provides thrilling new main points.”It tells us that the planet was once liveable and that the fashions for habitability are right kind,” stated the find out about’s lead writer, Ben Tutolo, affiliate professor with the Division of Earth, Power and Atmosphere within the College of Science on the College of Calgary, in a commentary.The minerals discovered by way of the rover most probably shaped in extraordinarily dry prerequisites thru chemical reactions between water and rock adopted by way of the method of evaporation. This procedure issues to a time when Mars had a thick sufficient environment, wealthy in carbon dioxide, to toughen liquid water at the floor. Alternatively, as the ambience thinned, that carbon dioxide would have begun becoming stone.
Chances are you’ll like
One standout mineral in Interest’s new discovery is siderite, an iron-rich carbonate present in strangely top quantities — between 5 and 10% by way of weight — along salts that dissolve simply in water. “The wider implications are the planet was once liveable up till this time, however then, because the [carbon dioxide] that were warming the planet began to precipitate as siderite, it most probably impacted Mars’ skill to stick heat,” stated Tutolo.What makes this in finding much more attention-grabbing is the presence of iron oxyhydroxides in the similar deposits. Those minerals recommend Mars can have as soon as additionally had a functioning carbon cycle — very similar to Earth’s — the place one of the crucial carbon dioxide locked in rocks in the end made its long ago into the ambience.Through evaluating Interest’s findings with orbital information, scientists consider an identical layers around the planet can have trapped as much as 36 millibars’ price of atmospheric carbon dioxide — sufficient to dramatically trade Mars’ local weather.Breaking area information, the newest updates on rocket launches, skywatching occasions and extra!This Martian discovery additionally ties in intently with paintings being achieved proper right here on Earth. Tutolo says he is been exploring techniques to fight local weather trade by way of turning human-made carbon dioxide into solid carbonate minerals — necessarily locking carbon away in rock.”What we are seeking to do on Earth to struggle local weather trade is one thing that nature can have already achieved on Mars,” he stated. “Finding out concerning the mechanisms of constructing those minerals on Mars is helping us to higher know how we will do it right here. Learning the cave in of Mars’ heat and rainy early days additionally tells us that habitability is an excessively fragile factor.”