As of late, NASA’s Parker Sun Probe will entire its 7th swing previous Venus — the spacecraft’s ultimate maneuver across the amber planet — in a flyby that may nudge the probe on a trajectory that may take it inside of 3.8 million miles of the solar’s floor. That would be the closest that any human-built object has come to our famous person.”We’re principally virtually touchdown on a celeb,” Nour Raouafi, an astrophysicist on the Johns Hopkins College Carried out Physics Laboratory and challenge scientist for the Parker Sun Probe undertaking, instructed BBC Information previous this yr. “This might be a enormous fulfillment for all humanity. That is identical to the moon touchdown of 1969.”The Parker Sun Probe, which is concerning the dimension of a small automotive, introduced in 2018 on a bold undertaking to “contact” the solar. Scientists had been hoping that it would decode a few of the most up to date mysteries about our famous person, equivalent to why the corona, the outermost layer of the solar’s tenuous environment, will get masses of occasions warmer the farther it stretches from the solar’s floor. Certainly, the probe has already began unraveling a few of these puzzles.Gravity assists from Venus were crucial in nudging Parker nearer to our famous person, because the spacecraft is based on the earth’s gravitational tides to cut back its orbital power and tighten its choreographed orbit across the solar. “Venus 7 is the vital gravity lend a hand for Parker Sun Probe to in the end succeed in its minimal sun distance,” Yanping Guo, who’s the undertaking design and navigation supervisor Johns Hopkins Carried out Physics Laboratory (APL) in Maryland, mentioned in a contemporary NASA remark.Whilst the probe is customized to check the solar, those repeated swings previous “Earth’s evil dual” — which scientists say has now not had sufficient robot guests previously many years — have caused Parker’s operators to activate its tools and acquire treasured bonus science. Right through Parker’s 3rd Venus flyby in July 2020, as an example, scientists had been shocked to seek out the spacecraft’s digital camera may just peer thru Venus’ dense clouds all of the method to its floor, revealing distinct options, equivalent to continental areas, plains and plateaus, carved onto the sector.The digital camera, known as the Extensive-Box Imager for Parker Sun Probe, or WISPR, additionally recorded the faint glide led to by way of warmth emanating from Venus’ nightside, which, at 860 levels Fahrenheit (460 Celsius), could be “like a work of iron pulled from a forge,” Brian Wooden of the Naval Analysis Laboratory in Washington, D.C. mentioned in a NASA remark. Portions of the WISPR pictures additionally seemed brighter than anticipated, suggesting the digital camera would possibly have picked up details about the Venusian floor now not noticed by way of earlier spacecraft, equivalent to delicate chemical variations at the floor or permutations in age, most likely led to by way of fresh lava flows.Breaking area information, the most recent updates on rocket launches, skywatching occasions and extra!To check the outside options in additional element, undertaking scientists will as soon as once more level WISPR towards Venus on Wednesday because the Parker Sun Probe swoops inside of 233 miles (376 km) of the planet’s floor.”As it flies over quite a lot of an identical and other landforms than the former Venus flybys, the Nov. 6 flyby will give us extra context to guage whether or not WISPR can assist us distinguish bodily and even chemical homes of Venus’ floor,” Noam Izenberg, a planetary geologist at APL, mentioned in a contemporary NASA remark.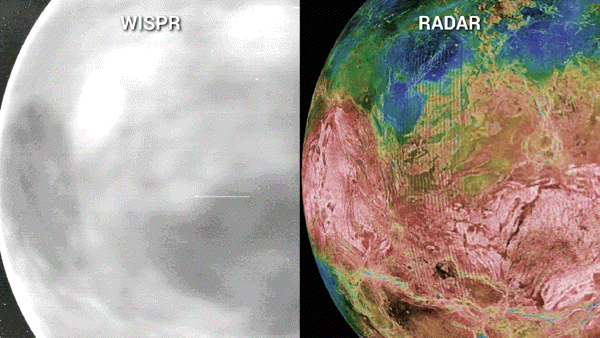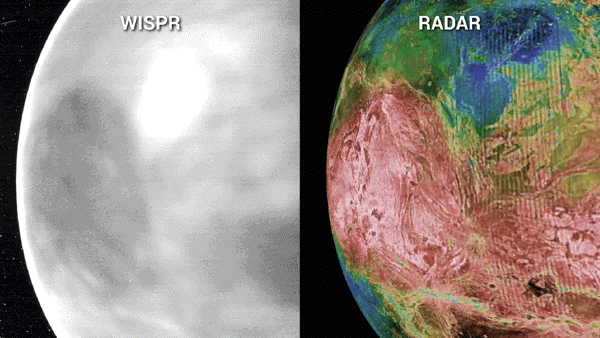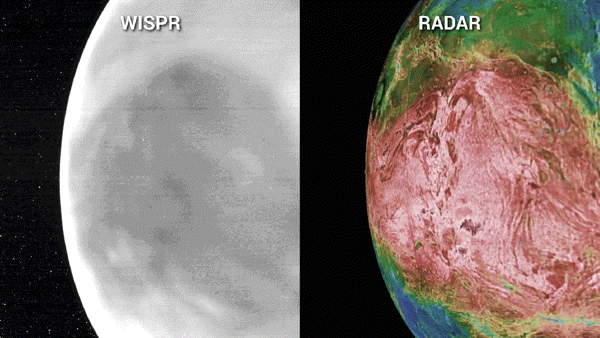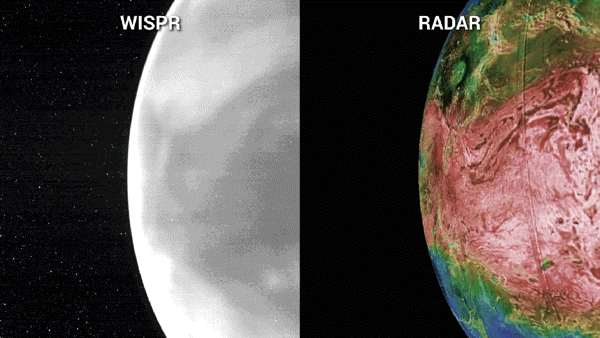 Left: A sequence of WISPR pictures of the nightside of Venus from Parker Sun Probe’s fourth flyby appearing close to infrared emissions from the outside. In those pictures, lighter sunglasses constitute hotter temperatures and darker sunglasses constitute cooler. Proper: A blended mosaic of radar pictures of Venus’ floor from NASA’s Magellan undertaking, the place the brightness signifies radar homes from easy (darkish) to tough (mild), and the colours point out elevation from low (blue) to top (pink). (Symbol credit score: NASA/APL/NRL (left), Magellan Staff/JPL/USGS (proper))On Christmas Eve, the Parker Sun Probe will graze the solar’s “floor” — the photosphere, or solar’s visual section — at a report 430,000 miles in step with hour (692,010 kilometers in step with hour). Undertaking keep an eye on might be out of touch with the spacecraft all the way through that point, however might be searching for a beacon tone on Dec. 27 that may verify the good fortune of closest manner and the spacecraft’s well being.
Left: A sequence of WISPR pictures of the nightside of Venus from Parker Sun Probe’s fourth flyby appearing close to infrared emissions from the outside. In those pictures, lighter sunglasses constitute hotter temperatures and darker sunglasses constitute cooler. Proper: A blended mosaic of radar pictures of Venus’ floor from NASA’s Magellan undertaking, the place the brightness signifies radar homes from easy (darkish) to tough (mild), and the colours point out elevation from low (blue) to top (pink). (Symbol credit score: NASA/APL/NRL (left), Magellan Staff/JPL/USGS (proper))On Christmas Eve, the Parker Sun Probe will graze the solar’s “floor” — the photosphere, or solar’s visual section — at a report 430,000 miles in step with hour (692,010 kilometers in step with hour). Undertaking keep an eye on might be out of touch with the spacecraft all the way through that point, however might be searching for a beacon tone on Dec. 27 that may verify the good fortune of closest manner and the spacecraft’s well being.
NASA’s Parker Sun Probe to fly by way of Venus as of late ahead of ancient solar stumble upon