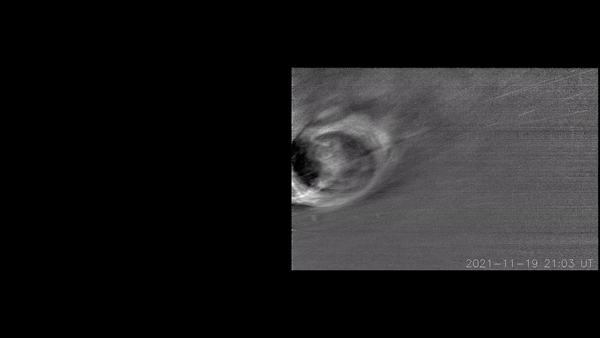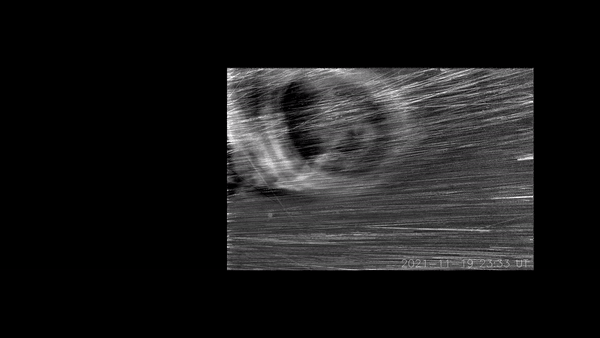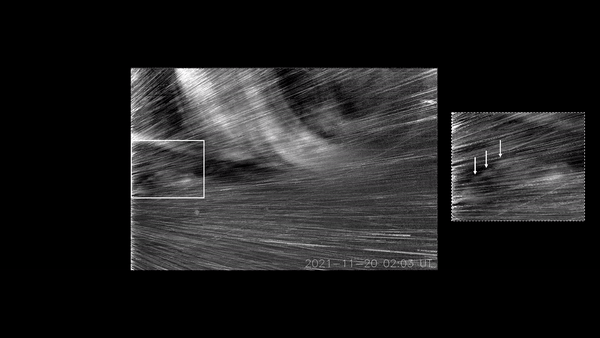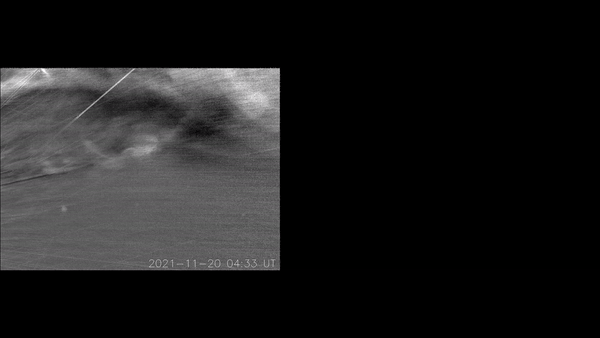
Each and every so frequently, the solar’s simmering magnetic discipline burps colossal clouds of plasma out into the distance past. Those are known as coronal mass ejections (CMEs). If one CME moves Earth, as an example, the end result can also be impressive auroras — and, just-as-spectacular disruptions {of electrical} grids and satellites.Now, NASA’s Parker Sun Probe has gotten a first-ever peek inside of a CME because it erupted from the solar. And what lies inside of seems to be a treasure trove for sun physicists. The probe’s visible-light-detecting, Huge-field Imager for Parker Sun Probe (WISPR) device stuck transparent, turbulent eddies inside the CME.The eddies are what physicists name Kelvin-Helmholtz instabilities (KHI). Physicists suppose KHI occasions happen each time one patch of fast-moving fluid interacts with some other. On Earth, KHI happens in clouds when the wind pace at one finish of the cloud isn’t like that on the different finish.Similar: NASA’s Parker Sun Probe smashes file for quickest human-made objectSolar physicists have inferred that KHI exist in CMEs, as plasma in a CME strikes at odds with the background sun wind. However they have got by no means had the correct apparatus, in the correct position, to watch the phenomena.”The turbulence that provides upward thrust to KHI performs a basic function in regulating the dynamics of CMEs flowing throughout the ambient sun wind,” stated Evangelos Paouris, a sun physicist at George Mason College, in a remark. “Therefore, figuring out turbulence is vital achieve a deeper figuring out of CME evolution and kinematics.”The Parker Sun Probe introduced on Aug. 12, 2018. Since then, the probe’s elliptical orbit has allowed it to go into the solar’s corona nearer than ever prior to — in essence, turning into the primary human-made object to go into the solar’s outer environment, simply 11.5 sun radii from the solar’s floor.Breaking area information, the newest updates on rocket launches, skywatching occasions and extra!And, even now, Parker Sun Probe has no longer entered its ultimate orbit. The probe has again and again flown previous Venus with a purpose to use the planet’s gravity to spice up its pace and tighten its orbit across the solar. In November of this 12 months, the probe will fly previous Venus a 7th time, tightening its loop concerning the solar once more — permitting it to go inside of simply 9.5 sun radii from the solar in 2025 and past.
NASA’s Parker Sun Probe makes 1st-of-its-kind commentary inside of a coronal mass ejection