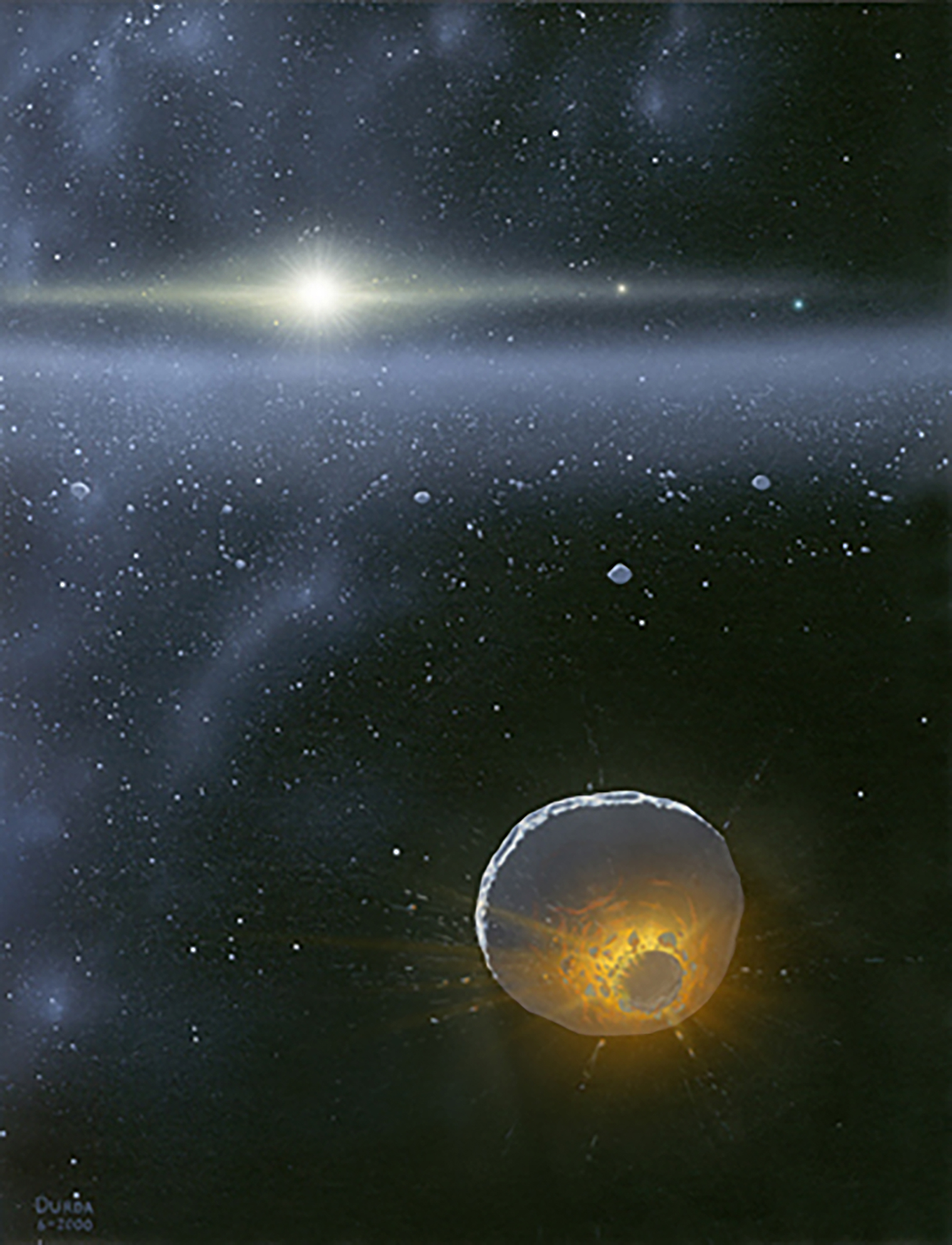
New observations from NASA’s New Horizons spacecraft trace that the Kuiper Belt – the huge, far-off outer zone of our sun gadget populated through loads of hundreds of icy, rocky planetary development blocks – would possibly stretch a lot farther out than we idea.
Rushing throughout the outer edges of the Kuiper Belt, virtually 60 occasions further from the Solar than Earth, the New Horizons Venetia Burney Pupil Mud Counter (SDC) software is detecting upper than anticipated ranges of mud – the tiny frozen remnants of collisions between greater Kuiper Belt gadgets (KBOs) and debris kicked up from KBOs being peppered through microscopic mud impactors from out of doors of the sun gadget.
The readings defy clinical fashions that the KBO inhabitants and density of mud will have to begin to decline a thousand million miles within that distance and give a contribution to a rising frame of proof that implies the outer fringe of the principle Kuiper Belt may just lengthen billions of miles farther than present estimates – or that there may just also be a 2d belt past the only we already know.
The effects seem within the Feb. 1 factor of the Astrophysical Magazine Letters.
“New Horizons is making the primary direct measurements of interplanetary mud a long way past Neptune and Pluto, so each remark may just result in a discovery,” mentioned Alex Doner, lead creator of the paper and a physics graduate pupil on the College of Colorado Boulder who serves as SDC lead. “The concept we would possibly have detected a longer Kuiper Belt — with an entire new inhabitants of gadgets colliding and generating extra mud – gives any other clue in fixing the mysteries of the sun gadget’s maximum far-off areas.”
Designed and constructed through scholars on the Laboratory for Atmospheric and House Physics (LASP) on the College of Colorado Boulder underneath the steerage {of professional} engineers, SDC has detected microscopic mud grains produced through collisions amongst asteroids, comets and Kuiper Belt gadgets all alongside New Horizons’ 5-billion-mile, 18-year adventure throughout our sun gadget – which after release in 2006 integrated historical flybys of Pluto in 2015 and the KBO Arrokoth in 2019. The primary science software on a NASA planetary undertaking to be designed, constructed and “flown” through scholars, the SDC counts and measures the sizes of mud debris, generating knowledge at the collision charges of such our bodies within the outer sun gadget.
The most recent, unexpected effects had been compiled over 3 years as New Horizons traveled from 45 to 55 astronomical gadgets (AU) from the Solar – with one AU being the gap between Earth and Solar, about 93 million miles or 140 million kilometers.
Those readings come as New Horizons scientists, the use of observatories just like the Eastern Subaru Telescope in Hawaii, have additionally came upon a bunch KBOs a long way past the standard outer fringe of the Kuiper Belt. This periphery (the place the density of gadgets begins to say no) used to be regarded as at about 50 AU, however new proof suggests the belt would possibly lengthen to 80 AU, or farther.
As telescope observations proceed, Doner mentioned, scientists are having a look at different imaginable causes for the prime SDC mud readings. One chance, possibly much less most likely, is radiation power and different components pushing mud created within the inside Kuiper Belt out previous 50 AU. New Horizons may just even have encountered shorter-lived ice debris that can’t achieve the internal portions of the sun gadget and weren’t but accounted for within the present fashions of the Kuiper Belt.
“Those new clinical effects from New Horizons could also be the primary time that any spacecraft has came upon a brand new inhabitants of our bodies in our sun gadget,” mentioned Alan Stern, New Horizons primary investigator from the Southwest Analysis Institute in Boulder. “I will’t wait to peer how a lot farther out those increased Kuiper Belt mud ranges pass.”
Now into its 2d prolonged undertaking, New Horizons is anticipated to have enough propellant and tool to perform throughout the 2040s, at distances past 100 AU from the Solar. That a long way out, undertaking scientists say, the SDC may just probably even file the spacecraft’s transition right into a area the place interstellar debris dominate the mud surroundings. With complementary telescopic observations of the Kuiper Belt from Earth, New Horizons, as the one spacecraft working in and amassing new details about the Kuiper Belt, has a novel alternative to be told extra about KBOs, mud assets and expanse of the belt, and interstellar mud and the mud disks round different stars.
The Johns Hopkins Carried out Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland, constructed and operates the New Horizons spacecraft and manages the undertaking for NASA’s Science Challenge Directorate. Southwest Analysis Institute, based totally in San Antonio and Boulder, Colorado, directs the undertaking by the use of Most important Investigator Alan Stern and leads the science crew, payload operations and come across science making plans. New Horizons is a part of NASA’s New Frontiers program, controlled through NASA’s Marshall House Flight Middle in Huntsville, Alabama.