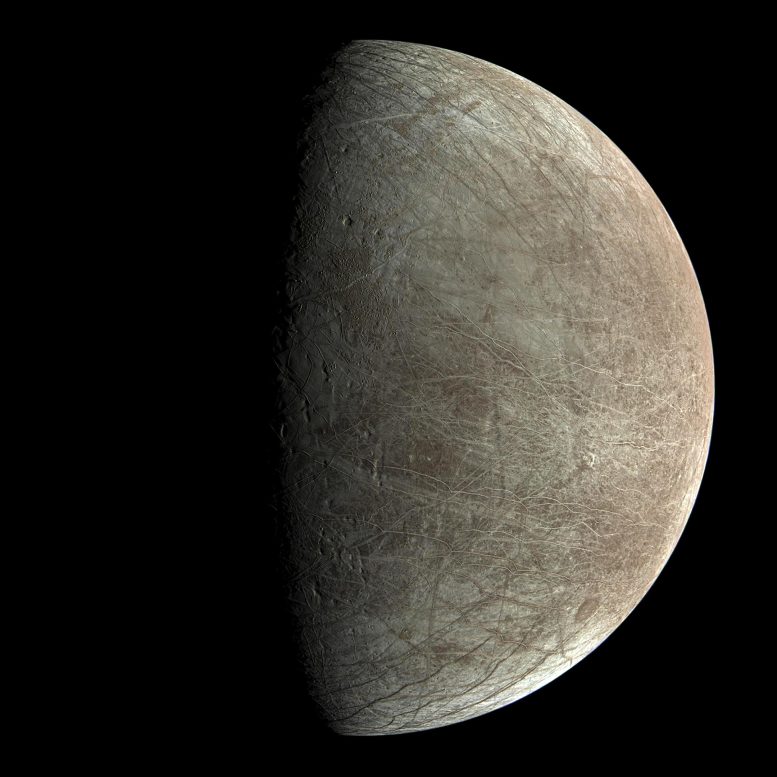
 Jupiter’s moon Europa was once captured through the JunoCam tool aboard NASA’s Juno spacecraft all over the venture’s shut flyby on September 29, 2022. The photographs display the fractures, ridges, and bands that crisscross the moon’s floor.. Credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech/SwRI/MSSS, Björn Jónsson (CC BY 3.0)NASA’s Juno has equipped photographs that toughen the idea of true polar wander on Europa, appearing the moon’s ice shell has shifted. Pictures from the solar-powered spacecraft printed intriguing options at the ice-encased Jovian moon, together with geological disruptions and attainable plume task, suggesting liquid water and brine achieving the skin.Pictures captured through the JunoCam visible-light digicam aboard NASA’s Juno spacecraft toughen the idea that the icy crust on the north and south poles of Jupiter’s moon Europa isn’t the place it was. Moreover, a high-resolution symbol from the spacecraft’s Stellar Reference Unit (SRU) displays indications of imaginable plume task and disruptions within the ice shell, suggesting that brine can have just lately bubbled to the skin.The JunoCam effects have been just lately revealed within the Planetary Science Magazine and the SRU effects have been revealed within the magazine JGR Planets.On September 29, 2022, Juno made its closest flyby of Europa, coming inside of 220 miles (355 kilometers) of the moon’s frozen floor. The 4 footage taken through JunoCam and one through the SRU are the primary high-resolution photographs of Europa since Galileo’s closing flyby in 2000.True Polar WanderJuno’s floor monitor over Europa allowed imaging close to the moon’s equator. When inspecting the knowledge, the JunoCam workforce discovered that at the side of the predicted ice blocks, partitions, scarps, ridges, and troughs, the digicam additionally captured irregularly dispensed steep-walled depressions 12 to 31 miles (20 to 50 kilometers) huge. They resemble massive ovoid pits in the past present in imagery from different places of Europa.An enormous ocean is assumed to are living underneath Europa’s icy external, and those floor options had been related to “true polar wander,” a idea that Europa’s outer ice shell is largely free-floating and strikes.
Jupiter’s moon Europa was once captured through the JunoCam tool aboard NASA’s Juno spacecraft all over the venture’s shut flyby on September 29, 2022. The photographs display the fractures, ridges, and bands that crisscross the moon’s floor.. Credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech/SwRI/MSSS, Björn Jónsson (CC BY 3.0)NASA’s Juno has equipped photographs that toughen the idea of true polar wander on Europa, appearing the moon’s ice shell has shifted. Pictures from the solar-powered spacecraft printed intriguing options at the ice-encased Jovian moon, together with geological disruptions and attainable plume task, suggesting liquid water and brine achieving the skin.Pictures captured through the JunoCam visible-light digicam aboard NASA’s Juno spacecraft toughen the idea that the icy crust on the north and south poles of Jupiter’s moon Europa isn’t the place it was. Moreover, a high-resolution symbol from the spacecraft’s Stellar Reference Unit (SRU) displays indications of imaginable plume task and disruptions within the ice shell, suggesting that brine can have just lately bubbled to the skin.The JunoCam effects have been just lately revealed within the Planetary Science Magazine and the SRU effects have been revealed within the magazine JGR Planets.On September 29, 2022, Juno made its closest flyby of Europa, coming inside of 220 miles (355 kilometers) of the moon’s frozen floor. The 4 footage taken through JunoCam and one through the SRU are the primary high-resolution photographs of Europa since Galileo’s closing flyby in 2000.True Polar WanderJuno’s floor monitor over Europa allowed imaging close to the moon’s equator. When inspecting the knowledge, the JunoCam workforce discovered that at the side of the predicted ice blocks, partitions, scarps, ridges, and troughs, the digicam additionally captured irregularly dispensed steep-walled depressions 12 to 31 miles (20 to 50 kilometers) huge. They resemble massive ovoid pits in the past present in imagery from different places of Europa.An enormous ocean is assumed to are living underneath Europa’s icy external, and those floor options had been related to “true polar wander,” a idea that Europa’s outer ice shell is largely free-floating and strikes.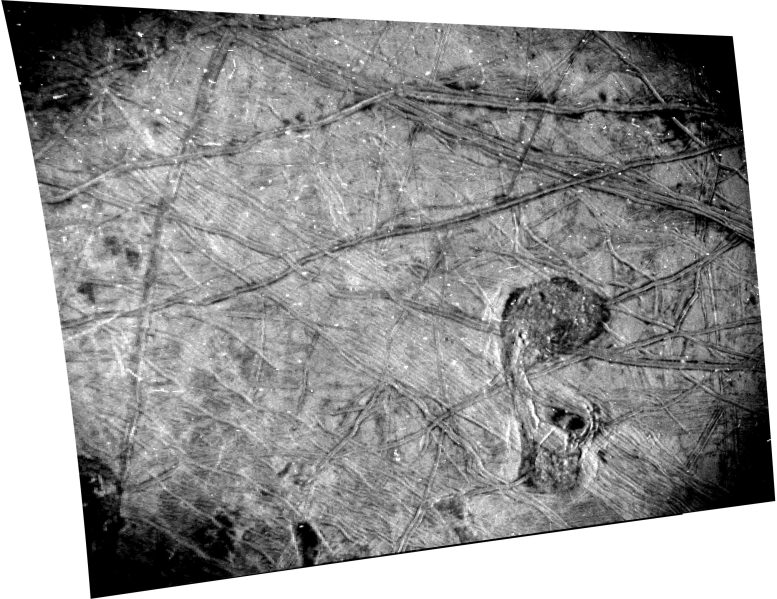 This black-and-white symbol of Europa’s floor was once taken through the Stellar Reference Unit (SRU) aboard NASA’s Juno spacecraft all over the September 29, 2022, flyby. The chaos function nicknamed “the Platypus” is noticed within the decrease proper nook. Credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech/SwRI“True polar wander happens if Europa’s icy shell is decoupled from its rocky internal, leading to excessive tension ranges at the shell, which result in predictable fracture patterns,” stated Sweet Hansen, a Juno co-investigator who leads making plans for JunoCam on the Planetary Science Institute in Tucson, Arizona. “That is the primary time that those fracture patterns had been mapped within the southern hemisphere, suggesting that true polar wander’s impact on Europa’s floor geology is extra in depth than in the past recognized.”The high-resolution JunoCam imagery has additionally been used to reclassify a previously distinguished floor function from the Europa map.“Crater Gwern is not more,” stated Hansen. “What was once as soon as considered a 13-mile-wide affect crater — one in every of Europa’s few documented affect craters — Gwern was once printed in JunoCam information to be a suite of intersecting ridges that created an oval shadow.”
This black-and-white symbol of Europa’s floor was once taken through the Stellar Reference Unit (SRU) aboard NASA’s Juno spacecraft all over the September 29, 2022, flyby. The chaos function nicknamed “the Platypus” is noticed within the decrease proper nook. Credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech/SwRI“True polar wander happens if Europa’s icy shell is decoupled from its rocky internal, leading to excessive tension ranges at the shell, which result in predictable fracture patterns,” stated Sweet Hansen, a Juno co-investigator who leads making plans for JunoCam on the Planetary Science Institute in Tucson, Arizona. “That is the primary time that those fracture patterns had been mapped within the southern hemisphere, suggesting that true polar wander’s impact on Europa’s floor geology is extra in depth than in the past recognized.”The high-resolution JunoCam imagery has additionally been used to reclassify a previously distinguished floor function from the Europa map.“Crater Gwern is not more,” stated Hansen. “What was once as soon as considered a 13-mile-wide affect crater — one in every of Europa’s few documented affect craters — Gwern was once printed in JunoCam information to be a suite of intersecting ridges that created an oval shadow.”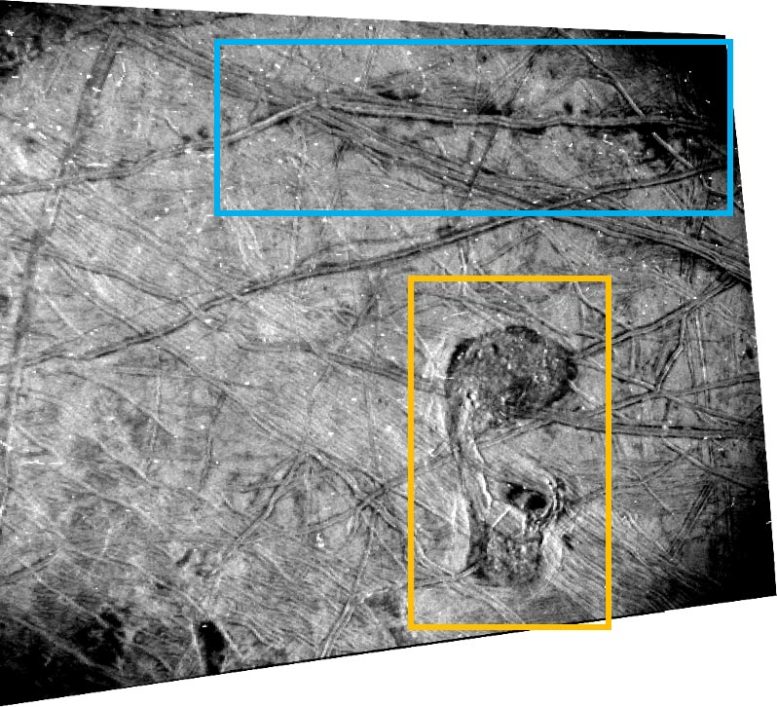 This annotated symbol of Europa’s floor from Juno’s SRU displays the site of a double ridge operating east-west (blue field) with imaginable plume stains and the chaos function the workforce calls “the Platypus” (orange field). Those options trace at present floor task and the presence of subsurface liquid water at the icy Jovian moon. Credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech/SwRIThe PlatypusAlthough all 5 Europa photographs from Juno are high-resolution, the picture from the spacecraft’s black-and-white SRU provides essentially the most element. Designed to discover dim stars for navigation functions, the SRU is delicate to low gentle. To keep away from over-illumination within the symbol, the workforce used the digicam to snap the nightside of Europa whilst it was once lit best through daylight scattered off Jupiter (a phenomenon referred to as “Jupiter-shine”).This leading edge strategy to imaging allowed complicated floor options to face out, revealing intricate networks of cross-cutting ridges and darkish stains from attainable plumes of water vapor. One intriguing function, which covers a space 23 miles through 42 miles (37 kilometers through 67 kilometers), was once nicknamed through the workforce “the Platypus” on account of its form.Characterised through chaotic terrain with hummocks, distinguished ridges, and darkish reddish-brown subject matter, the Platypus is the youngest function in its community. Its northern “torso” and southern “invoice” — hooked up through a fractured “neck” formation — interrupt the encircling terrain with a lumpy matrix subject matter containing a lot of ice blocks which might be 0.6 to 4.3 miles (1 to 7 kilometers) huge. Ridge formations cave in into the function on the edges of the Platypus.For the Juno workforce, those formations toughen the concept Europa’s ice shell can provide method in places the place wallet of briny water from the subsurface ocean are reward underneath the skin.About 31 miles (50 kilometers) north of the Platypus is a suite of double ridges flanked through darkish stains very similar to options discovered in different places on Europa that scientists have hypothesized to be cryovolcanic plume deposits.“Those options trace at present-day floor task and the presence of subsurface liquid water on Europa,” stated Heidi Becker, lead co-investigator for the SRU at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California, which additionally manages the venture. “The SRU’s symbol is a top quality baseline for particular puts NASA’s Europa Clipper venture and ESA’s (Ecu House Company’s) Juice missions can goal to seek for indicators of alternate and brine.”Europa Clipper’s center of attention is on Europa — together with investigating whether or not the icy moon may have prerequisites appropriate for existence. It’s scheduled to release at the fall of 2024 and arrive at Jupiter in 2030. Juice (Jupiter Icy Moons Explorer) introduced on April 14, 2023. The ESA venture will achieve Jupiter in July 2031 to check many goals (Jupiter’s 3 massive icy moons, in addition to fiery Io and smaller moons, at the side of the planet’s environment, magnetosphere, and rings) with a unique center of attention on Ganymede.Juno accomplished its 61st shut flyby of Jupiter on Would possibly 12. Its 62nd flyby of the fuel massive, scheduled for June 13, comprises an Io flyby at an altitude of about 18,200 miles (29,300 kilometers).References:“Juno’s JunoCam Pictures of Europa” through C. J. Hansen, M. A. Ravine, P. M. Schenk, G. C. Collins, E. J. Leonard, C. B. Phillips, M. A. Caplinger, F. Tosi, S. J. Bolton and Björn Jónsson, 21 March 2024, The Planetary Science Magazine.
This annotated symbol of Europa’s floor from Juno’s SRU displays the site of a double ridge operating east-west (blue field) with imaginable plume stains and the chaos function the workforce calls “the Platypus” (orange field). Those options trace at present floor task and the presence of subsurface liquid water at the icy Jovian moon. Credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech/SwRIThe PlatypusAlthough all 5 Europa photographs from Juno are high-resolution, the picture from the spacecraft’s black-and-white SRU provides essentially the most element. Designed to discover dim stars for navigation functions, the SRU is delicate to low gentle. To keep away from over-illumination within the symbol, the workforce used the digicam to snap the nightside of Europa whilst it was once lit best through daylight scattered off Jupiter (a phenomenon referred to as “Jupiter-shine”).This leading edge strategy to imaging allowed complicated floor options to face out, revealing intricate networks of cross-cutting ridges and darkish stains from attainable plumes of water vapor. One intriguing function, which covers a space 23 miles through 42 miles (37 kilometers through 67 kilometers), was once nicknamed through the workforce “the Platypus” on account of its form.Characterised through chaotic terrain with hummocks, distinguished ridges, and darkish reddish-brown subject matter, the Platypus is the youngest function in its community. Its northern “torso” and southern “invoice” — hooked up through a fractured “neck” formation — interrupt the encircling terrain with a lumpy matrix subject matter containing a lot of ice blocks which might be 0.6 to 4.3 miles (1 to 7 kilometers) huge. Ridge formations cave in into the function on the edges of the Platypus.For the Juno workforce, those formations toughen the concept Europa’s ice shell can provide method in places the place wallet of briny water from the subsurface ocean are reward underneath the skin.About 31 miles (50 kilometers) north of the Platypus is a suite of double ridges flanked through darkish stains very similar to options discovered in different places on Europa that scientists have hypothesized to be cryovolcanic plume deposits.“Those options trace at present-day floor task and the presence of subsurface liquid water on Europa,” stated Heidi Becker, lead co-investigator for the SRU at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California, which additionally manages the venture. “The SRU’s symbol is a top quality baseline for particular puts NASA’s Europa Clipper venture and ESA’s (Ecu House Company’s) Juice missions can goal to seek for indicators of alternate and brine.”Europa Clipper’s center of attention is on Europa — together with investigating whether or not the icy moon may have prerequisites appropriate for existence. It’s scheduled to release at the fall of 2024 and arrive at Jupiter in 2030. Juice (Jupiter Icy Moons Explorer) introduced on April 14, 2023. The ESA venture will achieve Jupiter in July 2031 to check many goals (Jupiter’s 3 massive icy moons, in addition to fiery Io and smaller moons, at the side of the planet’s environment, magnetosphere, and rings) with a unique center of attention on Ganymede.Juno accomplished its 61st shut flyby of Jupiter on Would possibly 12. Its 62nd flyby of the fuel massive, scheduled for June 13, comprises an Io flyby at an altitude of about 18,200 miles (29,300 kilometers).References:“Juno’s JunoCam Pictures of Europa” through C. J. Hansen, M. A. Ravine, P. M. Schenk, G. C. Collins, E. J. Leonard, C. B. Phillips, M. A. Caplinger, F. Tosi, S. J. Bolton and Björn Jónsson, 21 March 2024, The Planetary Science Magazine.
DOI: 10.3847/PSJ/ad24f4Reference: “A Complicated Area of Europa’s Floor With Hints of Contemporary Job Printed through Juno’s Stellar Reference Unit” through Heidi N. Becker, Jonathan I. Lunine, Paul M. Schenk, Meghan M. Florence, Martin J. Brennan, Candice J. Hansen, Yasmina M. Martos, Scott J. Bolton and James W. Alexander, 22 December 2023, Magazine of Geophysical Analysis: Planets.
DOI: 10.1029/2023JE008105JPL, a department of Caltech in Pasadena, California, manages the Juno venture for the important investigator, Scott Bolton, of the Southwest Analysis Institute in San Antonio. Juno is a part of NASA’s New Frontiers Program, which is controlled at NASA’s Marshall House Flight Heart in Huntsville, Alabama, for the company’s Science Project Directorate in Washington. The Italian House Company (ASI) funded the Jovian InfraRed Auroral Mapper. Lockheed Martin House in Denver constructed and operates the spacecraft.
NASA’s Juno Spacecraft Finds Dynamic Shifts on Europa’s Frozen Floor